Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
SFTP - Push Files
This type of job automatically pushes files to a remote host using SFTP.
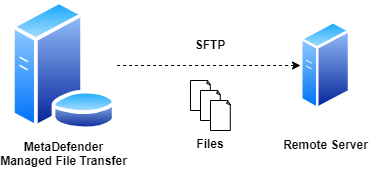
During the automated file transfer, only files with Available and Sanitized state within the source folders will be transfered.
Configuration
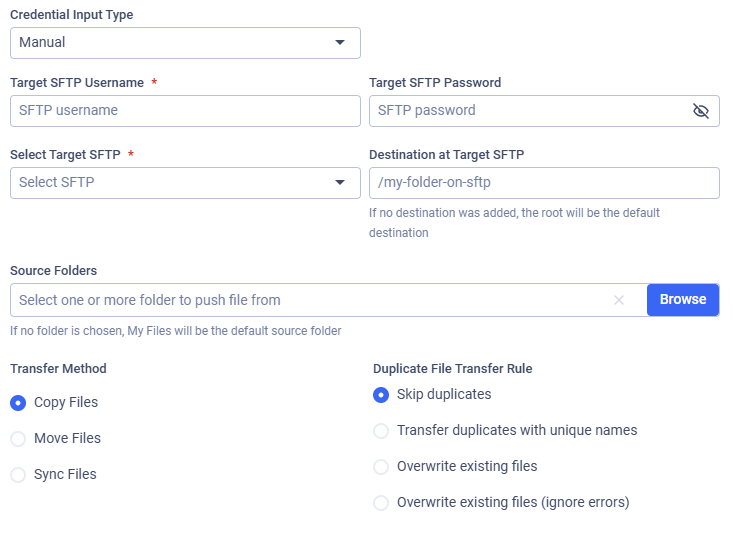
Credential Input Type
Two types of authentication can be used:
- Manual: username and password
- SSH Key: username and selecting previously stored private SSH key (see: My Credentials)
Target SFTP Username
The username to authenticate via SFTP on the selected host.
Target SFTP Password
The password to authenticate with through SFTP on the selected host. It is possible to provide an empty password.
In case of editing or duplicating a previously saved job, the password needs to be re-entered.
Select SSH Key
If the SSH Key credential input type was selected, beside adding the username which used to authenticate on the SFTP server, you should select the proper stored private SSH key to authenticate.
Select Target SFTP
Select the SFTP integration to use. Files will be pushed to the selected host. See: SFTP Integration
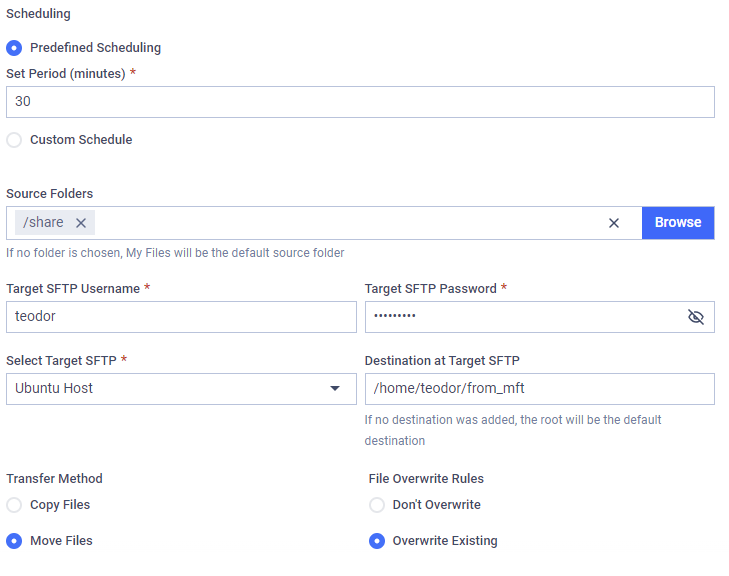
Provide Source Path(s)
Provide paths from which to recursively collect and push files from MetaDefender Managed File Transfer. You can configure any number of paths; if no path is added, the root ('/') will be the default source path.
Destination at Target SFTP
The destination path on the remote host. If the path does not exist, it will be created automatically.
Transfer Method
Decide what to do with the original files on MetaDefender Managed File Transfer:
- Copy Files: Files successfully pushed will remain intact on MetaDefender Managed File Transfer.
- Move Files: Files successfully pushed will be removed from MetaDefender Managed File Transfer.
- Sync Files: Keeps a remote destination folder identical to a local source folder.
If multiple source paths point to the same file, the file will only be deleted on the local instance if it was successfully pushed from all listed source paths.
For example, if move is enabled and there is a file located at /data/logs/log.txt and source paths /data and /data/logs are configured with the destination /push, the file will only be removed from the local instance if the push was successful for both /push/logs/log.txt and /push/log.txt.
Duplicate File Transfer Rule
Decide what to do if a file with the same absolute path already exists on the remote host:
- Skip duplicates: The file from MetaDefender MFT is not pushed to the destination.
- Transfer duplicates with unique names: The existing destination file is kept. The new file from MetaDefender MFT is pushed and saved at the destination with a unique name.
- Overwrite existing files: Push the file to the remote host, overwriting the existing one.
