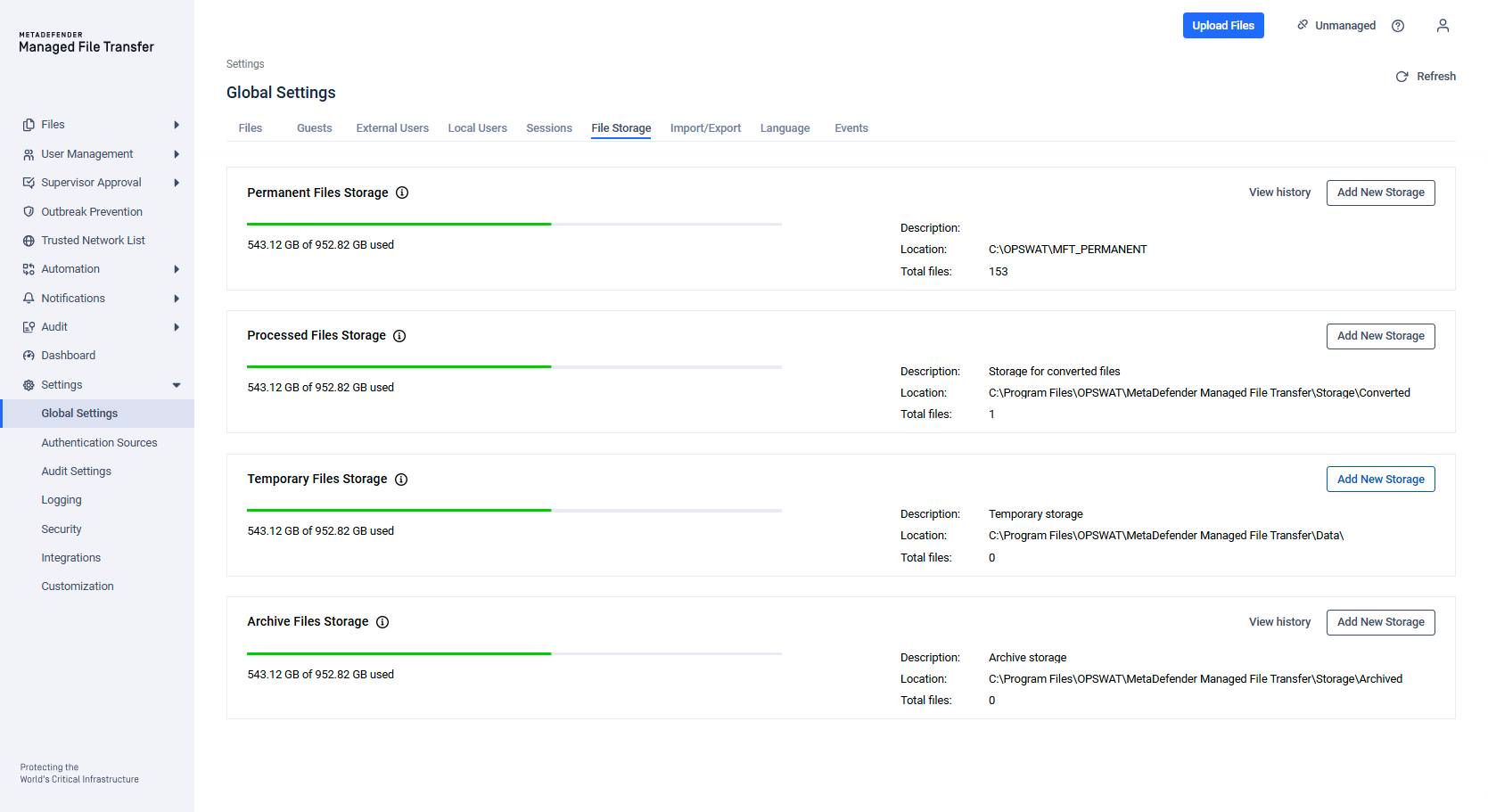
MetaDefender Managed File Transfer™ supports various types of storage (local, network, Amazon S3) for different purposes (temporary, processed, permanent, archived). Configure these storage types by navigating to the "Settings" → "File Storage" page.
