Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Why is HTTPS enabled in the UI, but the MetaDefender Core URL doesn’t change to HTTPS?
This article applies to all MetaDefender Core version 5.x on Windows Bases
Scenario
When you enable HTTPS for the MetaDefender Core UI to enhance security, you may notice that although the UI indicates HTTPS is enabled, the Core URL still appears as HTTP. This Knowledge Base article provides detailed instructions to resolve this issue and ensure the MetaDefender Core UI is properly accessible over HTTPS.
Root Cause
The MetaDefender Core Web Server uses NGINX as its underlying web server. Its configuration file is stored at:
C:\Windows\Temp\ometascan\nginx.conf
This file serves as the master configuration for the NGINX process.
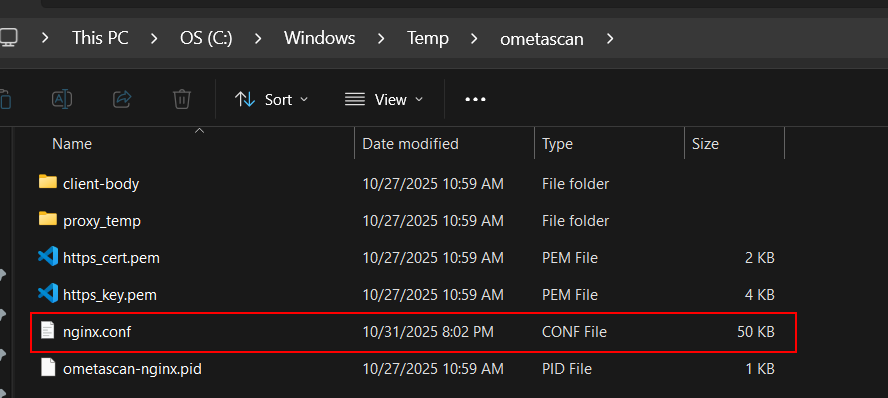
In certain environments—particularly those with Real-Time Protection (RTP) enabled—the configuration file may be automatically deleted. Once NGINX has successfully started, it loads the configuration into memory, so the removal of the file does not immediately affect the running web service.
However, if the nginx.conf file is missing, any subsequent configuration changes (such as enabling or disabling HTTPS) will not take effect, since NGINX cannot reload or update its settings without this file.
Symptom
After enabling HTTPS through the MetaDefender Core UI, you may encounter an error page when attempting to access the web interface. This indicates that the browser’s request did not reach the web server, suggesting that the NGINX web service is not properly serving HTTPS traffic or its configuration is missing or invalid.
