Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
DICOM anonymization
It is now possible to easily remove personal identifying information from the headers of DICOM images as well as those data which are burned on the DICOM images by using the PDLP DICOM Anonymization feature. Among the information that can be removed from DICOM files are the data related to the patient, the data related to the examination, as well as the data that relates to the physicians who have been involved in the process of generating the DICOM files.
Enabling DICOM anonymization
Policies > Workflow rules > Workflow name > Proactive DLP > Anonymization >DICOM
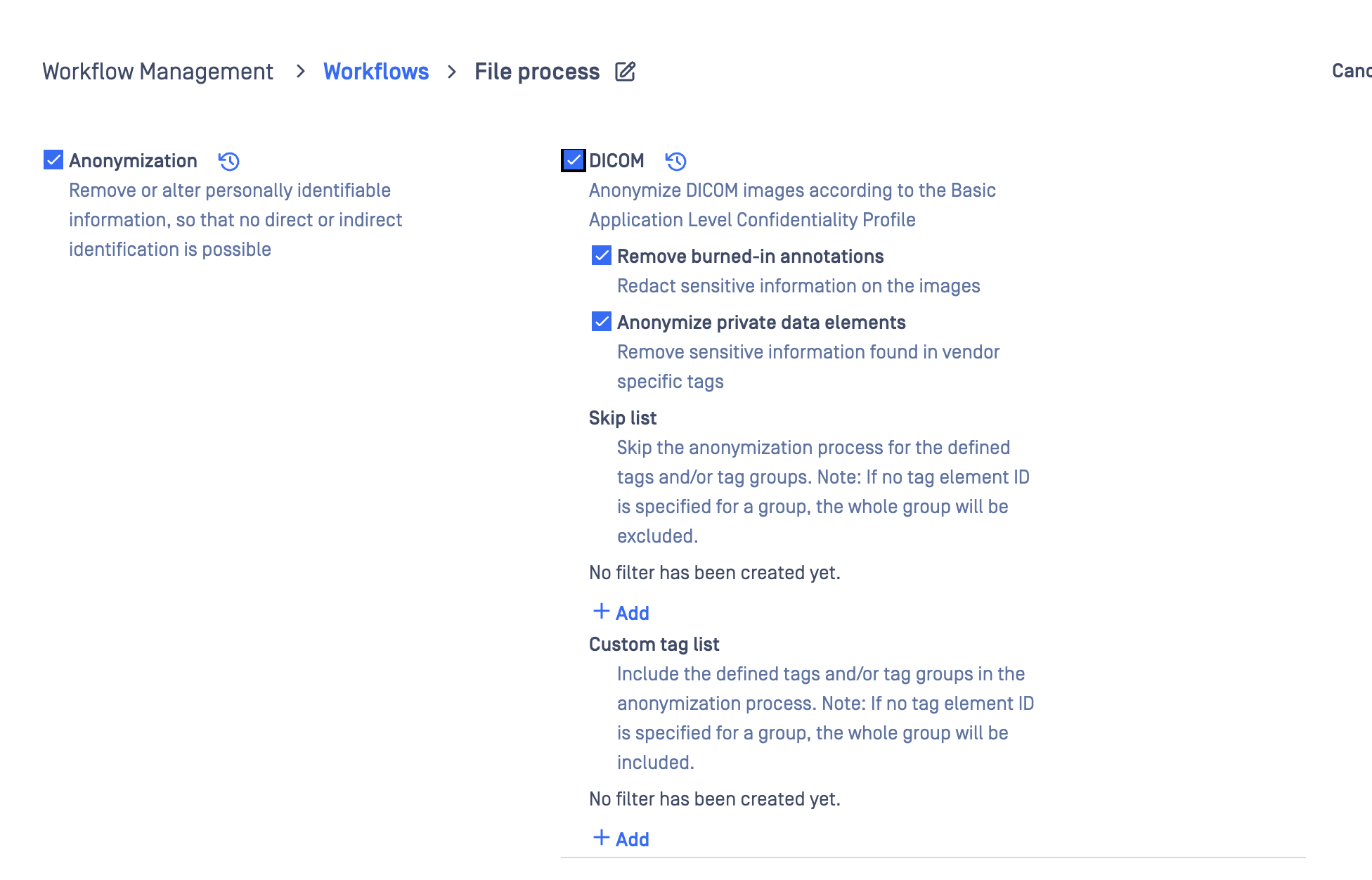
There are two options available when it comes to DICOM anonymization:
- In order to anonymize only the DICOM header, you will have to uncheck the "Remove burned-in annotations" option when setting up the DICOM anonymization feature
- To remove the burned-in PHI/PII from the DICOM images, you will need to make sure that the "Remove burnt-in annotations" box is checked.
