Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Sizing Guide
A Practical Guide
MetaDefender Storage Security (MDSS) is built for flexibility. It uses containers, which let you customize and adapt your development to match your specific needs. Getting the sizing right is crucial for performance and reliability as your workload directly impacts sizing. Proper sizing ensures smooth operation. This guide will help you understand the key components and make informed decisions.
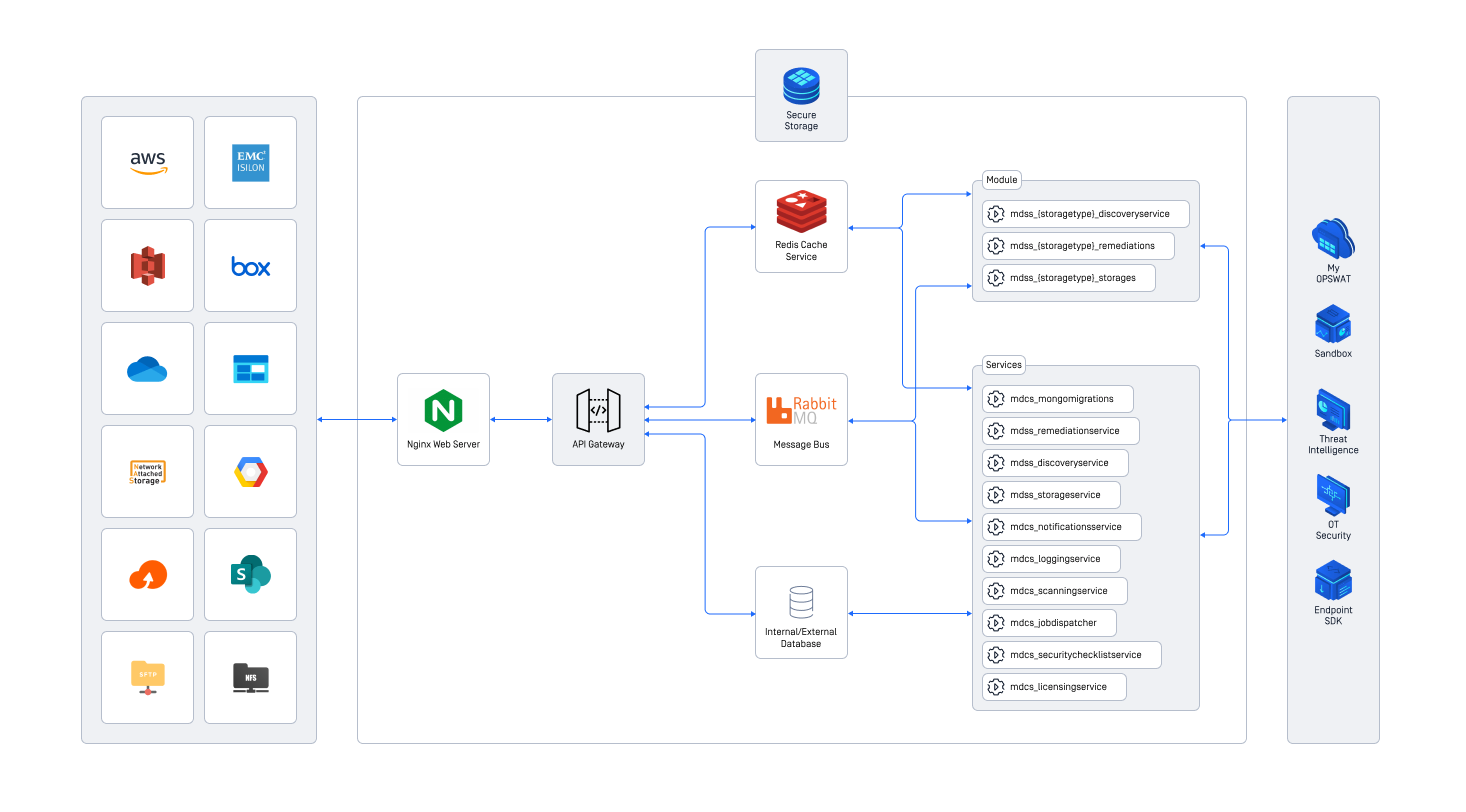
High level architecture of MetaDefender Storage Security
Shared Services
MDSS relies on several critical shared services:
- MongoDB (Database) for storing persistent data as scaling MongoDB ensures data integrity and performance.
- RabbitMQ (Message Broker) handles inter-component communication as horizontal scaling is vital for message throughput.
- Redis (Cache) provides fast data access, reducing latency as proper sizing ensures optimal caching efficiency.
Why These Services Matter:
- Scalability as these services are fundamental for scaling MDSS to handle increased loads.
- Stateful Services as they maintain data (state), requiring consistent accessibility across the system.
- Horizontal Scaling as adding more instances (horizontal scaling) is essential for high availability and performance.
Deployment Considerations for Specific Technologies
- Amazon AWS:
- as an RabbitMQ alternative consider Amazon ElastiCache for improved message broker performance in AWS environments. This can reduce latency and improve overall system responsiveness.
- for Database & Cache Optimization explore AWS-specific configurations for MongoDB and Redis for better performance and cost-efficiency. For example, using ElastiCache for Redis can offer optimized caching.