Storage types:
| Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Local | A storage represented by a local directory on the disk. |
| 2 | Network storage | A storage represented by a network location. |
| 3 | Amazon S3 storage | A bucket or a directory inside a bucket on Amazon S3 for saving files in the cloud. |
| 4 | S3 Compatible Storage | A bucket or a directory inside a bucket on S3 compatible storage for saving files in the cloud. |
Storage Purposes:
| Purpose | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Temporary | Used to save files before processing and for files scheduled for reprocessing |
| 2 | Processed | Used to save files sanitized by MetaDefender Core™ |
| 3 | Permanent | Used to save fully processed files available for download |
| 4 | Archive | Used to save files no longer needed but kept for audit purposes |
Adding a New Local Storage
Add a new local storage:
- Go to "Settings" → "File Storage"
- Choose the purpose (Permanent, Processed, Temporary, Archive) and click "Add New Storage"
- Fill out the required information
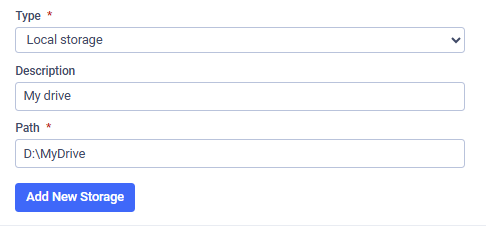
- Click "Add New Storage"
Adding a New Network Storage
MetaDefender Managed File Transfer™ supports connecting to Network Storage via the SMB (Server Message Block) protocol. This allows files to be read from or written to a shared network path, such as a NAS or Windows file share.
Samba is supported from protocol version SMB2_10.
| Input Field | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Path | The full UNC (Universal Naming Convention) path to the network share.
Example: \\server-name\share-name. | Yes |
| Domain | The domain of the user account used to access the share. If your environment uses domain-based authentication (such as Active Directory), provide the domain name here. | No |
| Username | The username for accessing the share. Required if the share is not publicly accessible or requires specific credentials. | No |
| Password | The password corresponding to the provided username. Only required when a username is specified. | No |