- Anonymize private data elements When enabled, the system will automatically remove vendor-specific private tags that may contain sensitive information. This ensures broader anonymization beyond standard DICOM fields.
- Skip list: users can define specific tags or tag groups that should be excluded from the anonymization process.
- Custom tag list: This option allows you to explicitly include certain tags or tag groups for anonymization, even if they are not part of the default DICOM confidentiality profile. Note: If no tag element is specified, selecting the group will include the entire group for anonymization.
Having set up the DICOM Anonymization, you can drop the DICOM file into your PDLP. Once the DICOM file has been dropped, PDLP will anonymize the file and you can download the anonymized version of the DICOM file at the end.
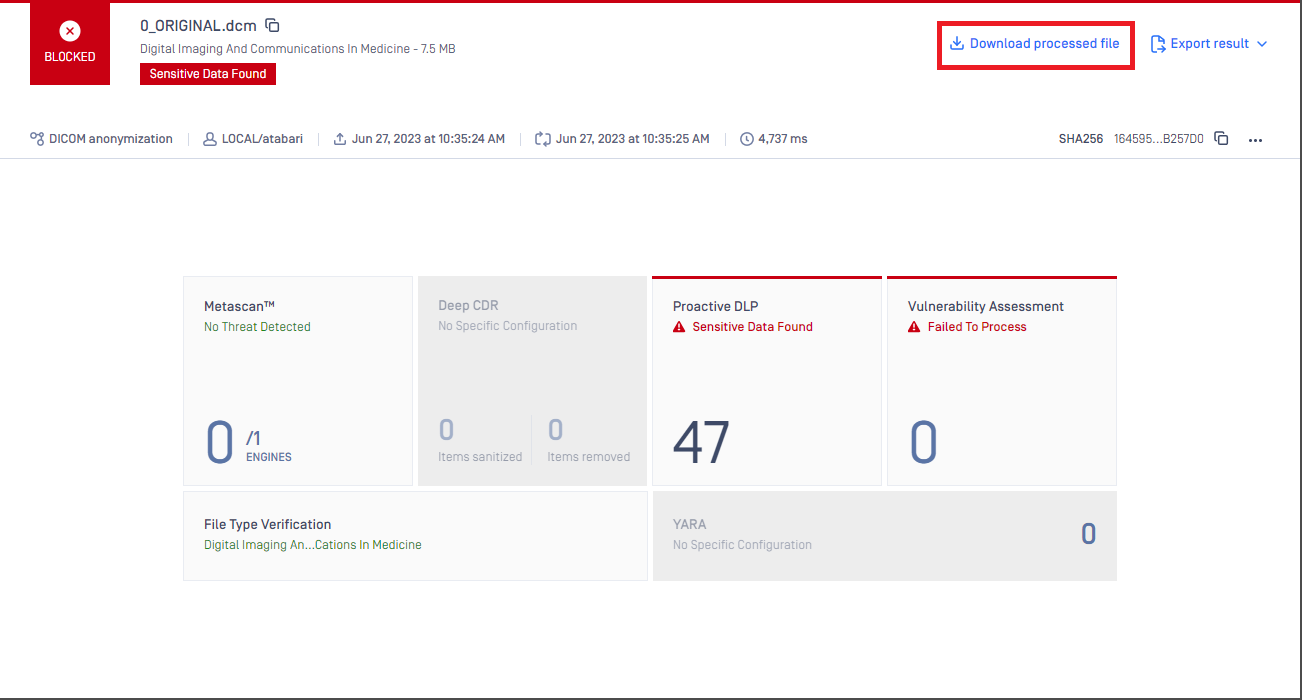
DICOM header metadata anonymization