Deployment Options
This table summarizes the various deployment options available for MDSS. It helps you understand the differences between each option and choose the one that best fits your needs.
| Small scale deployments | Medium scale deployments | Large scale deployments | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feature | Basic Deployment (Single Instance) | Basic Deployment with Self-Hosted Shared Services | Basic Deployment with Managed Services | Advanced Deployment with Self-Hosted Shared Services | Advanced Deployment with Managed Services | Cloud Deployment with Kubernetes (k8s) | MDSS Cloud (SaaS) |
| Best for | Small and predictable workloads | Small workloads, some flexibility, HA desired | Small workloads, with managed services | Medium workloads, manual scaling | Medium to Large workloads, no auto-scaling | Large workloads, dynamic scaling, cost-optimized | Scalable, secure, efficient cloud-based storage security solution |
| Scalability | |||||||
| High Availability | |||||||
| Auto-Scale Ready | |||||||
| Files / hour (Objects / hour) | 5,000 (125,000) | 20,000 (500,000) | 50,000 (1,250,000) | 100,000 (2,500,000) | 100,000 (2,500,000) | 100,000 or more | 500,000 or more |
| Recommended MD Core # | 2-4 | 4 or more | 4 or more | 4 or more | 4 or more | Tailored per customer | Tailored per customer |
| Recommended MDSS # | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 or more | 2 or more | Tailored per customer | Tailored per customer |
| Infrastructure complexity |
Understanding the Options
Basic Deployment (Single Instance):
- Pros - a simple setup, good for very small and predictable workloads.
- Cons - no scalability or high availability.
Basic Deployment with Self-Hosted Shared Services:
- Pros - offers some flexibility and basic high availability.
- Cons - more complex to manage than a single instance.
Basic Deployment with Managed Services:
- Pros - simpler management due to managed services.
- Cons - still limited scalability.
Advanced Deployment with Self-Hosted Shared Services:
- Pros - handles medium workloads, scalable.
- Cons - requires manual scaling, complex infrastructure.
Advanced Deployment with Managed Services:
- Pros - handles larger workloads, scalable.
- Cons - no auto-scaling, tailored sizing required.
Cloud Deployment with Kubernetes (k8s):
- Pros - ideal for large, dynamic workloads, auto-scaling, cost-optimized.
- Cons - requires Kubernetes expertise.
MDSS Cloud (SaaS):
- Pros - fully managed, highly scalable, secure, and efficient.
- Cons - less control over infrastructure.
Key Considerations
- How many files/objects do you process per hour?
- Do you need to handle increasing workloads?
- Is it critical for your system to be always available?
- How much effort are you willing to put into managing the infrastructure?
- Budget - SaaS solutions might have different cost structures compared to self-managed deployments.
Choosing the Right Option
- if you're just starting, a basic deployment might be sufficient.
- if you expect your workload to increase, consider advanced deployments or the SaaS option.
- if high availability is crucial, choose an option that supports it.
- if you want to minimize infrastructure management, consider managed services or SaaS.
How we tested and what it means
We tested MDSS with a mix of everyday files, like documents, images, and videos, to get realistic performance numbers. We started small and then scaled up to see how it handled larger workloads. However, remember that these are just guidelines. Your actual performance will depend on your files, network, and hardware. For critical systems, it's always best to test it out yourself.
The numbers in the deployment table are based on rigorous testing using a diverse set of real-world files. We didn't just use one type of file; we included a mix of:
- Documents - PDFs, Word files (DOC/X), Excel files (XLS/X), PowerPoint files (PPT/X)
- Executables - EXEs, MSIs (installation files)
- Images - BMP, JPG, PNG
- Media - MP3, MP4 (audio and video)
- Text and Archives - various text files and compressed archives
The Numbers Explained
- our starting point was 5,000 files, totaling 7,728.5 MB. The average file size was 1.55 MB.
- to see how MDSS handles bigger workloads, we replicated this dataset to create scenarios with 50,000 files and over 100,000 files. This helped us understand performance scaling.
The numbers in the table are meant to be guidelines. Real-world performance can vary due to:
- File Type Variations - some file types are processed faster than others.
- Network Speed - a slow network can impact throughput.
- Hardware Specs - the performance of your servers matters.
For mission-critical applications we strongly recommend running your own performance tests (benchmarks) in your specific environment before deploying MDSS in production. This will give you the most accurate picture of how MDSS will perform with your unique setup.
Basic Deployment (Single Instance)
This is the fastest and easiest way to get MetaDefender Storage Security (MDSS) up and running. Think of it as putting everything – storage, MDSS itself, and its MD Core processing – on one machine.