- Overwrite existing files (ignore errors): Push the file to the remote host, overwriting the existing one. This option ignores errors encountered when checking for the file’s existence. Use this only when SFTP server configurations prevent file-existence checks (e.g., listing permissions are disabled), but you still require the transfer to proceed.
The Overwrite existing files option does not perform any pre-check on either the local or remote file; it simply overwrites the remote file with the local one, even if both files contain the same data. This means if a file does not change on the local instance, the same file will be pushed repeatedly.
Sync Behavior for Deleted Files
Decide on the course of action if the selected transfer method is Sync Files.
- Delete from destination: If a file or folder is deleted from the source, it will also be deleted from the destination on the next job run. This ensures the destination remains an exact mirror of the source.
- Retain on destination: If a file or folder is deleted from the source, it will not be deleted from the destination. This option is useful when you want to use Sync to transfer new and updated files but need to prevent any data from being automatically removed from the destination.
Example
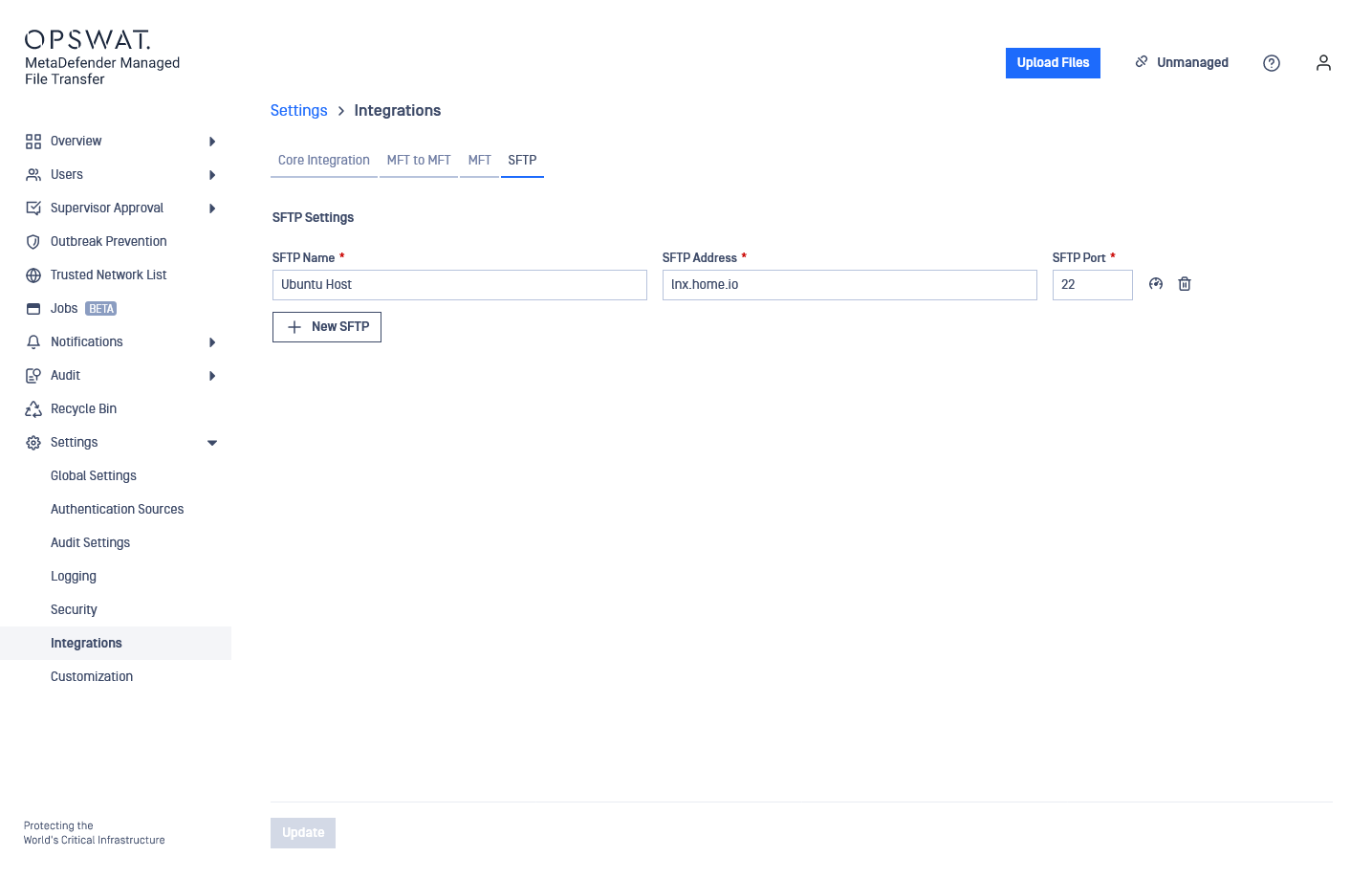
I want to push files to my remote Ubuntu 20.04 host from MetaDefender Managed File Transfer. I only want to push files that are under the share folder in my root directory, and I want this process to occur every 30 minutes. My username is teodor and my password is pass%123! on the remote host.
My Ubuntu host can be accessed at the FQDN lnx.home.io, where the SSH server is running and providing access on port 22. I want my files to be moved from my directory to the folder /home/teodor/from_mft on my Linux host. If a file already exists there, I want it to be overwritten.