To anonymize DICOM headers, we follow the DICOM standards so that we can be certain that all PII and PHI are anonymized according to the regulation's guidelines. In the following table you will find a list of the different actions we apply to different tag groups:
| Groups | Actions |
|---|---|
| D_TAGS | Replace with a non-zero length value that may be a dummy value |
| Z_TAGS | Replace with a zero length value, or a non-zero length value that may be a dummy value |
| X_TAGS | Completely remove the tag |
| U_TAGS | Replace all UID's random ones. Same UID will have the same replaced value |
| Z___D___TAGS | Replace with a non-zero length value that may be a dummy value |
| X___Z___TAGS | Replace with a zero length value, or a non-zero length value that may be a dummy value |
| X___D___TAGS | Replace with a non-zero length value that may be a dummy value |
| X_Z___D___TAGS | Replace with a non-zero length value that may be a dummy value |
| X_Z___U___STAR___TAGS | If it's a UID, then all numbers are randomly replaced. Else, replace with a zero length value, or a non-zero length value that may be a dummy value |
Table reference:
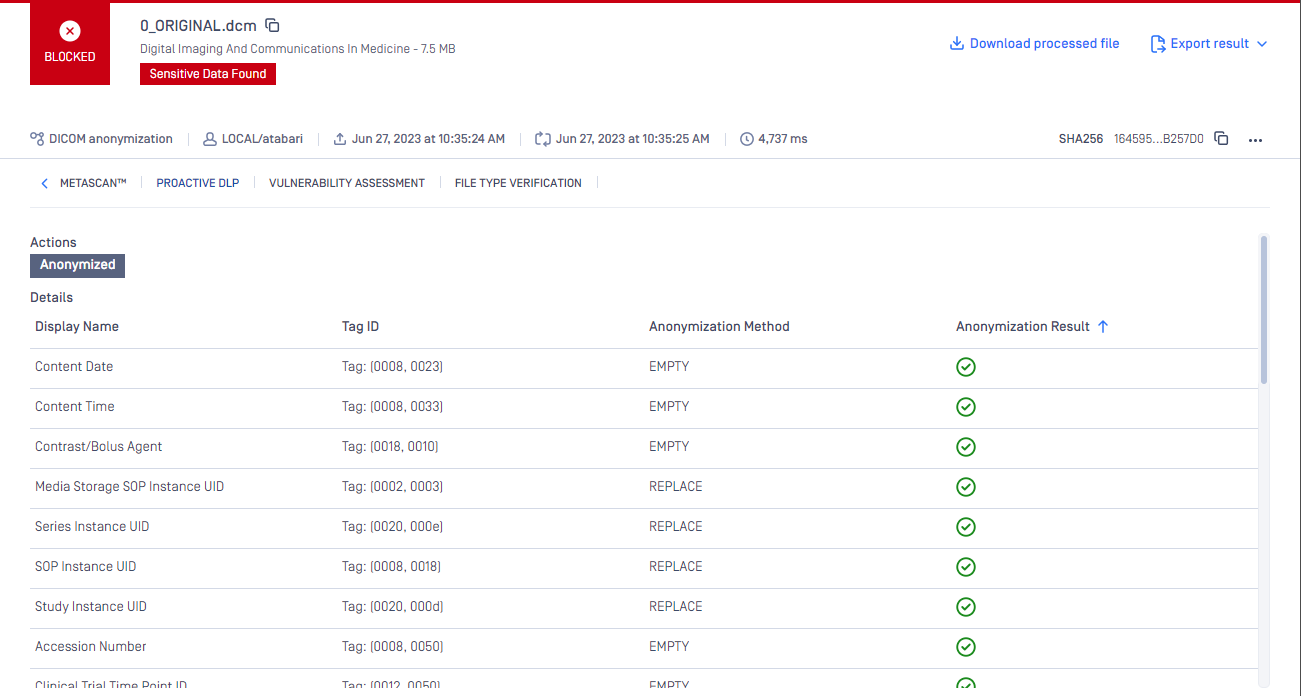
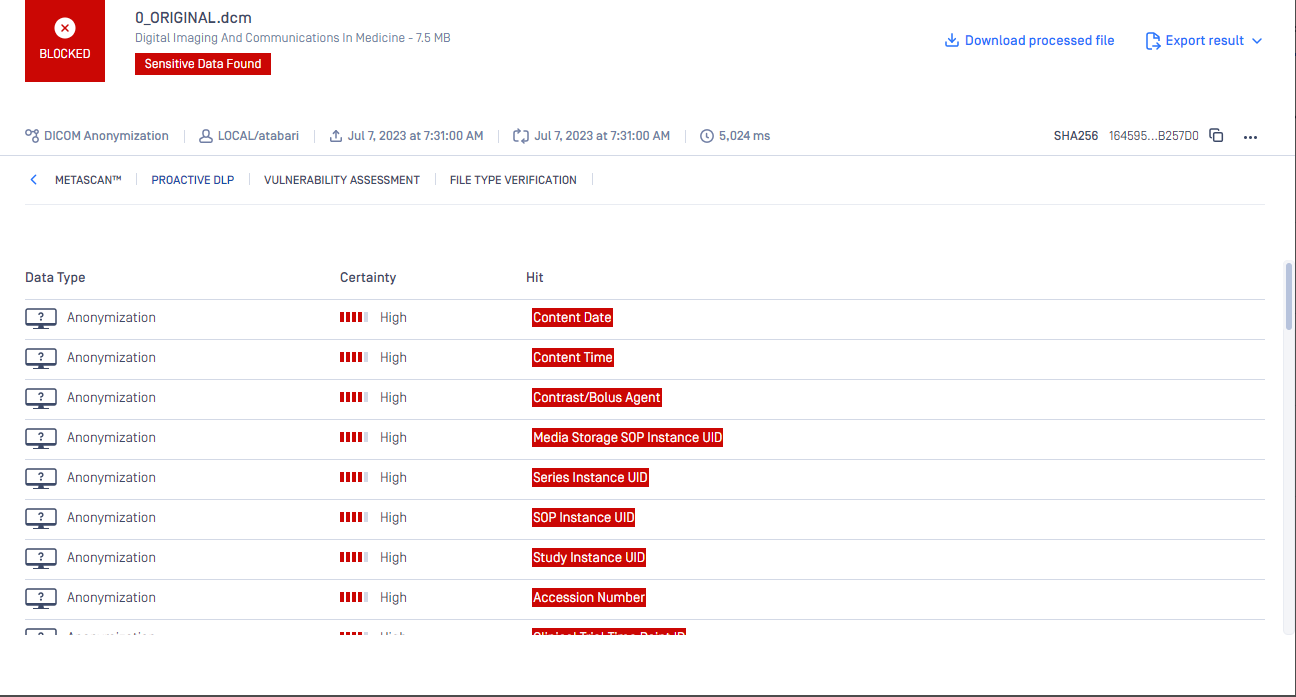
From MD core above 5.3.0 you can see what tags anonymized in the header of a DICOM file at the result pages. For MD core version less than 5.3.0 the DICOM Anonymization will perform the task and anonymize the file however we will not show anything in the result page.
MDCore > 5.3.0
MDCore < 5.3.0
DICOM image anonymization
Additionally, we are also capable of redacting (removing) sensitive content from DICOM images. With the powerful AI-based identification engine that has been added to the OPSWAT PDLP, we have been able to identify and redact the PII and PHI that is burned onto the medical images.