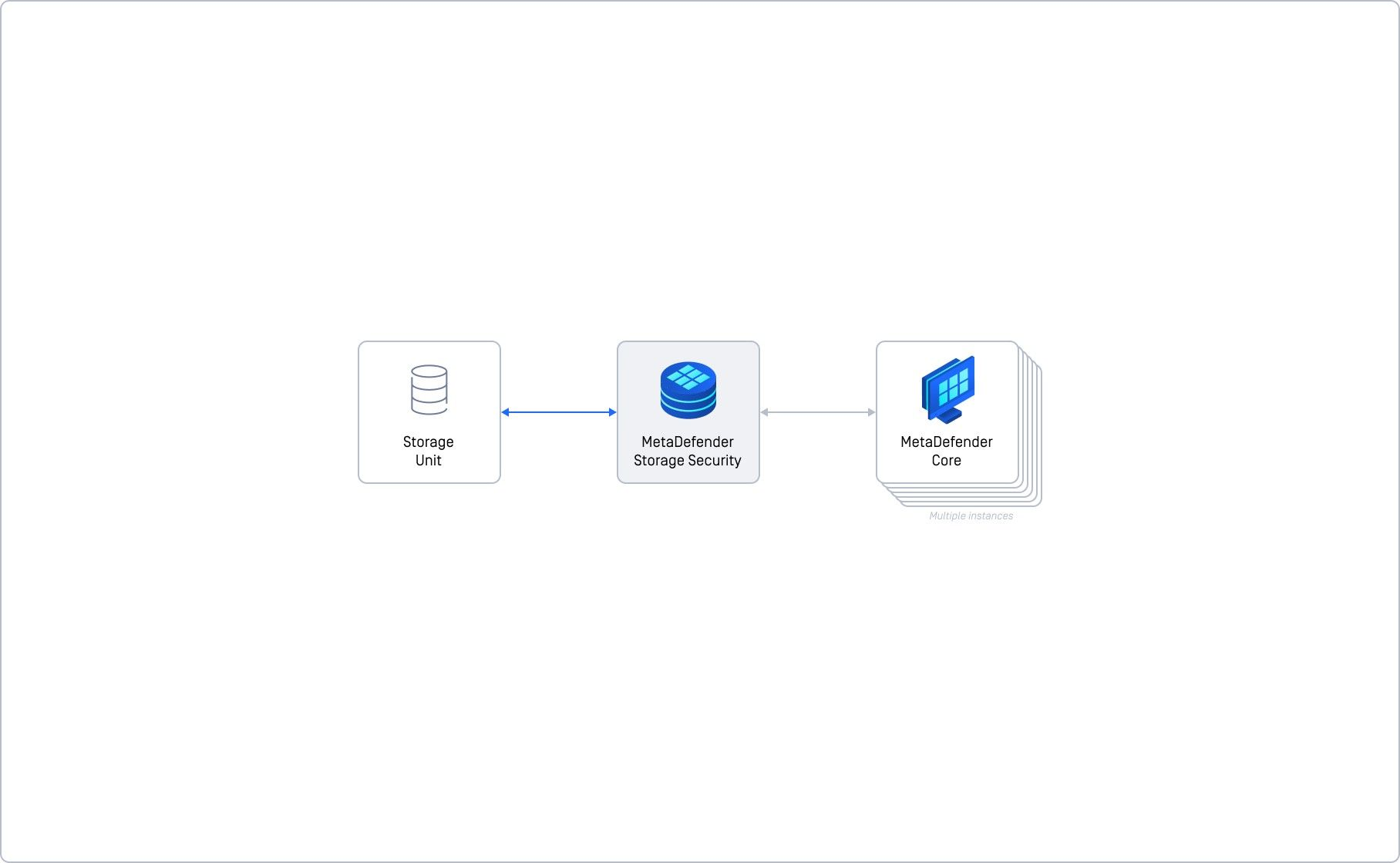
Imagine running MDSS on a single computer. It's fast to set up and good for small tasks. But if you need to handle a lot of work or can't afford any downtime, this isn't the right choice.
Who is it for?
- Small Workloads making it perfect for testing or very light usage.
- Quick Setup so ideal when you need MDSS running quickly without complex configurations.
Key Points
- All components run on one server.
- You can't add more servers to handle more load.
- If the server goes down, MDSS goes down.
- You can still reconfigure or upgrade MDSS on this setup.
Important Considerations
- Performance will vary depending on your server and file types.
- This setup is not recommended for live, critical systems where you need high availability or the ability to handle a lot of data.
- You get simplicity, but you lose the ability to scale and ensure continuous operation.
Further Resources
Basic Deployment with Self-Hosted Shared Services
This deployment takes the basic setup a step further by separating the core services (database, cache, and message broker) from the main MDSS instance. This gives you more control and improves performance, but adds complexity.
