Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
High Availability
This documentation describes the High Availability setup used for MetaDefender Managed File Transfer™ services in an active-passive configuration. It is designed to provide service continuity in case of node or infrastructure failures.
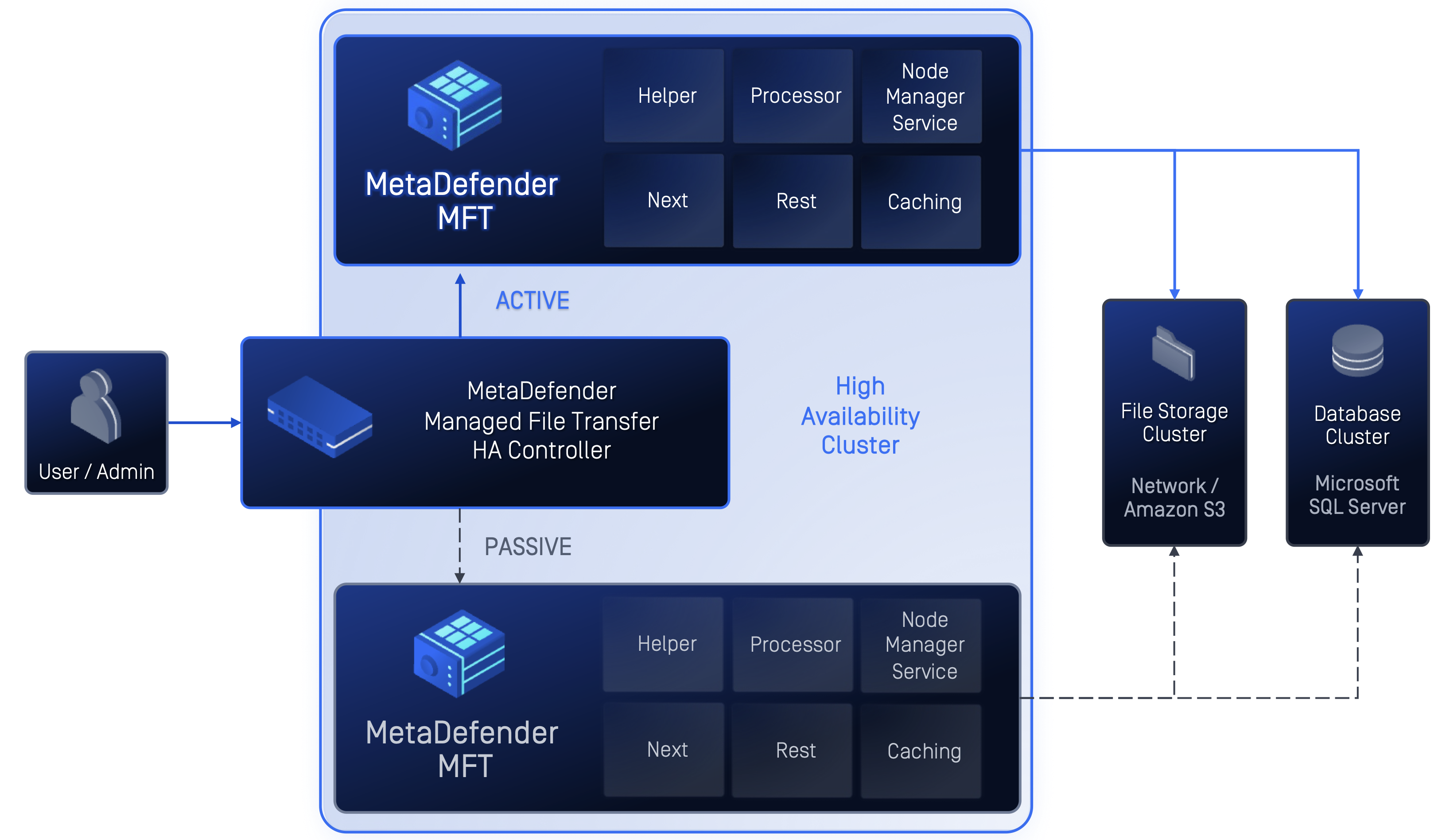
In an active-passive setup, one node is active and handles all traffic and operations, while the other node stays passive until needed.
| Component | Role |
|---|---|
| MetaDefender MFT High Availability Controller™ | Monitors health of service nodes; executes logic to trigger activation or deactivation. It is the arbiter of which node should be active. |
| Active MetaDefender® MFT Node | The service node currently handling client traffic. It is expected to handle full service load and maintain state. |
| Passive MetaDefender® MFT Node | Idle in standby mode. When instructed to activate, it starts up application services, connects to the shared storage and database, and begins serving requests. |
The MetaDefender MFT High Availability Controller™ continuously monitors the health of the active and passive nodes via configured health checks. If it detects that the active node is unhealthy (missed heartbeats, unresponsive services, etc.), the controller will:
- Mark the active node as unhealthy
- Activate the passive node
- Forward all incoming user requests to the newly elected active node
This strategy ensures MetaDefender® MFT continuity, minimizing downtime.
The HA cluster ensures that the application layer stays available during node failures, though availability and redundancy of the database and file storage are not governed by the cluster itself. HA cluster does not attempt to manage external dependencies, such as databases or file storage.
For more details about the failover mechanism, click here.