If the network share allows guest or anonymous access, the username, password, and domain fields can be left empty.
Add a new network storage:
- Go to "Settings" → "File Storage"
- Choose the purpose (Permanent, Processed, Temporary, Archive) and click "Add New Storage"
- Fill out the required information
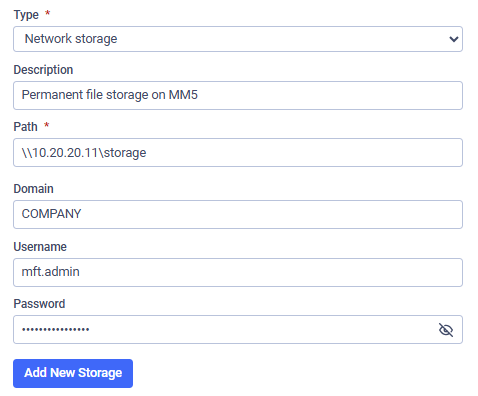
- Click "Add New Storage"
Adding a New Cloud Storage in Amazon S3
Add a new cloud storage:
- Go to "Settings" → "File Storage"
- Choose the purpose (Permanent, Processed, Temporary, Archive) and click "Add New Storage"
- Fill out the required information
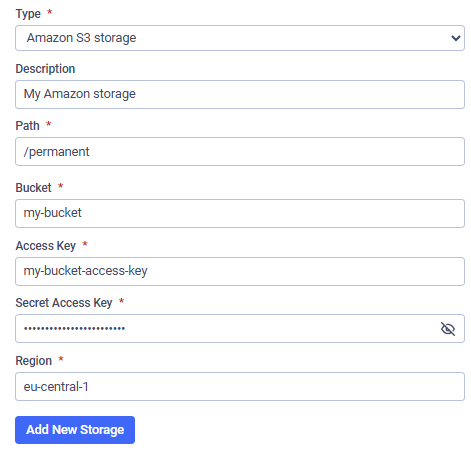
- Click "Add New Storage"
Adding S3 Compatible Storage
Add a new S3 compatible storage:
- Go to "Settings" → "Storage"
- Choose the purpose (Permanent, Processed, Temporary, Archive) and click "Add New Storage"
- Fill out the required information (input values are case sensitive)
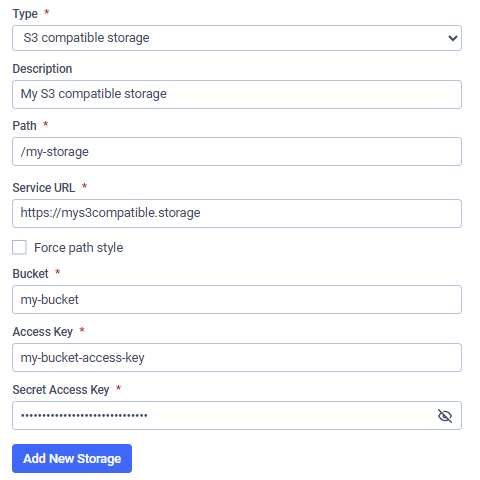
- Click "Add New Storage"
Storage history
After a new storage was added, the previously used storage becomes inactive. The information about the previously used storages - individually of each purpose - can be reached by clicking on the "View history":
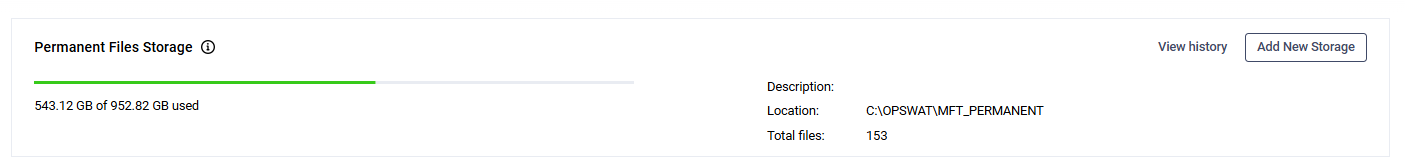
On the detailed storage history page you can check the ground information for the inactive storage(s):
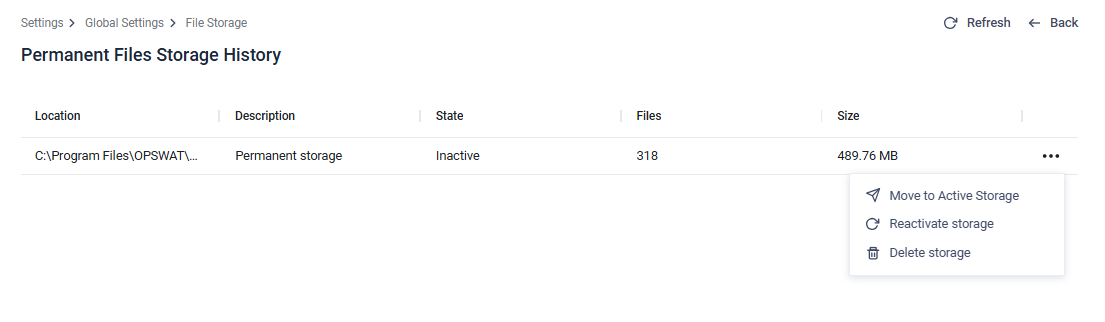
By clicking on the three dot action button you can choose from different actions:
- Move to Active Storage: move the files from the inactive storage to the currently used active storage. The process may take a long time depending on the number and size of the files, but it can be followed on the appearing process corner modal. Please note that the closing of the process modal won't cancel the moving process.
- Reactivate storage: set the selected inactive storage as the active one (the active will be inactivated)
- Delete storage: Deletes the inactive storage if it is no longer needed