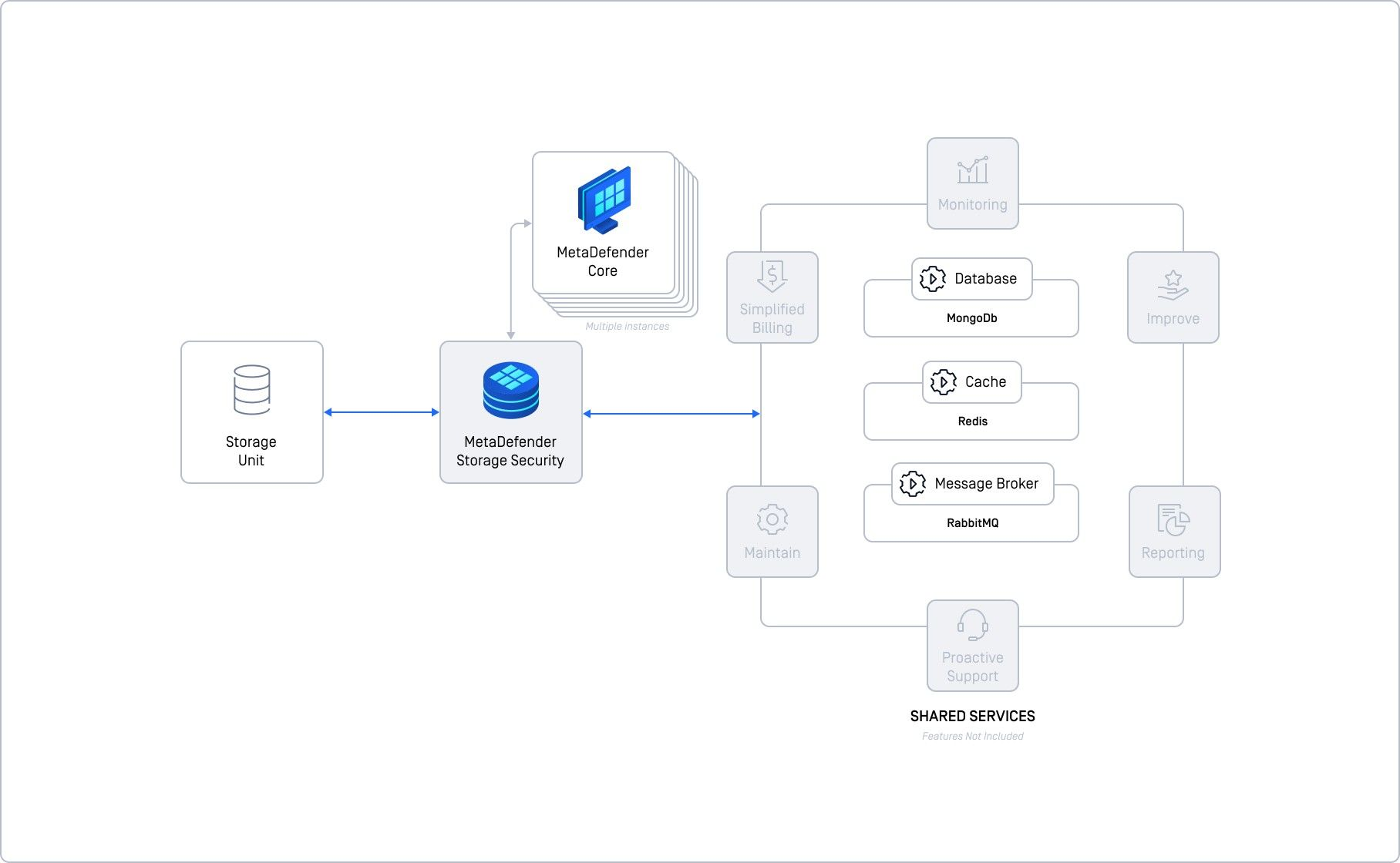
Instead of running everything on one machine, you're now running the database, memory cache, and communication hub on separate machines. This gives you more control and better performance, but you're also responsible for setting everything up and keeping it running smoothly.
Who is it for?
- Small to Medium Workloads as it can handle up to 20,000 files per hour with proper resources.
- Organizations with IT Expertise as it requires in-house expertise to manage the infrastructure.
Key Components & Their Roles
- MongoDB (Database) stores data.
- Redis (Cache) speeds up data access.
- RabbitMQ (Message Broker) manages communication between components.
Key Points
- each shared service runs on its own server/VM.
- you are responsible for installing, configuring, and maintaining these services.
- Requires more technical knowledge and effort.
- Can handle larger workloads compared to a single instance.
- You can scale individual services, but it's not as seamless as a fully cloud-native setup.
Important Considerations
- You need to configure replication for high availability.
- Make sure sufficient resources are allocated to each shared service.
- Running all shared services on a single VM defeats the purpose of this setup and impacts performance.
- While better than a single instance, it's still possible to have single points of failure if not configured correctly.
- Once all services are deployed and ready to be used, please follow Self-hosted shared services
Further Resources
Basic Deployment with Managed Services
Instead of managing the database, cache, and message broker yourself, you let the cloud provider handle it. You focus on setting up and scaling MDSS, while the cloud takes care of the underlying infrastructure. Think of it as renting managed services instead of buying and maintaining them yourself.
