Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
MetaDefender Security Gateway Examples
This appendix shows examples of unilateral file transfer and streaming processes and a bilateral streaming process.
File transfer
After you configure MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE and RED and the transfer parameters, files placed in a specified location on a customer server in the BLUE zone transfer automatically to a specified location on a server in the RED zone.
MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE monitors the specified location on the customer server in the BLUE zone for new files. When a new file is detected, MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE monitors that file until it is considered accessible (i.e., no longer being written to), then reads the file and transfers the data to MetaDefender Security Gateway RED.
MetaDefender Security Gateway RED transfers the file to the specified location on the customer server in the RED zone. After a file is transferred, MetaDefender Security Gateway removes it from its original location.
This example shows a general file transfer flow. While FTP is shown, the flow applies to Windows File Share as well.
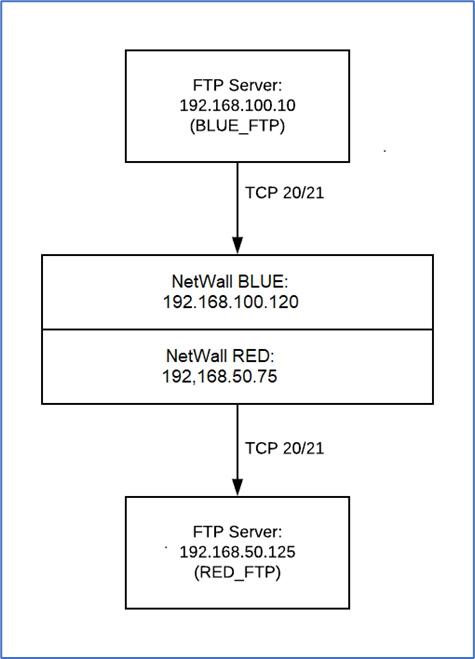
The example configures MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE to monitor a customer-owned FTP server in the BLUE zone and MetaDefender Security Gateway RED to transfer the data to a customer-owned FTP server in the RED zone.
MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE configuration:
- Enabled: (checked)
- FTP User: blueuser
- FTP Password/Re-enter Password: bluepassword
- FTP Server: 192.168.100.10
- FTP Share: blue_ftp
MetaDefender Security Gateway RED configuration (example values given):
- Enabled: (checked)
- FTP User: reduser
- FTP Password/Re-enter Password: redpassword
- FTP Server: 192.168.100.125
- FTP Share: red_ftp
The following sequence occurs when a file is transferred from the BLUE zone to the RED zone:
- MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE (192.168.100.120) monitors the location on the BLUE zone FTP server (192.168.100.10) specified in FTP Share.
- When MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE detects a file, it monitors the file until is it no longer being written to.
- MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE downloads the file, using FTP, transfers the file to MetaDefender Security Gateway RED (192.168.50.75), and deletes the file from its original location on the BLUE zone FTP server.
- MetaDefender Security Gateway RED initiates an FTP connection to the RED zone FTP server (192.168.50.125).
- MetaDefender Security Gateway RED uploads the file to the RED zone FTP server.
Unilateral streaming
Streaming is used to transfer UDP or TCP data from the BLUE zone to the RED zone.
The following example shows TCP streaming for a syslog.
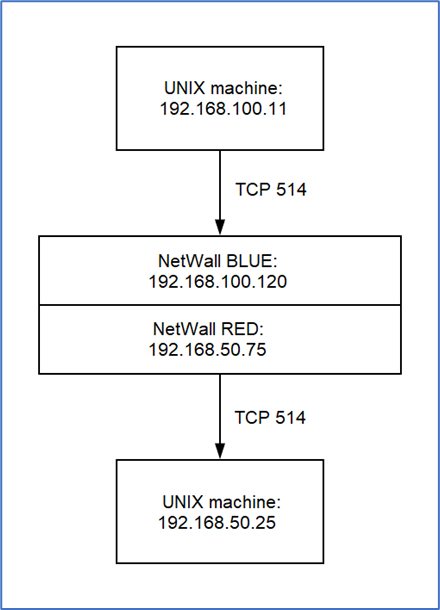
This example configures a UNIX machine in the BLUE zone to send syslog data to a UNIX machine in the RED zone.
The TCP Streaming Configuration for MetaDefender Security Gateway:
- Source IP: 192.168.100.11
- Destination IP: 192.168.50.25
- Source Port: 514
- Destination Port: 514
- Type: TCP Unilateral
- Max Sessions: 1
- Description: Syslog to server in RED zone
This configuration allows the BLUE zone UNIX machine to establish a session with the UNIX machine in the RED zone, both using port 514.
The BLUE zone UNIX machine uses the MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE IP address (192.168.100.120) as the address of the RED zone UNIX machine.
The following sequence occurs when a BLUE zone UNIX machine attempts to send a syslog to the RED zone UNIX machine:
MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE (192.168.100.120) listens for connections on 514. When it receives the TCP request, it identifies the IP address of the BLUE zone UNIX machine (192.168.100.11). If that IP address was not listed as a Source IP, the connection is dropped and a message is logged to Syslog.
MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE assigns a unique identifier (UUID) to this connection instance and sends a connect request to MetaDefender Security Gateway RED (192.168.50.75).
MetaDefender Security Gateway RED receives the connect request and tries to open a TCP connection with the RED zone UNIX machine (192.168.50.25).
MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE reads the connection status (good or fail) from MetaDefender Security Gateway RED.
MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE receives the connection status.
- If the connection status is failed, the connection between MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE and the BLUE zone UNIX machine is dropped.
- If the connection status is good, the syslog data from the BLUE zone UNIX machine is sent to MetaDefender Security Gateway RED, using the UUID as a reference.
MetaDefender Security Gateway RED receives the syslog data and sends it to the RED zone UNIX machine.
If the connection between MetaDefender Security Gateway RED and the RED zone UNIX machine fails MetaDefender Security Gateway RED drops the connection with the UNIX machine.
MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE reads the connection status from v RED and drops its connection with the BLUE zone UNIX machine if the connection status is failed.
If the connection between MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE and the BLUE zone UNIX machine fails, or if the UNIX machine closes the connection gracefully, MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE sends a close request to MetaDefender Security Gateway RED.
MetaDefender Security Gateway RED terminates its connection with the RED zone UNIX machine.
Bilateral streaming
The following example shows bilateral TCP streaming for a MySQL server.
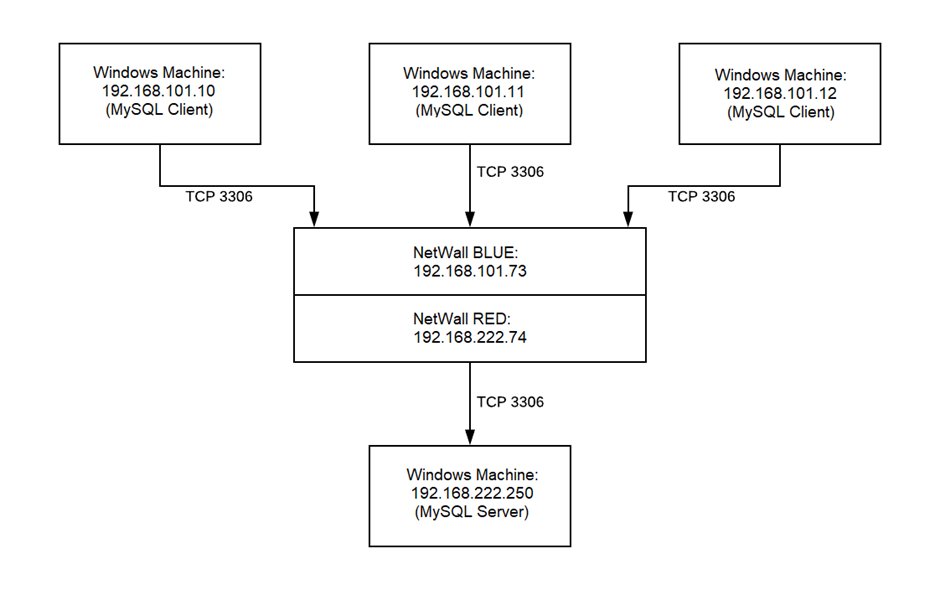
The above example configures three MySQL Windows machines in the BLUE zone to exchange data with a MySQL Server machine (192.168.222.250) in the RED zone.
The TCP Streaming Configuration for MetaDefender Security Gateway:
- Source IP: 192.168.101.10;192.168.101.11;192.168.101.12
- Destination IP: 192.168.222.250
- Source Port: 3306
- Destination Port: 3306
- Type: TCP Bilateral
- Max Sessions: 3
- Description: MySQL Server Test
This configuration allows the three BLUE zone Windows computers to establish independent and concurrent sessions with the MySQL Server in the RED zone, all using port 3306.
The MySQL Clients on the BLUE zone computers use the MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE IP address (192.168.101.73) as the address of the MySQL server.
The following sequence occurs when a BLUE zone computer (i.e., 192.168.101.10) attempts to connect to the MySQL server:
MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE (192.168.101.73) listens for connections on 3306. When it receives the TCP request, it identifies the IP address of the BLUE initiating computer (192.168.101.10). If that IP address was not listed as a Source IP, the connection is dropped and a message is logged to Syslog.
MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE assigns a unique identifier (UUID) to this connection instance and then sends a connect request to MetaDefender Security Gateway RED (192.168.222.74).
MetaDefender Security Gateway RED receives the connect request and tries to open a TCP connection with the MySQL server (192.168.222.250).
MetaDefender Security Gateway RED sends the connection status (good or fail) back to MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE using the assigned UUID as a reference.
MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE receives the connection status.
- If the connection status is fail, the connection between MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE and the Windows machine (192.168.101.10) is dropped.
- If the connection status is good, all TCP data from the Windows machine is sent to MetaDefender Security Gateway RED, using the UUID as a reference. Note that only the TCP data payload is sent to MetaDefender Security Gateway RED. All Network-related data (IP address, MAC address, etc.) is removed before the data is sent to MetaDefender Security Gateway RED.
MetaDefender Security Gateway RED receives the data payload and sends it to the MySQL server.
- If the connection between MetaDefender Security Gateway RED and the MySQL server fails, the fail status is sent back to MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE and MetaDefender Security Gateway RED drops the connection with the MySQL Server. MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE then drops its connection with the MySQL Windows Client (192.168.100.10).
- If the connection between MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE and the MySQL Windows Client fails, or if the MySQL Windows Client closes the connection gracefully, MetaDefender Security Gateway BLUE sends a close request to MetaDefender Security Gateway RED.
MetaDefender Security Gateway RED terminates its connection with the MySQL Server.