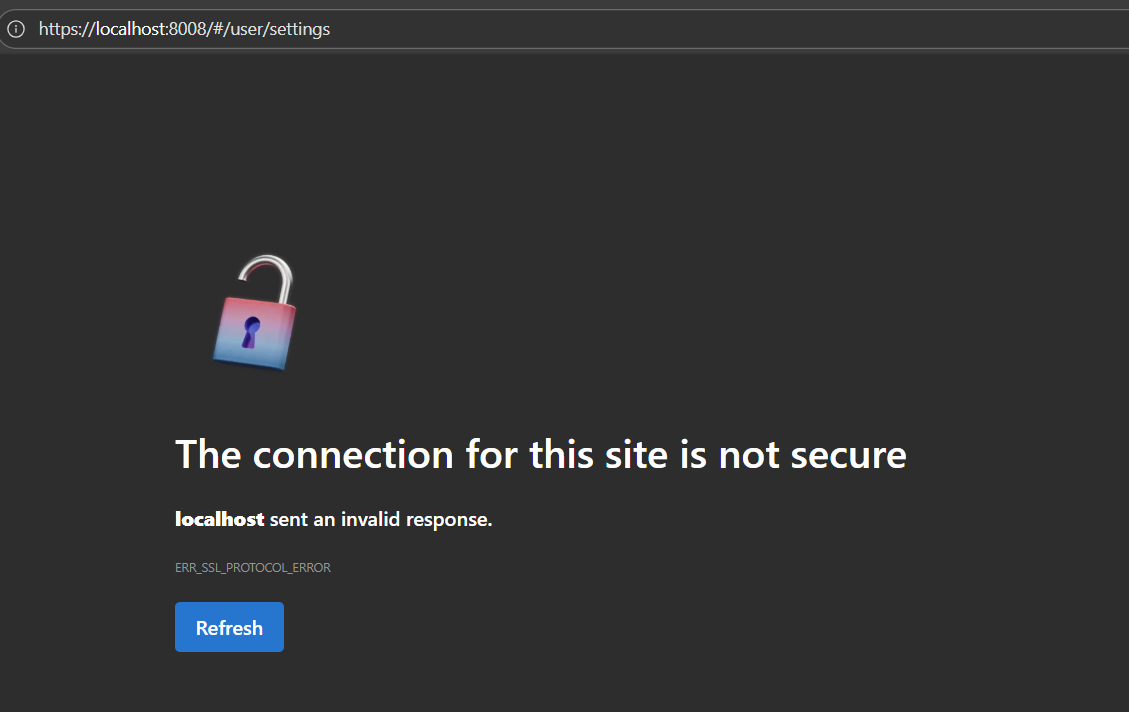
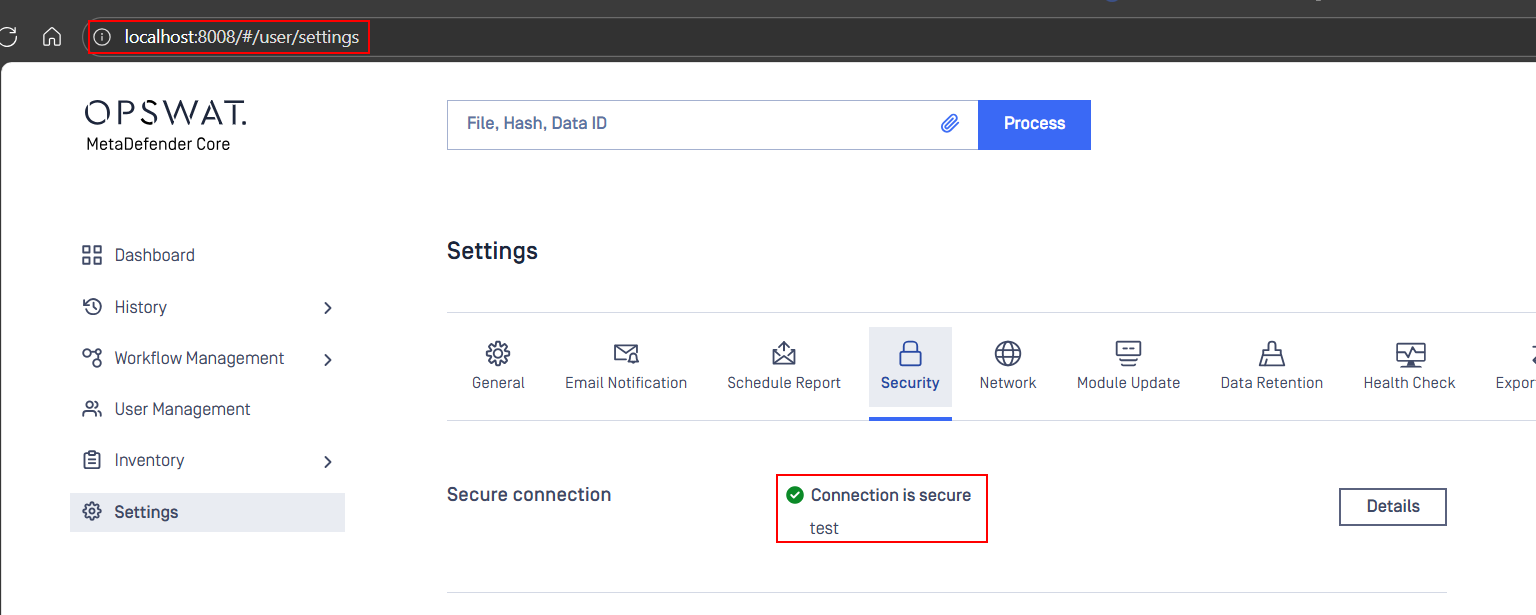
When you try to access the MetaDefender Core UI using HTTP instead of HTTPS, the interface loads successfully. However, upon reviewing the HTTPS settings in the UI, you can see that the HTTPS option is already enabled, as shown below.
This indicates that HTTPS has been configured, but the Core instance continues to serve the web interface over HTTP due to missing or invalid NGINX configuration files.
Resolution
Navigate to the following directory:
C:\Windows\Temp\ometascan
If the ometascan folder does not exist or is empty, there is no need to worry — this can be automatically regenerated by restarting the MetaDefender Core service.
Follow the steps below:
- Stop the MetaDefender Core service.
- Start the service again.
During startup, MetaDefender Core checks for the ometascan temporary folder.
- If the folder or its configuration files are missing, the system will automatically recreate them and regenerate the required NGINX configuration files.
- Once the process completes, the web service will resume normal operation, and HTTPS will be automatically re-enabled.
If you notice that RTP keeps deleting the nginx.conf file in the folder “C:\Windows\Temp\ometascan”, you can add this folder to the RTP exclusion list to prevent the file from being removed.
If Further Assistance is required, please proceed to log a support case or chat with our support engineer at Home - My OPSWAT .