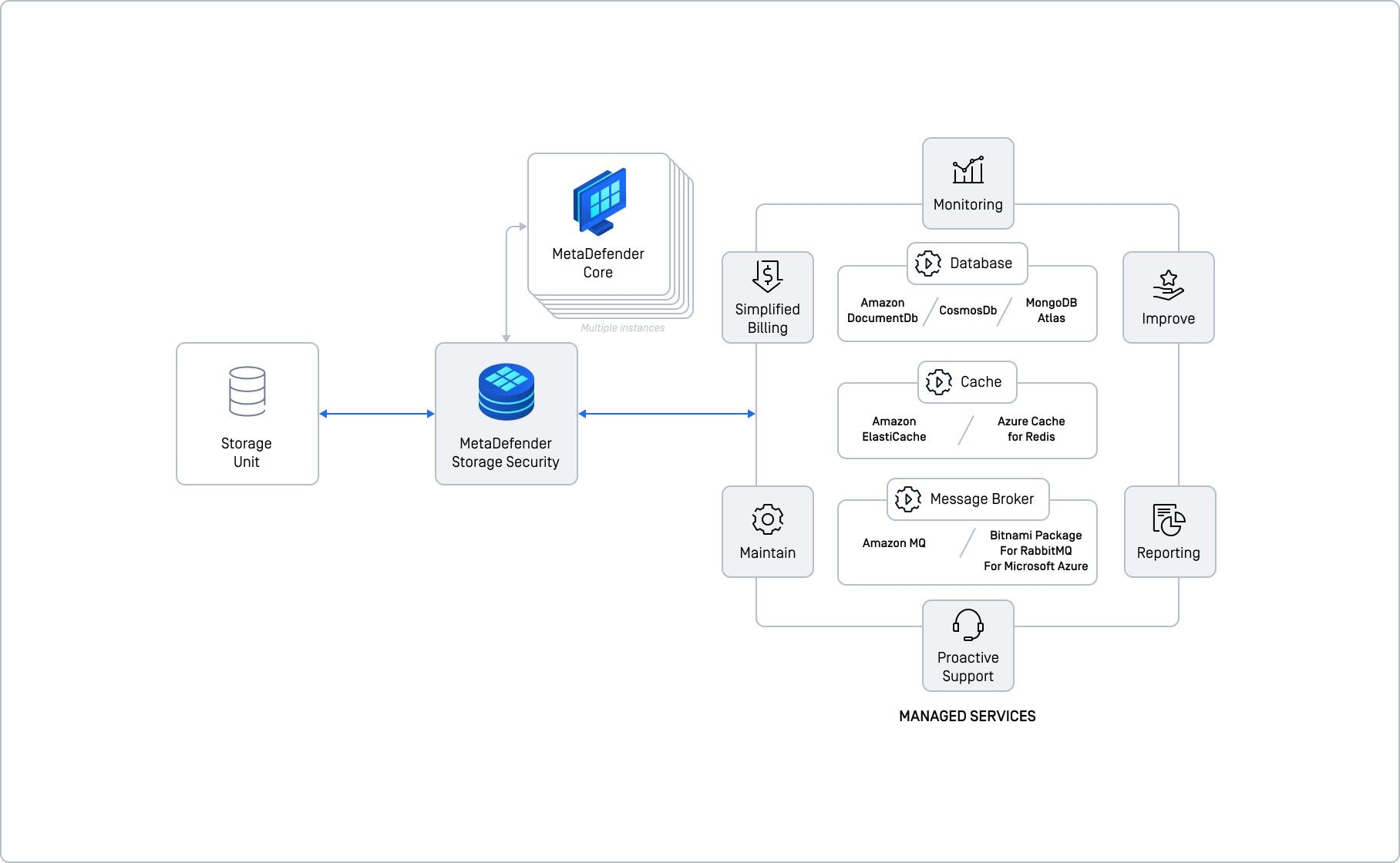
This deployment builds on the basic model by using managed cloud services for the shared components (database, cache, message broker). This means you leverage the cloud provider's expertise to handle the infrastructure, simplifying your setup.
Who is it for?
- Cloud-First Organizations, organizations heavily reliant on cloud infrastructure.
- Organizations Seeking Simplicity as it reduces the burden of managing infrastructure.
- Workloads up to 50,000 Files/Hour - achievable with sufficient cloud resources and MDSS and MD Core instances.
Key Advantages
- Cloud provider handles maintenance, monitoring, and scaling of shared services.
- Ideal for organizations already using cloud services like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
- Reduces operational overhead compared to self-hosting.
- Benefits from cloud-provided features like enhanced monitoring, reporting, and proactive support.
Example: Amazon AWS Integration
- Database - use Amazon DocumentDB.
- Cache - use Amazon ElastiCache for Redis.
- Message Broker - use Amazon MQ.
Adaptable to Other Clouds
This approach can be adapted to Azure and Google Cloud, using their respective managed services. Please follow this page. for more information regarding integrating with various cloud providers.
Key Points
- You don't manage the shared services directly.
- Your primary focus is on configuring and scaling MDSS itself.
- Leverage the cloud provider's scalability for shared services.
- Benefit from the cloud provider's redundancy and reliability.
Important Considerations
- Managed services have associated cloud costs, which need to be factored in.
- Requires understanding cloud service integrations and their complexity
Advanced Deployment with Self-Hosted Shared Services
This deployment is for high-performance needs, using multiple MDSS and MD Core instances and self-hosted shared services (database, cache, message broker). It's significantly more complex than the basic setups but offers superior performance and reliability.
