Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
How Do I Setup Syslog connect to Splunk Cloud by using Universal Forwarder?
This article applies to all MetaDefender Core releases deployed on Linux systems.
This KB, I will provide the guideline to setup integrate with Splunk Cloud. Splunk Cloud requires Universal Forwarder, therefore, we need to setup Universal Forwarder first. In this KB I am using RedHat 9.2 (Plow) to setup so the command in this KB will be runned on RedHat and package system should be RPM.
root>15:50:19 (Core) # cat /etc/redhat-releaseRed Hat Enterprise Linux release 9.2 (Plow)1 - Install Universal Forwarder
In your Splunk Instance, you can select this to setup Universal Forwarder
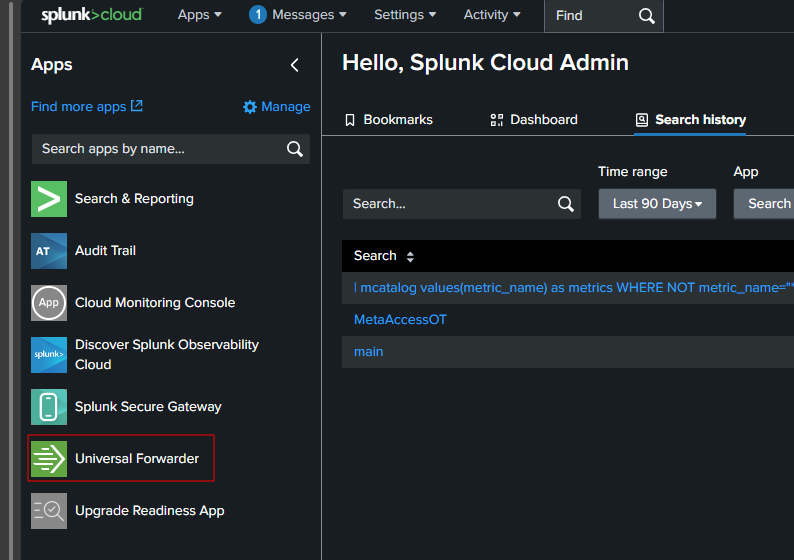
Then, you can follow this Splunk instruction to setup
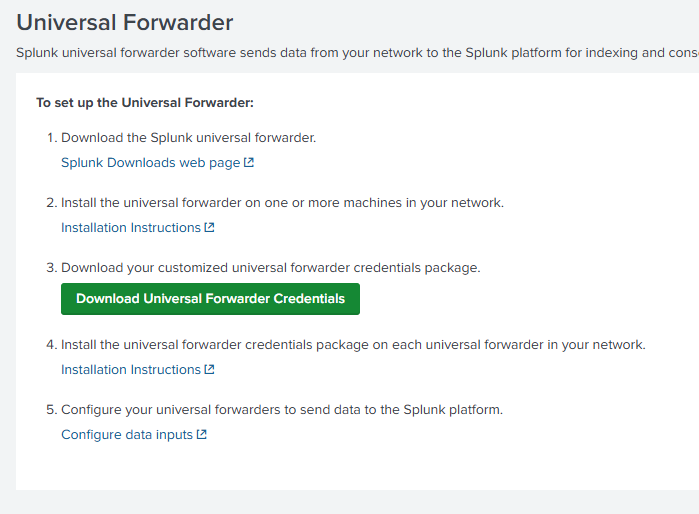
After downloading the installer and credential files as shown in the screenshot below, you can proceed with setting up the Splunk Universal Forwarder.
- Installer file:
splunkforwarder-10.0.0-e8eb0c4654f8.x86_64.rpm - Credential file:
splunkclouduf.spl
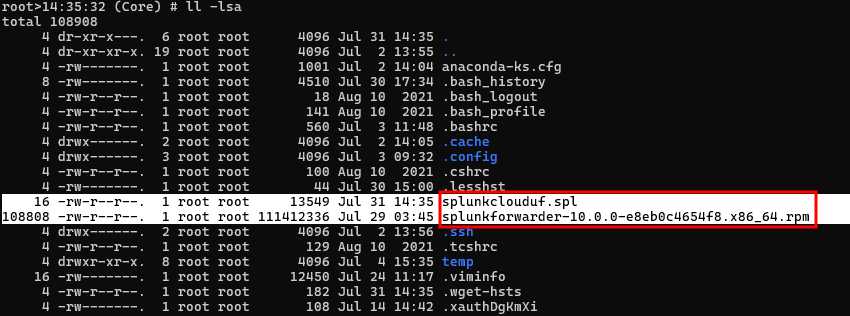
Install the Splunk Universal Forwarder using the following command:
Step 1: Create the Splunk user and group.