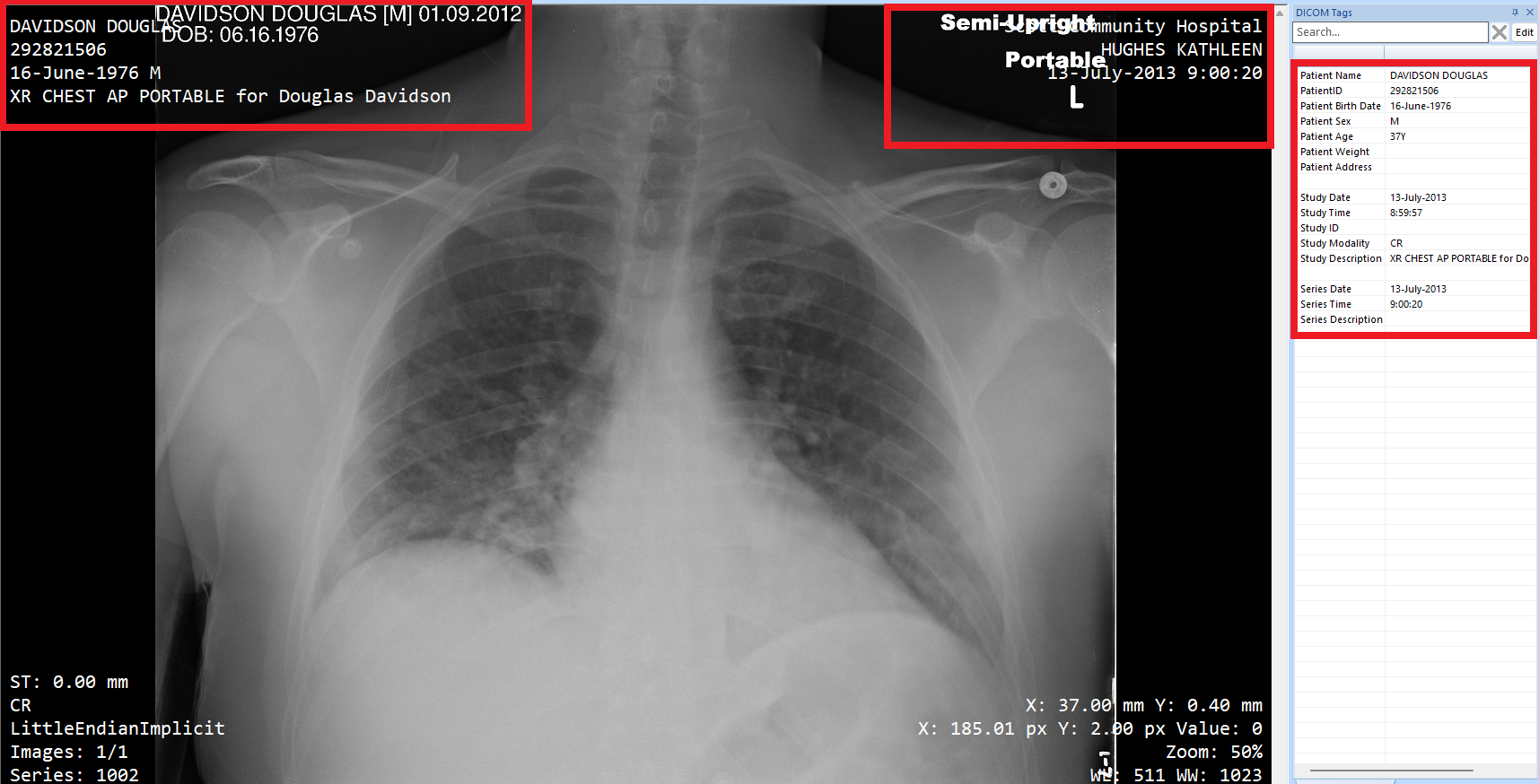
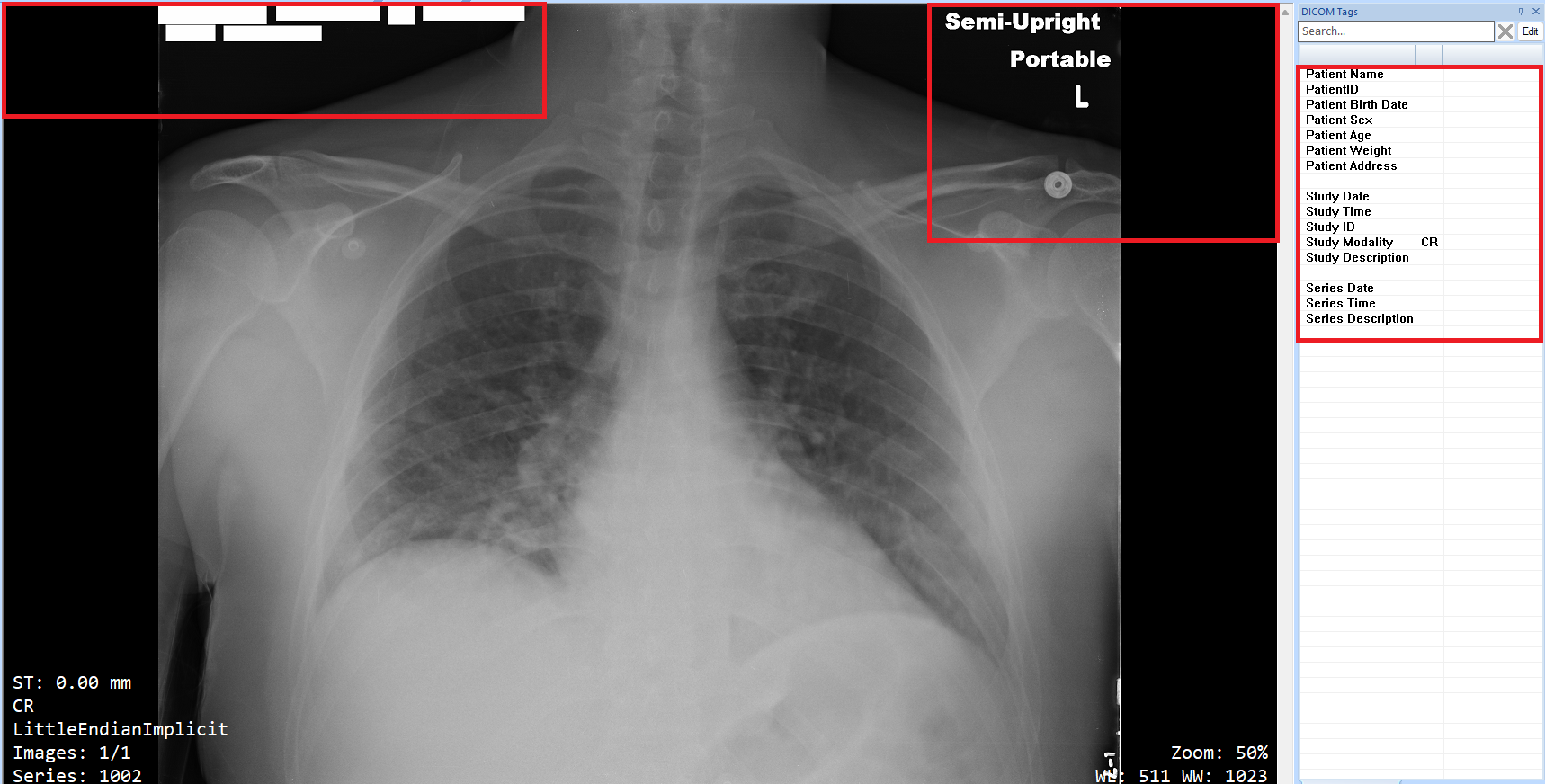
The information provided in these images is fake and it does not depict a real patient in any way.
Before
After
Supported image types
- Explicit VR Little Endian
- Implicit VR Little Endian
- Explicit VR Big Endian
- Deflated Explicit VR Little Endian
- RLE Lossless
- JPEG Baseline
- JPEG Extended
- JPEG2000 Lossless
- JPEG2000
Supported NLP entities
- PERSON: A full name consists of a first name, a middle name, or initials, and a last name
- LOCATION: Geographic or political location (cities, provinces, countries, international regions, bodies of water, mountains)
- NRP: Nationality, religion, or political affiliation of a person.
- DATE_TIME: Dates or periods smaller than a day, whether absolute or relative
This feature uses AI functionality to detect and redact PII (Personally Identifiable Information) and PHI (Protected Health Information) from DICOM file types. You have the option to enable or disable the AI-powered feature within the configuration settings. By default, this feature is disabled but can be activated or deactivated at any time based on user preference. If you enable the AI-powered feature, OPSWAT will not use your content to train or fine-tune its services. You should not rely on any results generated from AI-based functionality without verifying them.