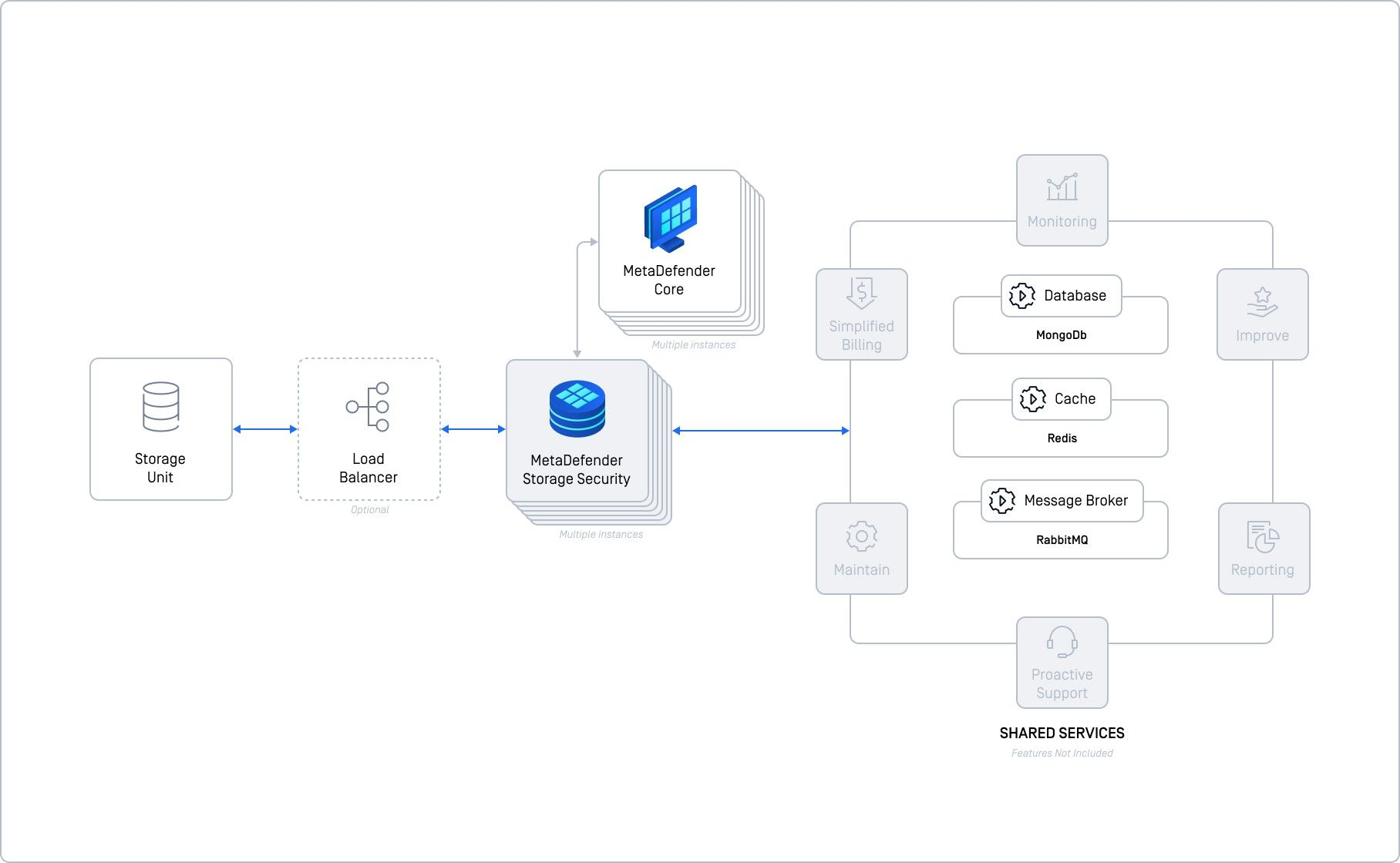
This setup is like building a powerful engine. You're running multiple MDSS and MD Cores and managing the database, cache, and communication hub yourself. This gives you high performance, but it's also more complex to set up and maintain.
Who is it for?
- High-Throughput Environments, organizations processing large volumes of files.
- Organizations with Strong IT Infrastructure as it requires in-house expertise to manage the complexity.
Key Components & Their Roles
- Multiple MDSS Core Instances - allows parallel processing for higher throughput.
- MongoDB (Database) - stores data.
- Redis (Cache) - speeds up data access.
- RabbitMQ (Message Broker) - manages communication between components.
Key Points
- Requires more planning and technical expertise.
- Can handle up to 100,000 files per hour with sufficient resources.
- You are responsible for installing, configuring, and maintaining all components.
- Allows scaling through multiple MDSS Core instances and shared services.
- Achieved through database replication and careful configuration.
Important Considerations
- Requires significant hardware resources for all components.
- Effective monitoring is essential due to the increased complexity.
- While better than basic setups, careful planning is needed to avoid single points of failure.
- Our testing showed 2 MDSS instances with 4 MDSS Core instances yielded substantial performance improvements.
- Once all services are deployed and ready to be used, please follow Production considerations to connect MDSS to them.
Further Resources
- Advanced deployments | System Requirements
- Self-hosted shared services
- Installation
- Production considerations for Unix-based deployments
- Production considerations for Windows-based deployments
Advanced Deployment with Managed Services
This setup uses multiple MetaDefender Storage Security (MDSS) instances and leverages your cloud provider's managed services for the database, cache, and message broker. It's designed for high throughput and simplifies management.