useradd -m splunkfwdgroupadd splunkfwdStep 2: Install the Splunk software, as described in the installation instructions for your platform in Installation instructions. Create the $SPLUNK_HOME directory wherever desired.
export SPLUNK_HOME="/opt/splunkforwarder"mkdir $SPLUNK_HOMEStep 3: Running command to install package.
rpm -i splunkforwarder-10.0.0-e8eb0c4654f8.x86_64.rpmThe output should be
rpm -i splunkforwarder-10.0.0-e8eb0c4654f8.x86_64.rpmwarning: splunkforwarder-10.0.0-e8eb0c4654f8.x86_64.rpm: Header V4 RSA/SHA256 Signature, key ID b3cd4420: NOKEYverify that this sytem has all the commands we will require to perform the preflight stepno need to run the splunk-preinstall upgrade checkcompleteStep 4: Run the chown command to change the ownership of the Splunk directory and all its contents to the user that will run the Splunk software.
Step 5: run the command below to start
$SPLUNK_HOME/bin/splunk startor this command
$SPLUNK_HOME/bin/splunk start --accept-licenseYou will be prompted to create a new administrator username and password. After entering the required information, you should see the following output:
Warning: Attempting to revert the SPLUNK_HOME ownershipWarning: Executing "chown -R splunkfwd:splunkfwd /opt/splunkforwarder"This appears to be your first time running this version of Splunk.Splunk software must create an administrator account during startup. Otherwise, you cannot log in.Create credentials for the administrator account.Characters do not appear on the screen when you type in credentials.Please enter an administrator username: adminPassword must contain at least: * 8 total printable ASCII character(s).Please enter a new password:Please confirm new password:Creating unit file...Important: splunk will start under systemd as user: splunkfwdThe unit file has been created.......All preliminary checks passed.Starting splunk server daemon (splunkd)...DoneTo verify, you can run this command below
$SPLUNK_HOME/bin/splunk versionThe output should be:
Warning: Attempting to revert the SPLUNK_HOME ownershipWarning: Executing "chown -R splunkfwd:splunkfwd /opt/splunkforwarder"Splunk Universal Forwarder 10.0.0 (build e8eb0c4654f8)2 - Install the forwarder credentials
To install the forwarder credentials, run the following command:
$SPLUNK_HOME/bin/splunk install app splunkclouduf.splIt will prompt you for the username and password you set during the Splunk Forwarder installation.
Once completed, you should see an output confirming the action, followed by a prompt to restart Splunk.
Warning: Attempting to revert the SPLUNK_HOME ownershipWarning: Executing "chown -R splunkfwd:splunkfwd /opt/splunkforwarder"Couldn't change ownership for /opt/splunkforwarder/etc/deployment-apps: Operation not permittedApp '/opt/splunkforwarder/etc/deployment-apps/splunkclouduf.spl' installedYou need to restart the Splunk Server (splunkd) for your changes to take effect.To restart Splunk, you can run this command
$SPLUNK_HOME/bin/splunk restartThe output should be
All preliminary checks passed.Starting splunk server daemon (splunkd)...DoneTo configure Splunk to listen for syslog, create the file /opt/splunkforwarder/etc/system/local/inputs.conf and add the following settings:
cat /opt/splunkforwarder/etc/system/local/inputs.conf# For TCP syslog (optional)[tcp://1514]index = mainsourcetype = syslogdisabled = 0To verify whether the Splunk Universal Forwarder (UF) port is open, you can use the following command:
netstat -ntlp | grep 1514tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:1514 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1071882/splunkd3 - Integrate MD Core syslog with Splunk Universal Forwarder.
If you are using MD Core on Linux (Red Hat, Ubuntu, or Debian), you can configure syslog by adding the settings below to the /etc/ometascan/ometascan.conf file.
These settings should be placed directly beneath the [logger] section.
syslog=tcp://10.40.192.43:1514syslog_level=infoFor example
[global]dbmode=1restaddress=*restport=8008[logger]log_rotation=1logfile=/var/log/ometascan/ometascan.logloglevel=infonginx_log_rotation=1nginx_logfile=/var/log/ometascan/nginx-ometascan.logsyslog=tcp://<IP_SPLUNK_UNIVERSAL_FORWARDER>:1514syslog_level=infoThen, restart MD Core service.
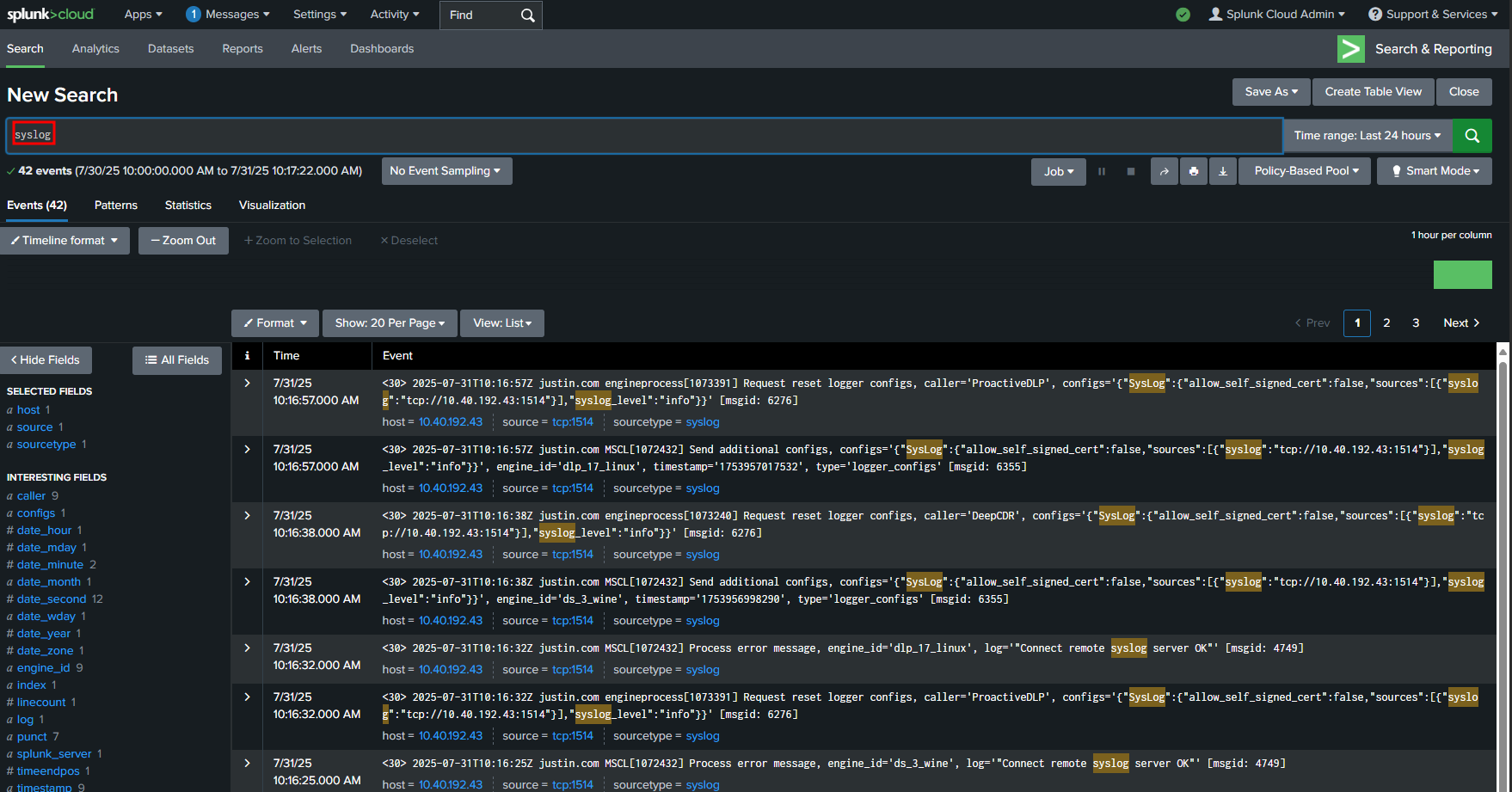
systemctl restart ometascanNow, go back to your Splunk instance and search for "syslog" — you should see entries related to MD Core appearing there.
If Further Assistance is required, please proceed to log a support case or chatting with our support engineer.

