Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Regular expressions
Regular expressions, or regex, are a way to search for specific patterns in text. In PDLP, they help find and protect sensitive information. If you're looking for a specific pattern, you can introduce your own regex to define additional sensitive info. This section will introduce how regular expressions work in the PDLP. We'll go over each part step by step.
Enabling regular expression
Policies > Workflow rules > "Workflow name" > Proactive DLP > Check for regular expressions
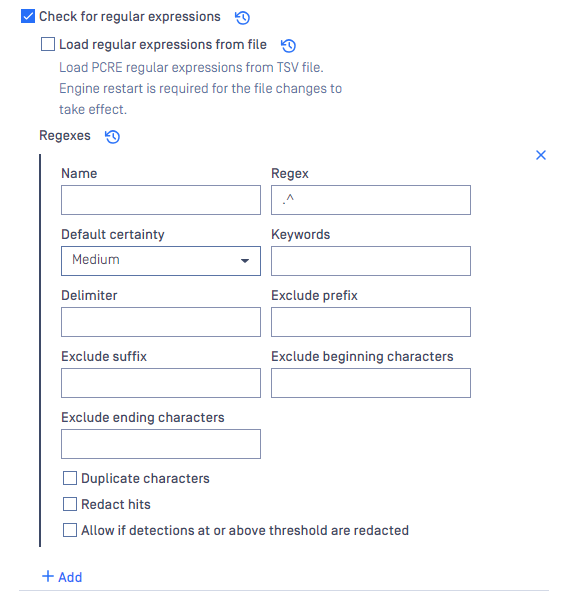
Let's discuss each section and provide an example:
Name
- The label or identifier for the regular expression pattern
- Example: Bank Account Number
Regex
- The specific pattern or sequence you're trying to match in the text.
- Example: \d{8,17}\b
Default certainty
- A confidence level assigned to matches of this regex pattern.
- Example: High
Keywords
- Specific words or terms related to the regex pattern that might assist in its identification.
- Example: Bank, Account Number, Bank Account Number, USA Bank
Delimiter
- Validates a match by checking the surrounding characters. Only match the exact standalone string.
- Example: ;
Exclude prefix
- Characters or patterns to ignore directly before the regex match.
- Example: Invalid-
Exclude suffix
- Characters or patterns to ignore directly after the regex match.
- Example: -Invalid
Exclude beginning characters
- Applied to data that matches the Data identifier Pattern. If a hit starts with the given patterns, it will be excluded.
- Example: {
Exclude ending characters
- Applied to data that matches the Data identifier Pattern. If a hit ends with the given patterns, it will be excluded.
- Example: }
Duplicate characters
- Ensure that a string of digits are not all the same.
Redact hits
- Determines if matches should be redact or replaced with substitute characters.
Allow if detections at or above threshold are redacted
- It allows data to pass if the match is at or above the threshold.
Below are some examples of regular expressions you can use
| Name | Description | Regular Expression |
|---|---|---|
The regex matches on any email. For example: | (?:^|\s)[\w!#$%&'*+/=?^`{|}~-](\.?[\w!#$%&'*+/=?^`{|}~-])*@\w+[.-]?\w*\.[a-zA-Z]{2,3}\b | |
The regex matches on email with a specific domain. For example: | (?:^|\s)[\w!#$%&'*+/=?^`{|}~-](\.?[\w!#$%&'*+/=?^`{|}~-])*@company.com | |
| U.S. Phone Number | The regex matches on a U.S. Phone number. For example:
| (?:(?:\+?1[-.\s])?\(?\d{3}\)?[-.\s])?\d{3}[-.\s]\d{4}(?:\s(?:x|#|[eE]xt[.]?|[eE]xtension){1} ?\d{1,7})?\b |
| U.S. Address | The regex matches on a full U.S. Address. For example:
| \d{1,5}(\s[\w\-.,]*){1,6},\s[A-Z]{2}\s\d{5}\b |
| Full name | The regex matches on a string that contains “Full name“ keyword and 2 or 3 words. For example:
| Full name:\s[A-Z][a-z]+(?:[ \t]*[A-Z]?[a-z]+)?[ \t]*[A-Z][a-z]+\b |
| U.S. Driver license number | The regex matches on a State Driver's license number. For example:
| California: \b[A-Za-z]{1}[0-9]{7}\b |
| U.S. Bank Account number | The regex matches on a string that contains the “Bank Account Number“ keyword and an 8 to 17 digits number. For example:
| Bank Account Number\W*\d{8,17}\b |
| U.S. Passport number | The regex matches on a string that contains a Passport related keyword and a 9 digits number. For example:
| (Passport Number|Passport No|Passport #|Passport#|PassportID|Passportno|passportnumber)\W*\d{9}\b |
| Date of Birth | The regex matches on a date with the YYYY/MM/DD format and a "Date of birth:" or "Birthday:" prefix (Year min: 1900, Year max: 2020). For example:
| (Date of birth:|Birthday:)\s+(?:19\d{2}|20[01][0-9]|2020)[-/.](?:0[1-9]|1[012])[-/.](?:0[1-9]|[12][0-9]|3[01])\b |
| Date of Birth | The regex matches on a date with the DD/MM/YYYY format and a "Date of birth:" or "Birthday:" prefix (Year min: 1900, Year max: 2020). For example:
| (Date of birth:|Birthday:)\s+(?:0[1-9]|[12][0-9]|3[01])[-/.](?:0[1-9]|1[012])[-/.](?:19\d{2}|20[01][0-9]|2020)\b |
| Date of Birth | The regex matches on a date with the MM/DD/YYYY format and a "Date of birth:" or "Birthday:" prefix (Year min: 1900, Year max: 2020). For example:
| (Date of birth:|Birthday:)\s+(?:0[1-9]|1[012])[-/.](?:0[1-9]|[12][0-9]|3[01])[-/.](?:19\d{2}|20[01][0-9]|2020)\b |