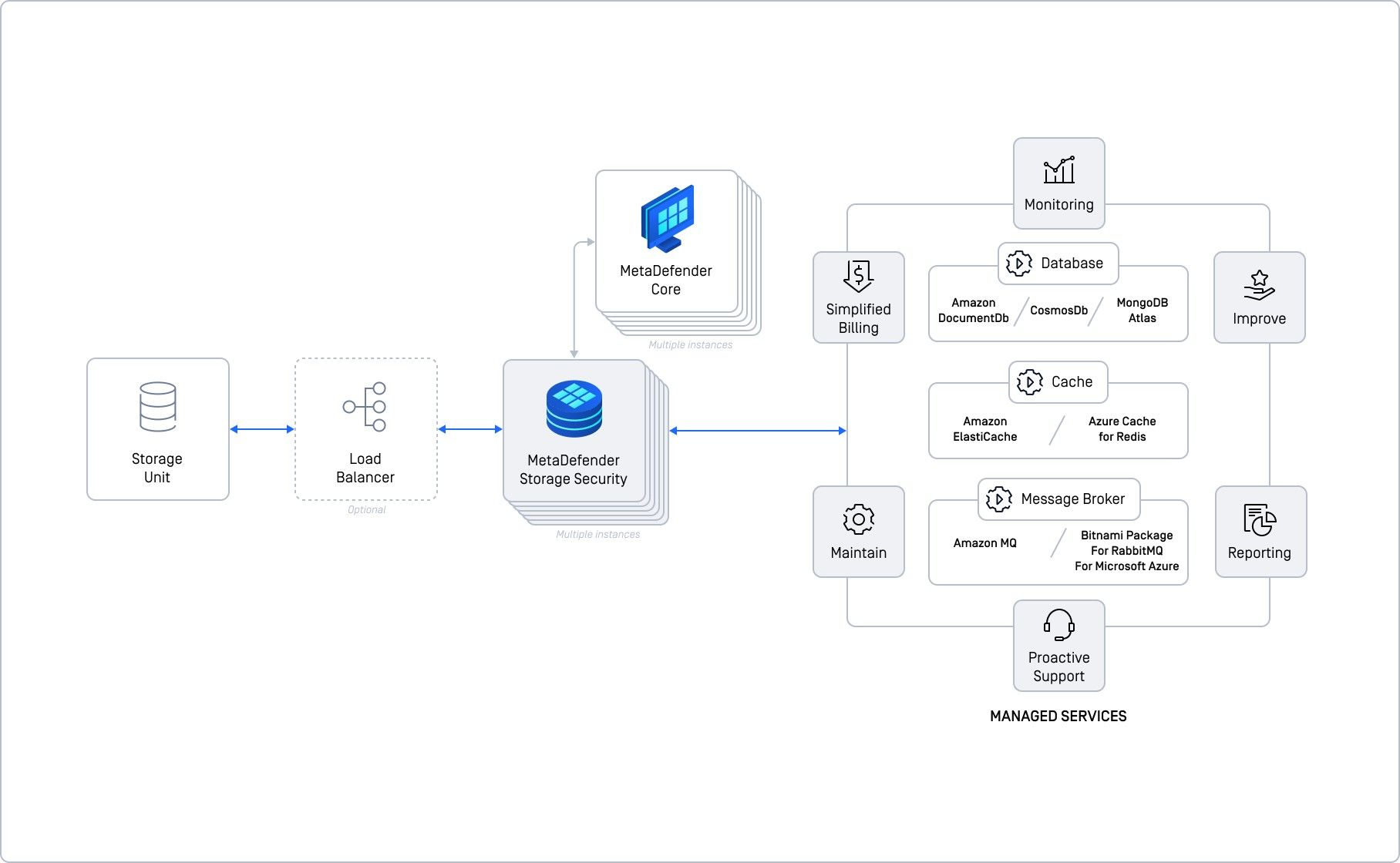
Imagine having a team of experts (your cloud provider) handle the backend infrastructure, allowing you to focus on scaling and managing your MDSS instances. This setup is powerful and efficient for high-volume workloads.
Who Should Use This
- Organizations processing a lot of files.
- Cloud-Centric Businesses who already leveraging cloud infrastructure.
Why It's Powerful
- Multiple MDSS instances handle large workloads efficiently.
- Your cloud provider handles the underlying infrastructure (database, etc.).
- Ideal if you're already using cloud services.
- Get monitoring, reporting, and proactive support from your cloud provider.
Example (AWS)
- Database use Amazon DocumentDB
- Cache use Amazon ElastiCache
- Message Broker use Amazon MQ
Adaptable to Azure & Google Cloud: You can use similar services from those providers. For more information on integrating with various cloud providers, please follow this page.
Key Benefits
- You manage the MDSS instances, not the database, cache, etc.
- Cloud providers ensure redundancy and availability.
- Tested to handle 100,000 files/hour (with 2+ MDSS and 4+ MDSS Core instances).
Important Note: Cloud managed services have associated costs.
Cloud Deployment with Kubernetes (k8s)
This is our recommended option for maximum scalability, high availability, and handling large volumes of data. It uses Kubernetes to automate deployment, scaling, and management of MDSS in a cloud environment.
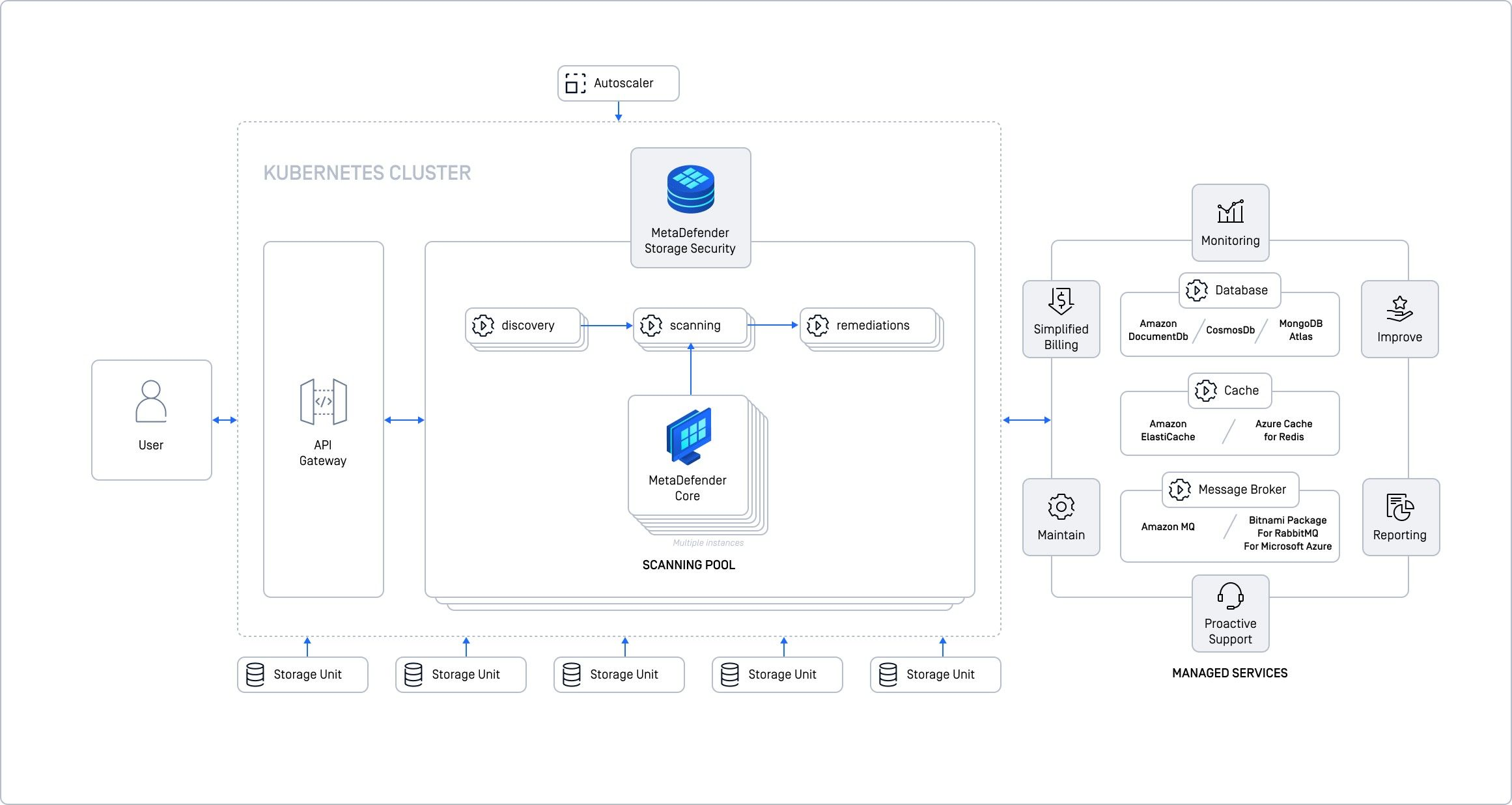
Kubernetes is like an automated control system for your cloud deployment. It lets you scale MDSS easily, ensures it stays running, and optimizes resource usage. If you need high performance and availability, this is the way to go.
Who Should Use This?
- Organizations handling massive amounts of data.
- Organizations Prioritizing High Availability, needing minimal downtime.
- Cloud-Savvy Teams familiar with Kubernetes.
Why Use Kubernetes?
- Dynamically adjust resources based on workload.
- Distributes MDSS across multiple nodes to minimize downtime.
- Optimize resource allocation for each component.
- Kubernetes handles load balancing, autoscaling, and more.
Key Components & Cloud Integration
- Kubernetes (k8s) orchestrates the deployment.
- Managed Cloud Services for database, cache, message broker (e.g., AWS EKS, Azure AKS, Google GKE).
Examples
- For AWS - use Amazon DocumentDB, Amazon ElastiCache, Amazon MQ
- Users of Azure or Google Cloud can adapt this model to employ their respective managed services with Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) or Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). For detailed guidance on integrating with various cloud providers, please follow:
Key Points
- Kubernetes automates many deployment tasks.
- Easily scale up or down as needed.
- Kubernetes ensures high availability.
- Integrates with cloud monitoring, reporting, etc.
Important Considerations
- Requires understanding Kubernetes concepts.
- You need a Kubernetes cluster set up before deploying MDSS.
- MDSS is deployed using a Helm chart available on GitHub.
Preparing Your Kubernetes Cluster for MDSS Deployment
Pre-Deployment Steps
Before you deploy MetaDefender Storage Security (MDSS), your Kubernetes cluster must be fully prepared. This involves:
- Configuring load balancing for optimal traffic distribution.
- Enabling autoscaling to dynamically adjust resources.
- Ensuring persistent storage for data retention (if needed).
- Establishing proper connectivity to external services.
Deployment Process
Once your Kubernetes cluster is configured, you can deploy MDSS using our Helm chart:
Detailed Instructions
For comprehensive guidance on deploying and configuring MDSS within a standard Kubernetes cluster, refer to:

