Hardening
Use TLS whenever it is supported by Microsoft 365.
Email Gateway Security supports SMTP-over-TLS (SMTPS) or StartTLS for both inbound and outbound SMTP connections.
For details see the SMTP servers section in Configuration/Settings and Configuration/Server profiles.
Under certain conditions - especially when integrated to Microsoft 365 as an outbound gateway - Email Gateway Security may be exploited as an open relay.
For details (risks and resolution) see Configuration/Hardening.
Overview
This document describes how Microsoft 365 and MetaDefender Email Gateway Security can be interconnected.
This method does not require redirecting the MX record.
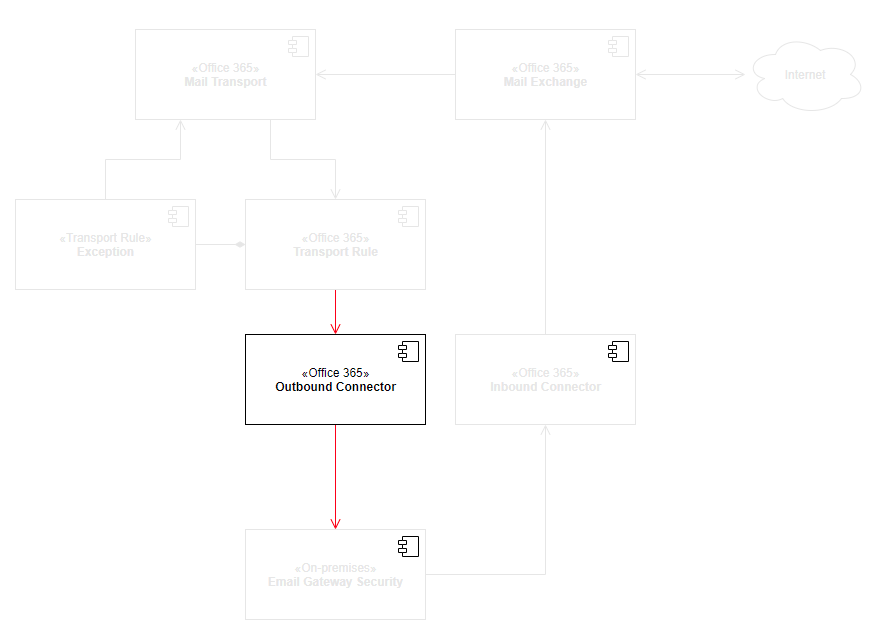
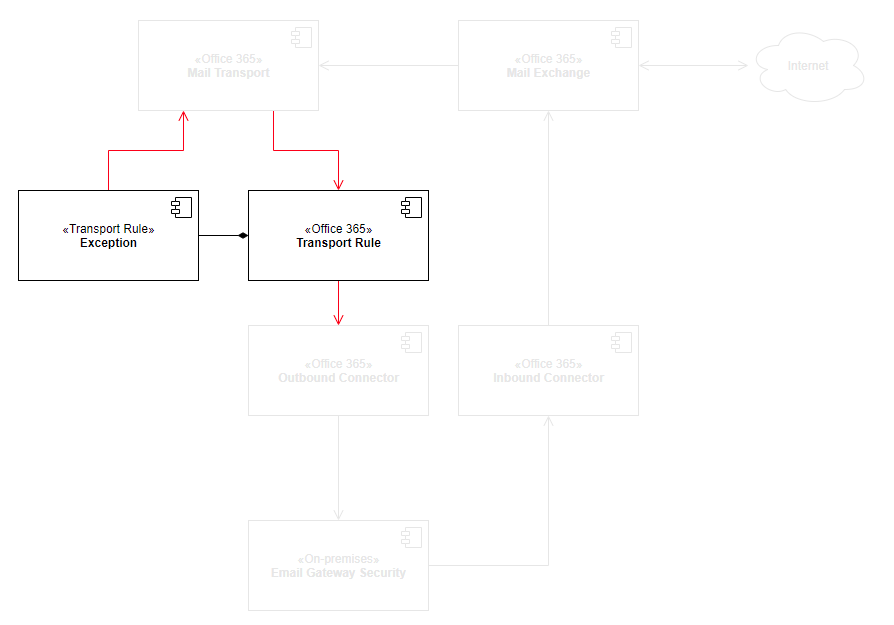
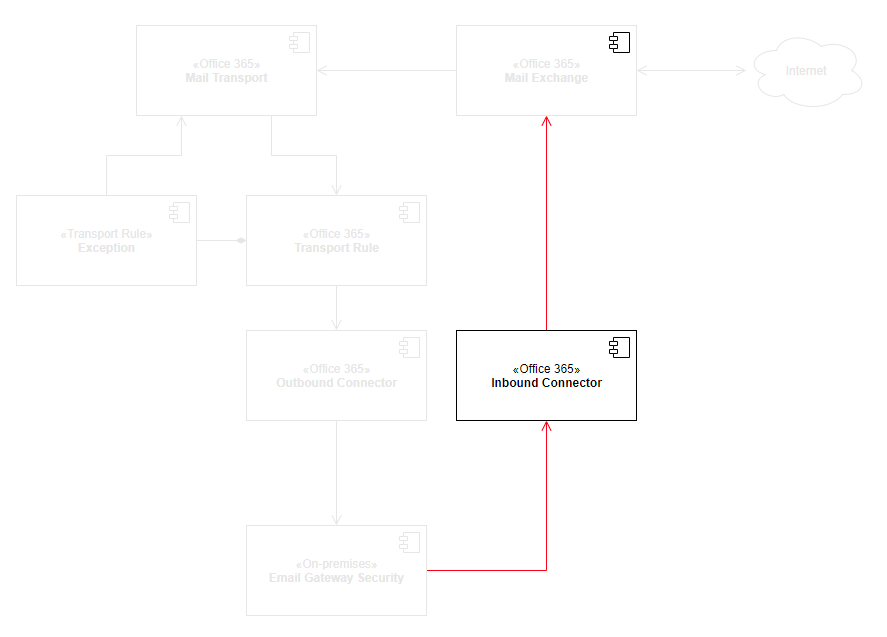
The high level architecture and components affected by this setup is as follows:

Email Gateway Security use connector based integration to Microsoft 365. This way Email Gateway Security can be in-line opposed to currently available API based integrations where Email Gateway Security would be notified about a received email only after the email have been delivered to the user's inbox.
The connector based integration prefers security and can block any threats without exposing the users to them.
Process inbound, outbound and internal email
As the transport rule applies to all email, Email Gateway Security will process inbound, outbound and Exchange internal messages, too.
This behavior can be finetuned adjusting the appropriate parameters of the transport rule.
For details see step 4 in the section Transport rule to forward to Email Gateway Security and the sub-section Customizing what emails to send to Email Gateway Security below.
Known issues
HELO/EHLO name must be properly set
If the FQDN is not properly set in Email Gateway Security for the HELO/EHLO SMTP command on connecting to the Microsoft 365 Mail Exchange, Email Gateway Security may get blocked by Microsoft 365.
The blocked status of the sending SMTP client of Email Gateway Security may be queried from Spamhaus.
Visit the following URL to check: https://www.spamhaus.org/query/ip/<IP address of the sending interface>.
For details see sender_helo_domain under Configuration/Registry configuration.
Azure VMs blocked to connect to port 25
Outbound connections to port 25 are blocked for Microsoft Azure virtual machines (and most probably for other IaaS VMs and ISPs) by default.
For details see https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-network/troubleshoot-outbound-smtp-connectivity.
Outbound SMTP port must be port 25
There is no option to configure the SMTP port for the outbound connector in Microsoft 365. This means that Email Gateway Security's SMTP interface must be configured to listen on port 25 (instead of the default 10025).
For details see SMTP servers.
An other implication is that Email Gateway Security must be accessible from Microsoft 365 on port 25. This may require the appropriate firewall settings to be changed for the organization.
Only StartTLS supported for outbound SMTP
Microsoft 365 does not support SMTP over TLS for the outbound connector. To configure an encrypted connection for the outbound connector, set Email Gateway Security's Settings > Security / SMTP Server Connection Settings / SMTP connection encryption to STARTTLS optional or STARTTLS required.
For details see SMTP servers.
Exchange Online setup propagation delays
Changes in Microsoft 365 Exchange may take time (several minutes) to apply.
Email Gateway Security setup
Overview
We will create a hook in Microsoft 365 email flow to forward emails to Email Gateway Security for processing.
Email Gateway Security will receive the connections from Microsoft 365 on SMTP port 25, and will forward the processed emails to Microsoft 365 email exchange to SMTP port 25.

The following configuration must be performed:
- Inbound SMTP configuration to receive emails on port 25, and
- Security Rule configuration to relay to Microsoft 365 mail exchange.
Inbound SMTP configuration
Configure Email Gateway Security’s SMTP server to listen on port 25 (by default Email Gateway Security listens on port 10025). For details see Configuration/Settings.
Security rule configuration
Email Gateway Security’s Security Rules must be configured to forward processed emails back to Microsoft 365’s mail exchange.
Perform the following steps:
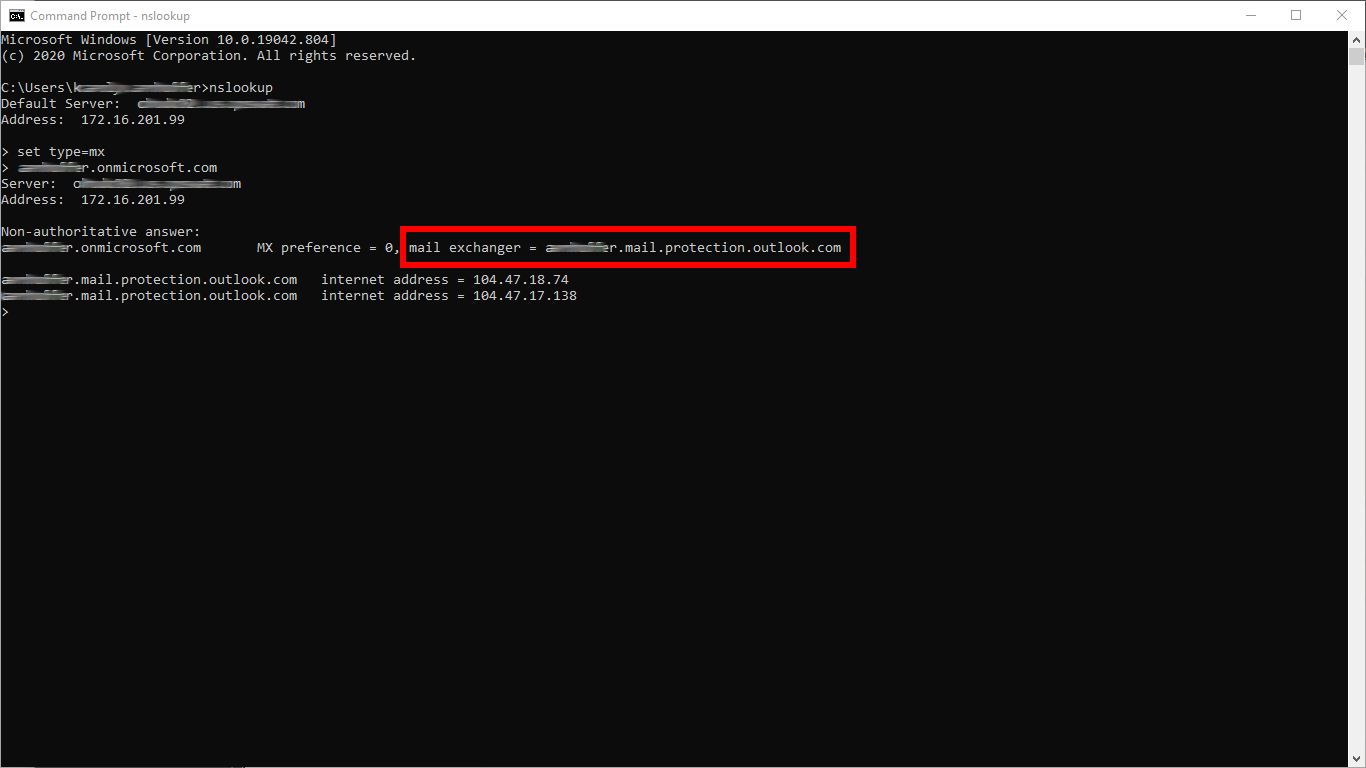
- Discover your Microsoft 365 mail exchange FQDN Issue the following commands:
Example:
- Create an SMTP type server profile that points to the mail exchange discovered in the previous step. For details see Configuration/Server profiles.
For example if your mail exchange is your.domain.com then specify this as the SMTP server URL address:
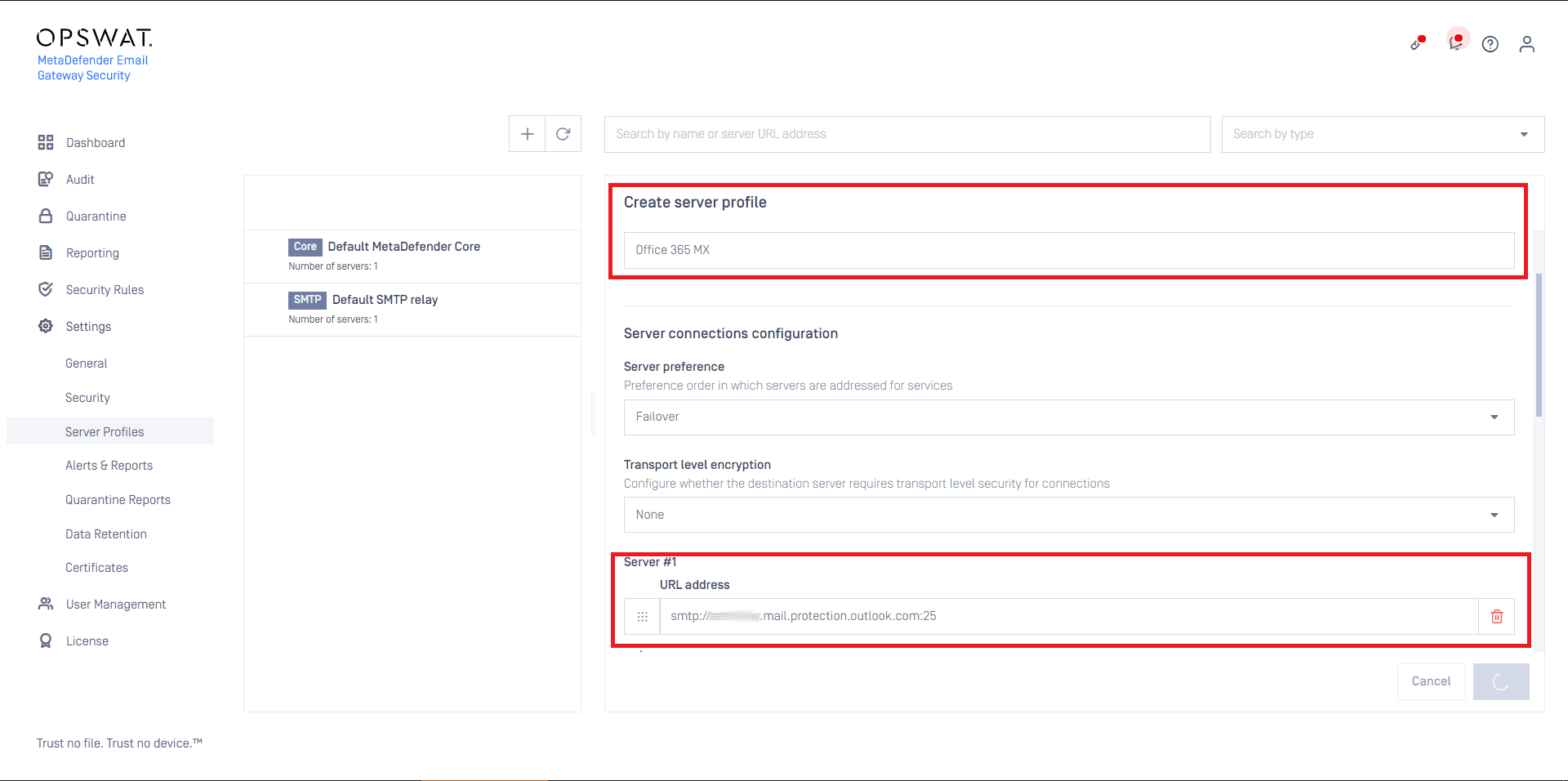
- Set this SMTP server profile as the SMTP relay server profile for security rules that are intended to process email from Microsoft 365. For details see Configuration/Policy.
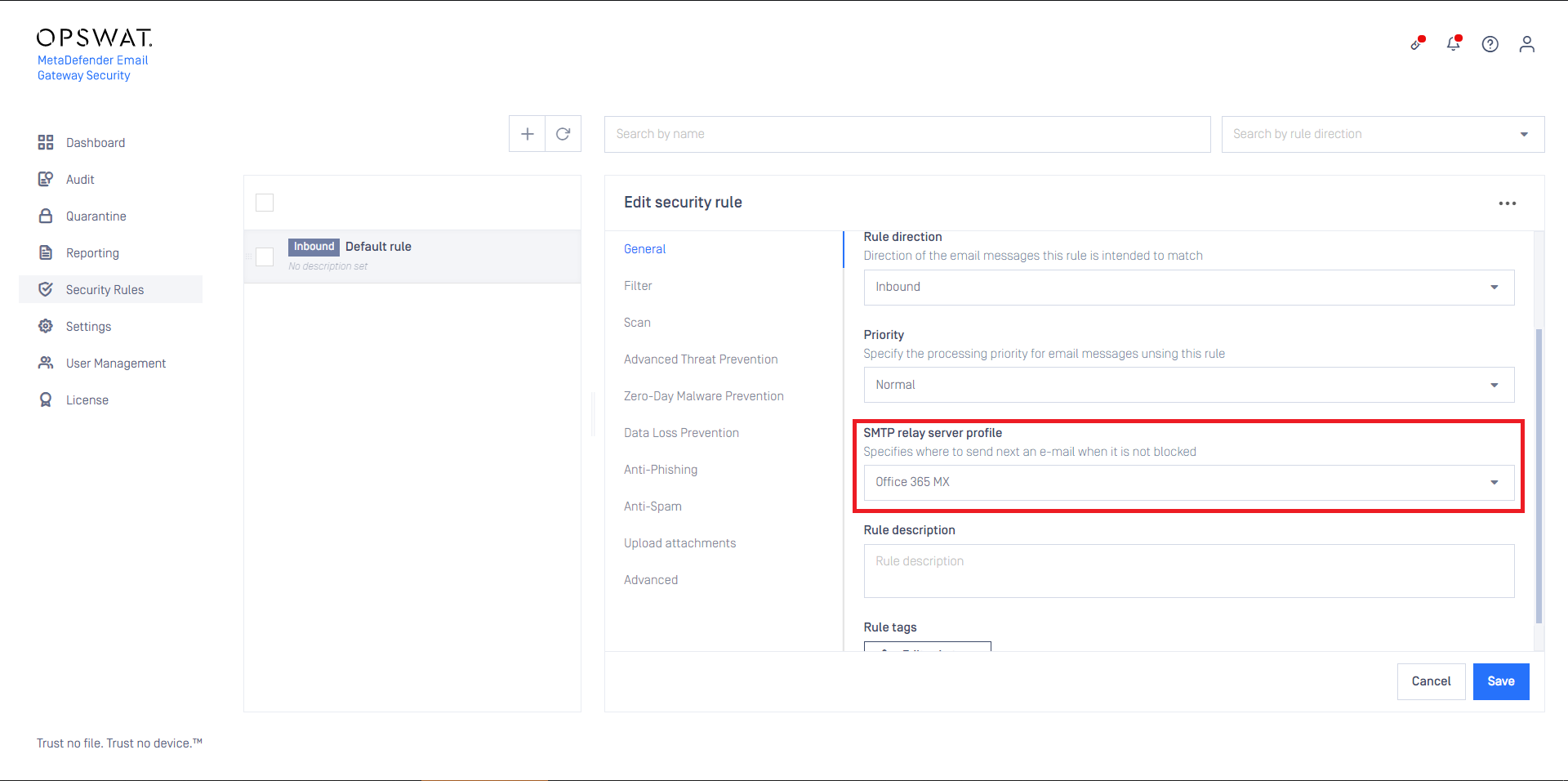
Email Gateway Security is now ready to receive emails from Microsoft 365, and then return them there after processing.
Customizing how to process emails in Email Gateway Security
Depending on what emails are sent to Email Gateway Security by Microsoft 365 for processing (for details see sub-section Customizing what emails to send to Email Gateway Security), different processing rules may be required. These rules can be created normally just like for any other use-case.
For details see Configuration/Policy.
In certain cases not all email is desired to be processed by Email Gateway Security. In these cases the range of emails to be forwarded can be configured setting *Apply this rule if… accordingly.
Example
Let us assume, that at an organization all email needs to be processed by Email Gateway Security (assuming that the Microsoft 365 side transport rule is set properly, for details see section Transport rule to forward to Email Gateway Security):
- For inbound email: regular processing,
- For outbound email: Proactive DLP only.
We can easily achieve this by Email Gateway Security side security rules properly.
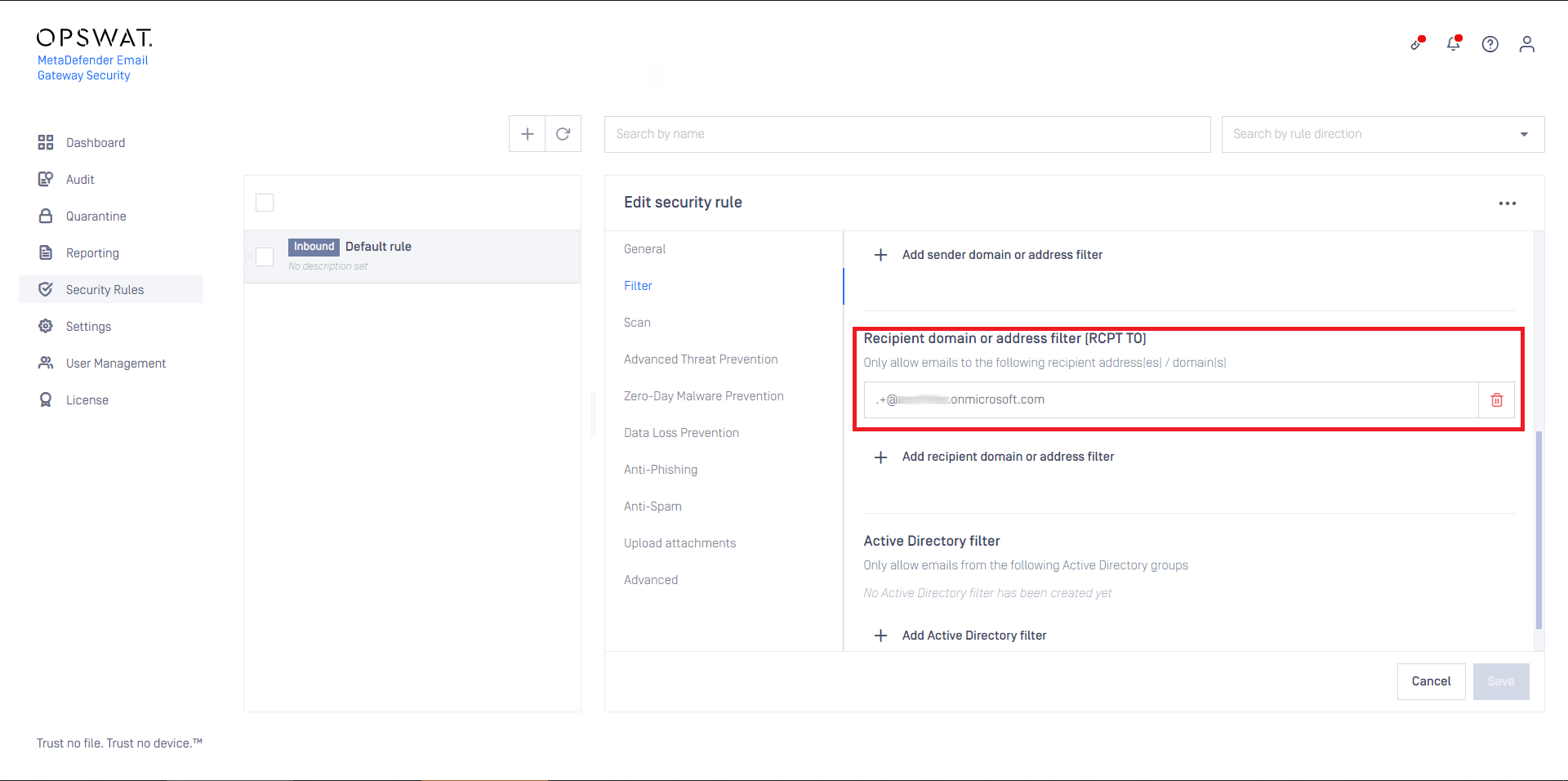
Inbound security rule
For regular inbound processing follow these steps:
- Create a MetaDefender Core type server profile that is connected to the MetaDefender Email Gateway Security rule on MetaDefender Core (or reuse the Default MetaDefender Core profile)
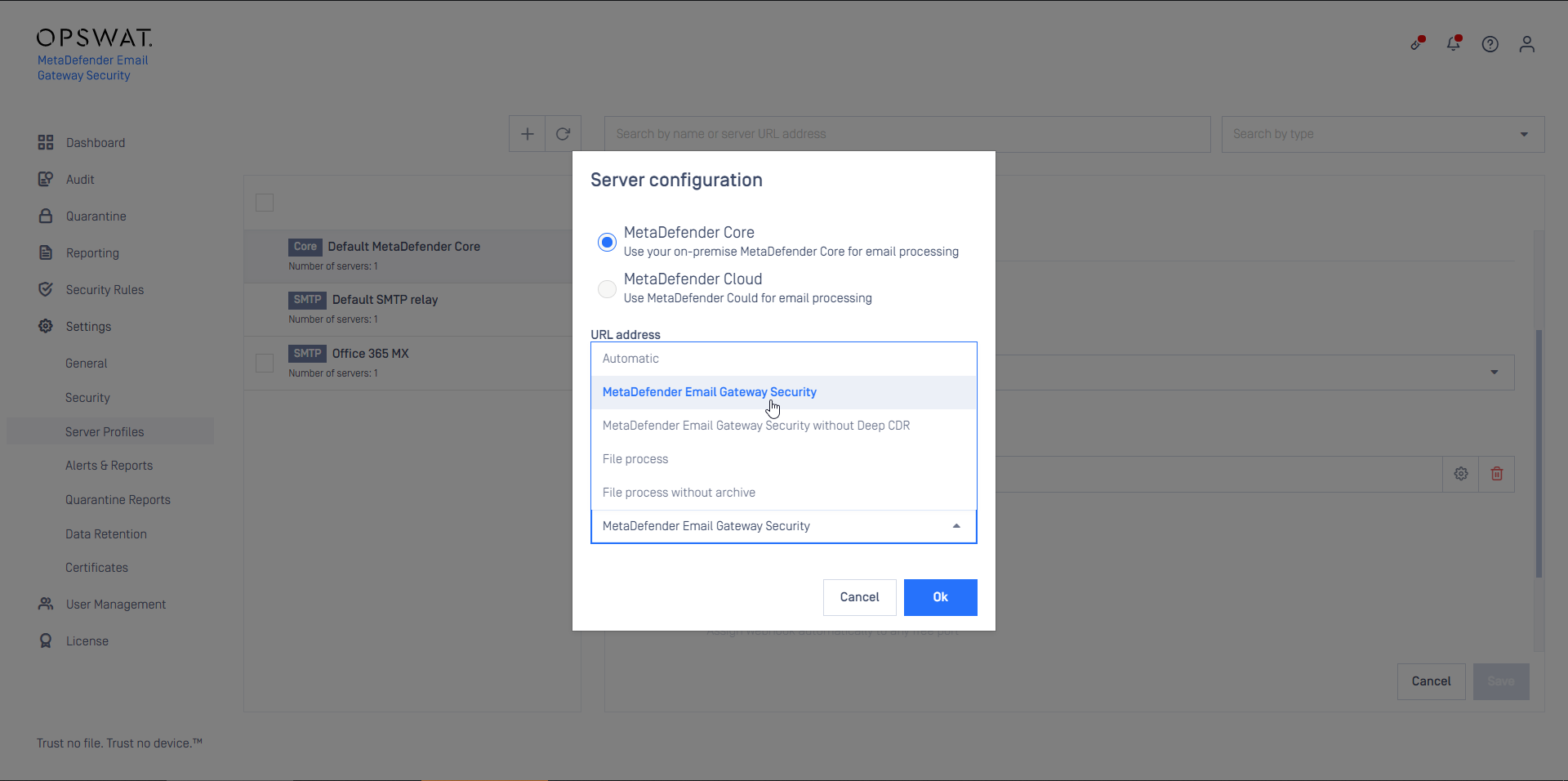
- Create a Security Rule (or reuse the Default rule) that will use the server profile created in the previous step
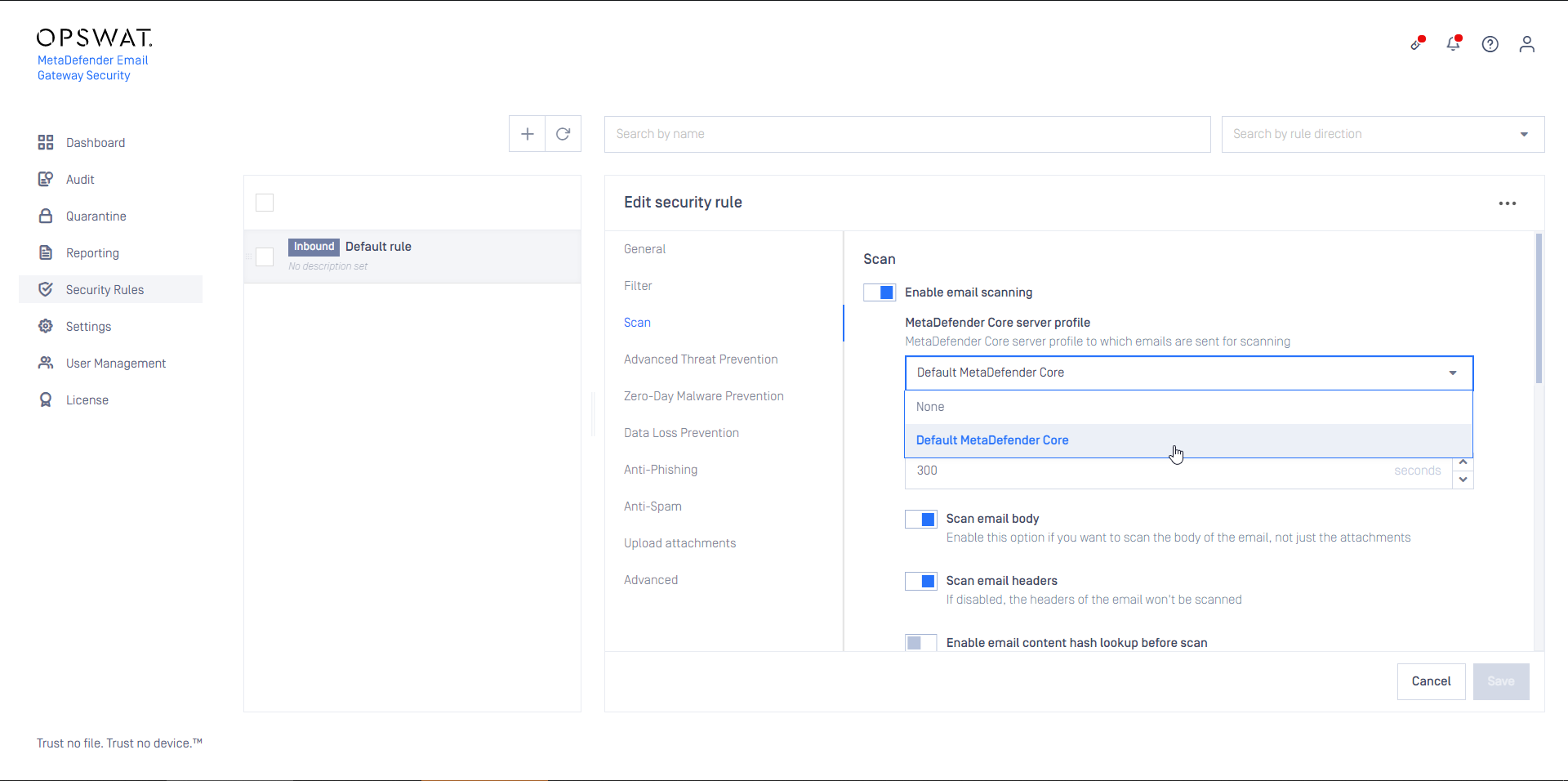
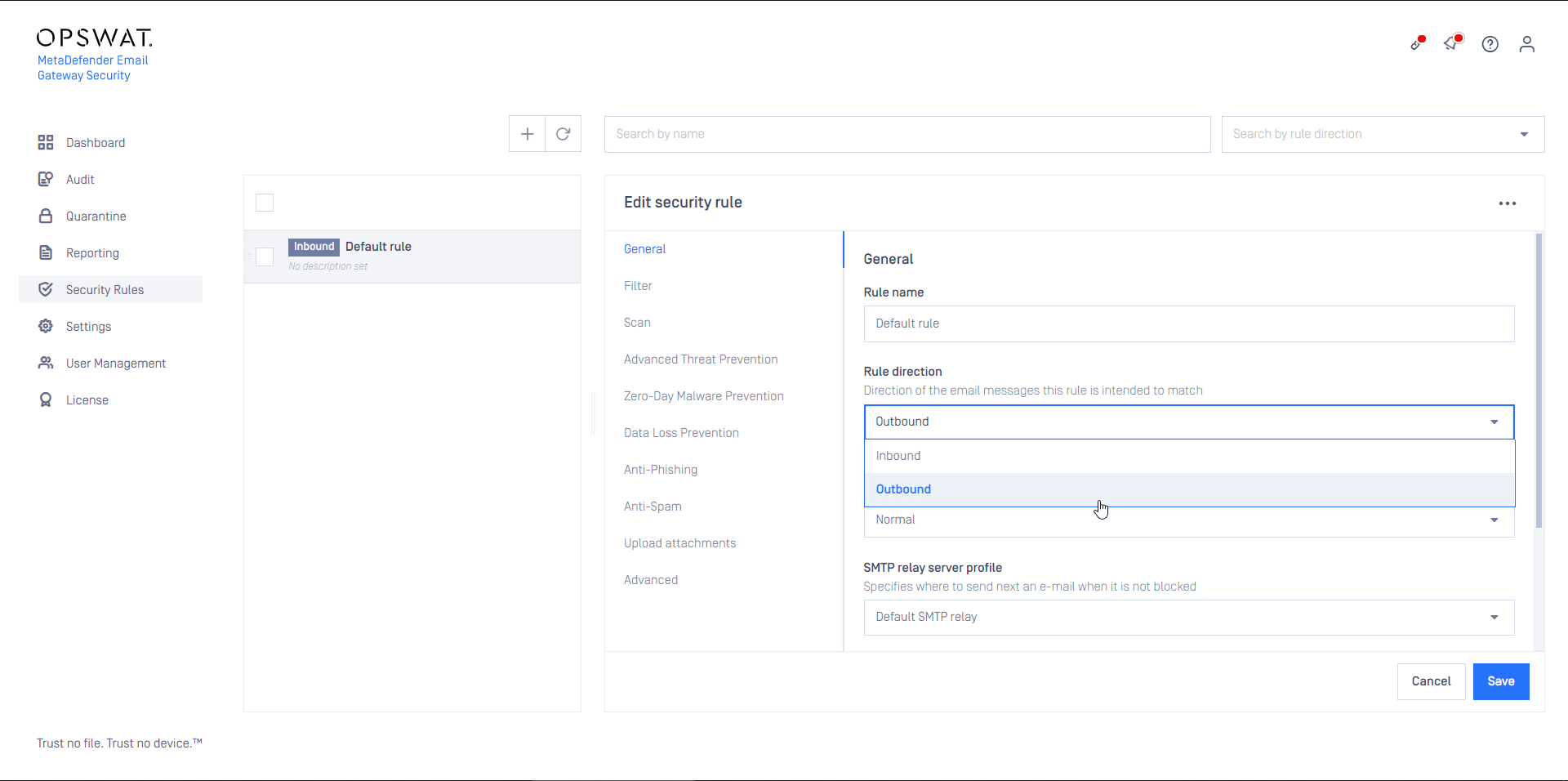
- Configure this rule as Inbound
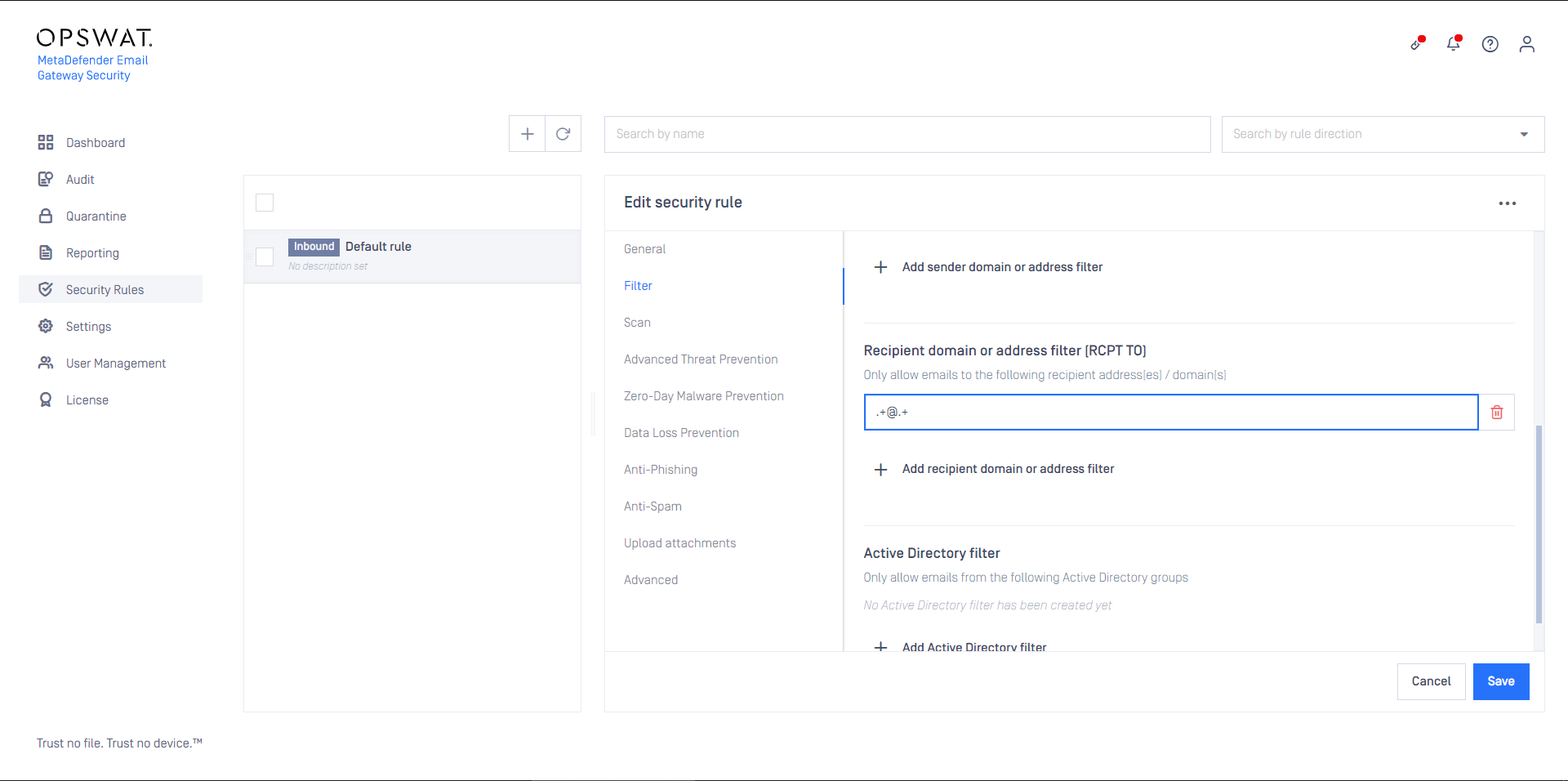
- Set the rule filters to match inbound email in your organization and save the rule
Outbound security rule
For DLP only outbound processing follow these steps:
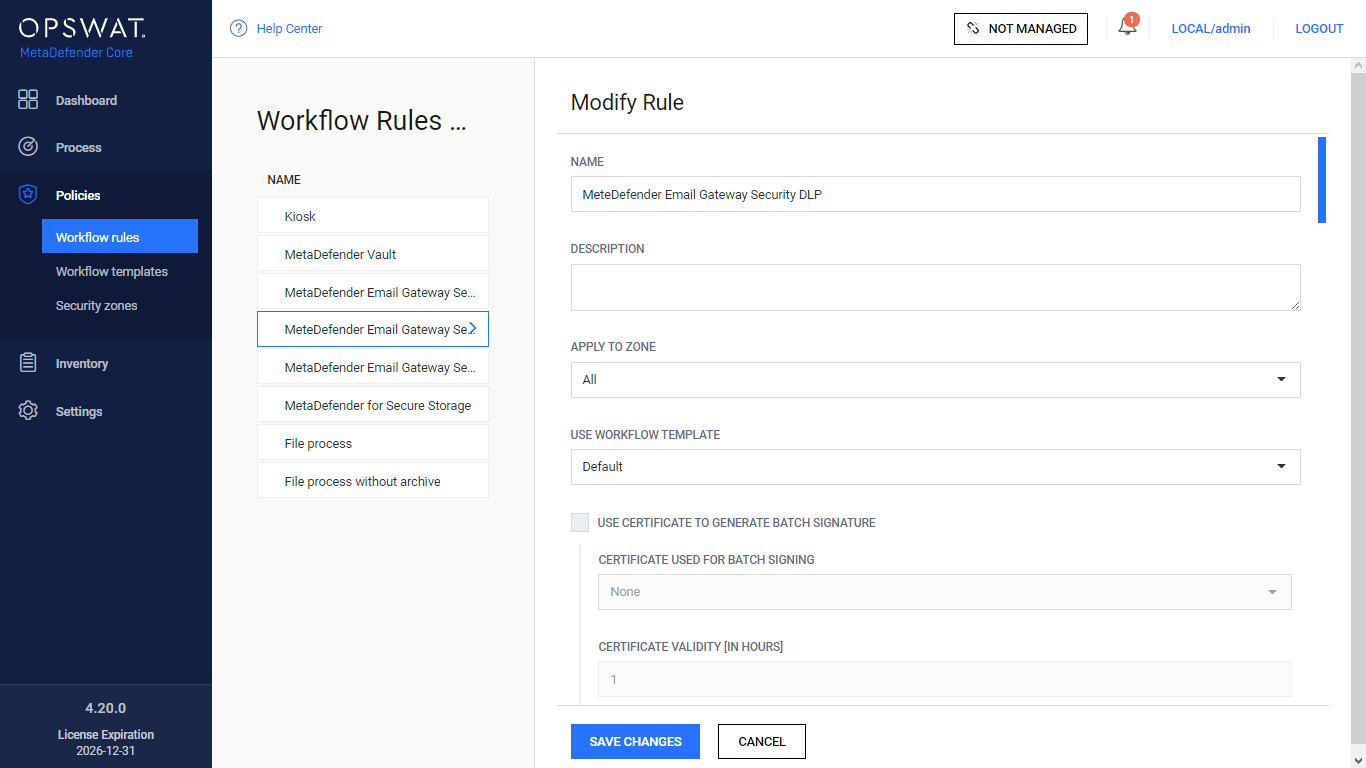
- Create a MetaDefender Core side Workflow:
- NAME: MetaDefender Email Gateway Security DLP
- LIMIT TO SPECIFIED USER AGENTS: mdemailsecurity
- SCAN / ENABLE MALWARE SCAN: disabled
- DEEP CDR: all disabled
- PROACTIVE DLP / ENABLE PROACTIVE DLP: enabled (and configured appropriately)
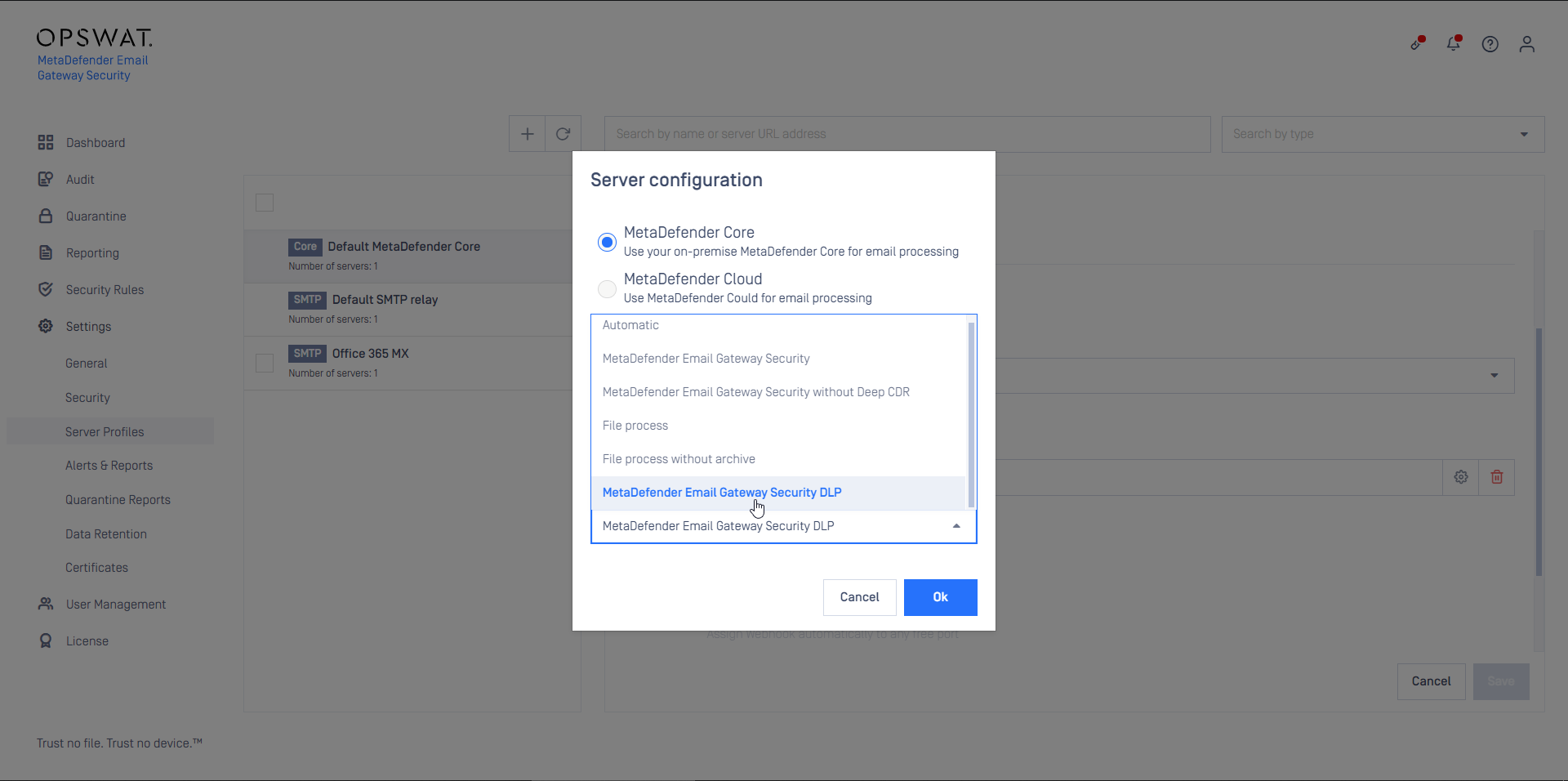
- Create a MetaDefender Core type server profile in Email Gateway Security that is connected to the MetaDefender Email Gateway Security DLP rule created in the previous step on MetaDefender Core
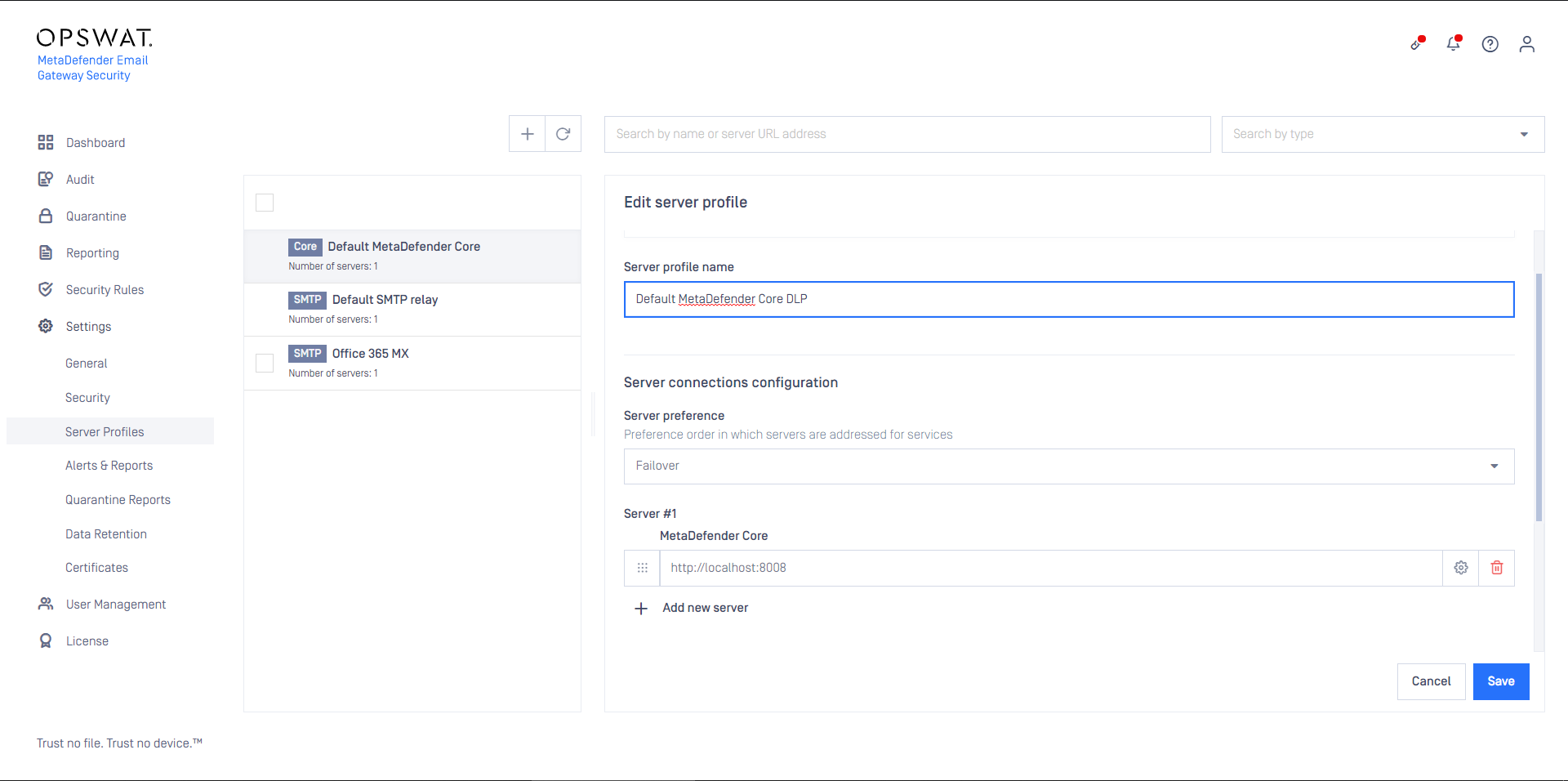
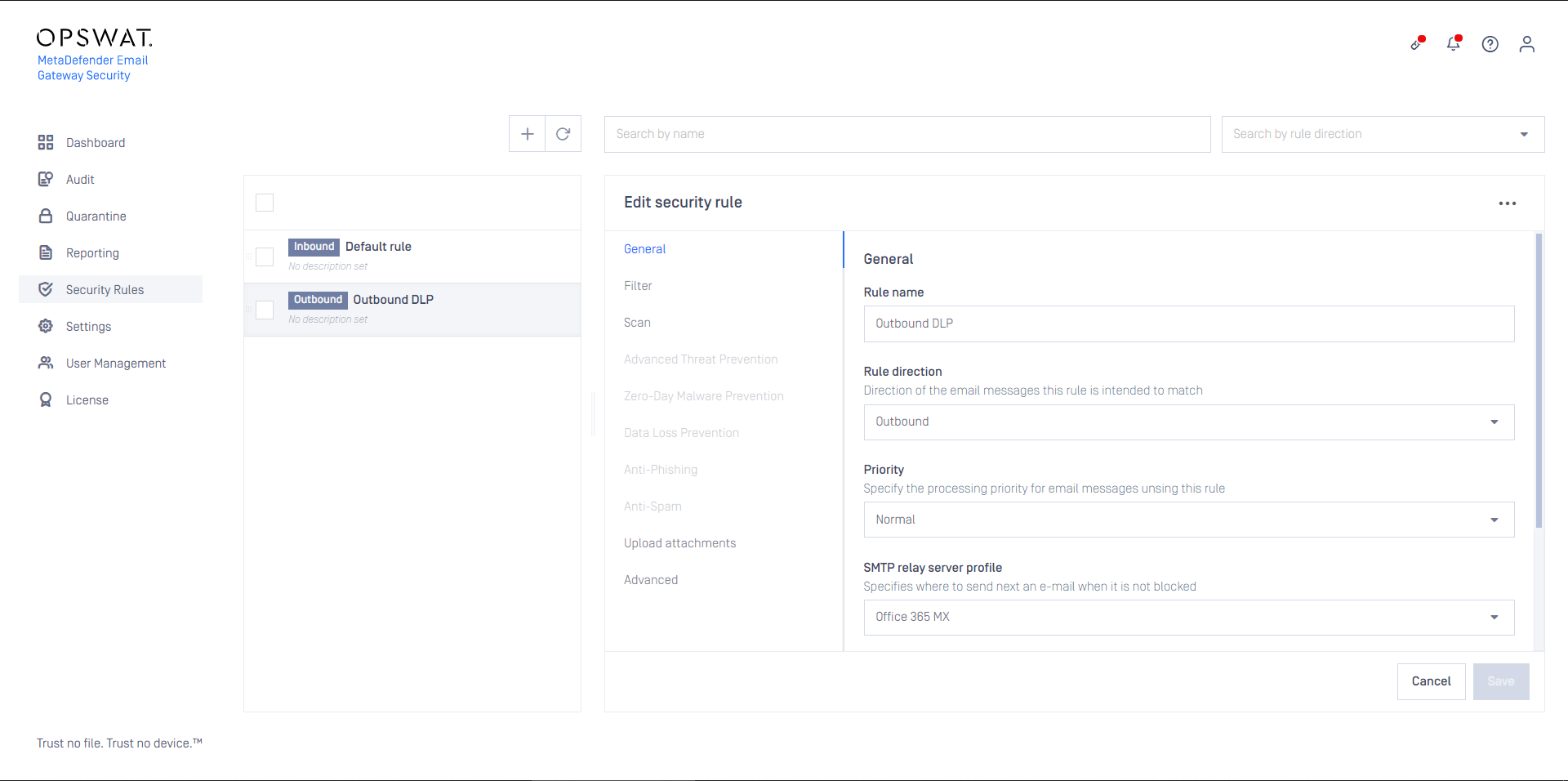
- Create a Security Rule that will use the server profile created in the previous step
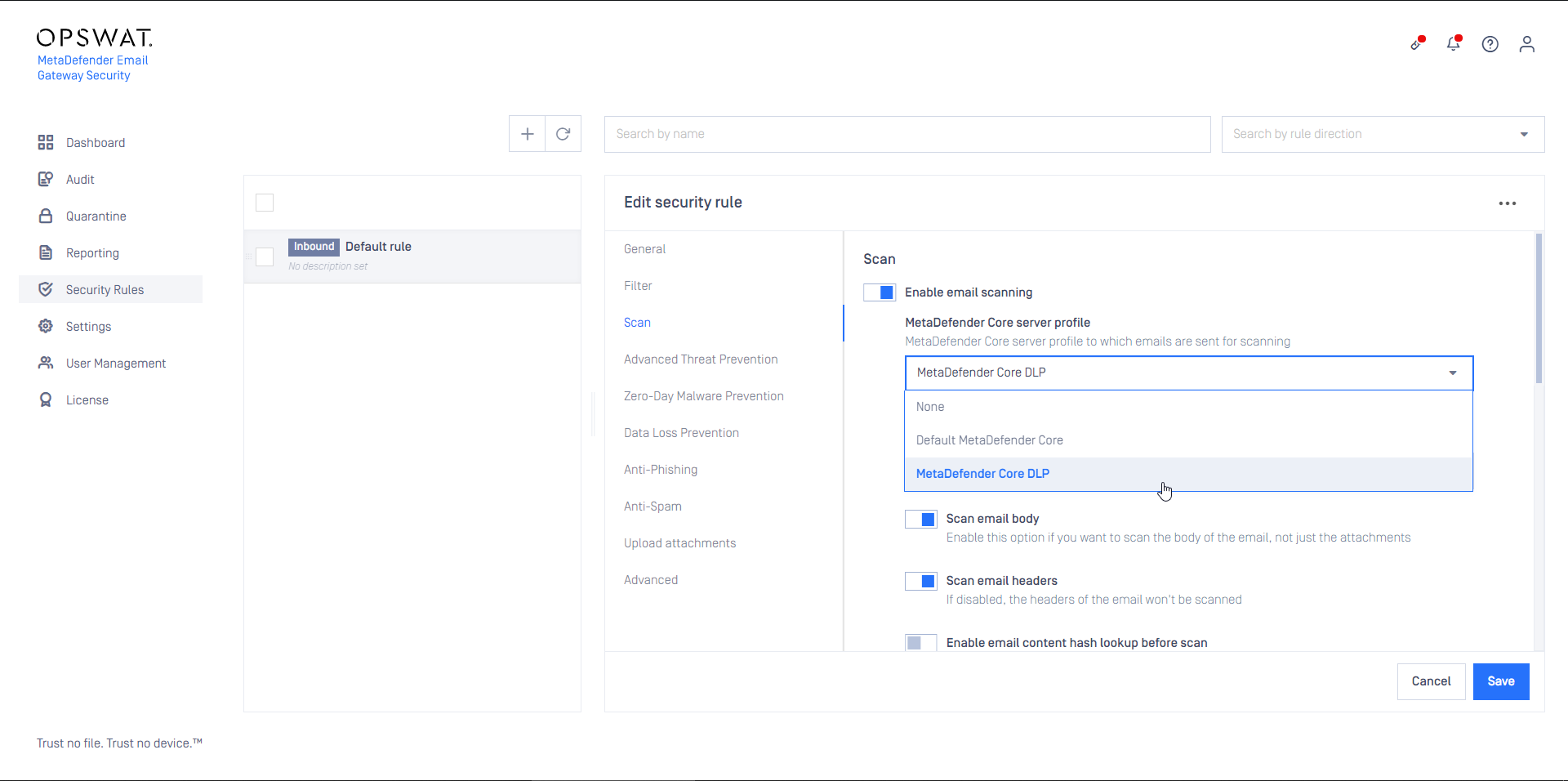
- Configure this rule as Outbound
- Set the rule filters to match outbound email in your organization and save the rule
With proper order of the rules we only need to define filters for the inbound email only.
All email that does not match the filters of the inbound rule will fall back to the outbound rule.
Microsoft 365 setup
Overview
We will create a hook in Microsoft 365 email flow to forward emails to Email Gateway Security for processing.
We will create a transport rule to forward emails to Email Gateway Security through an outbound connector.
Then we will create an inbound rule to configure Microsoft 365 to receive emails back from Email gateway Security.
The configuration is done in Exchange admin center available at https://admin.exchange.microsoft.com/.
Connector to Email Gateway Security
The connector to Email Gateway Security is required so that Microsoft 365 can forward emails to Email Gateway Security for processing.
Perform the following steps:
- In Exchange admin center go to Mail flow > Connectors
- Click Add a connector
- This connector will route email from Microsoft 365 to Email Gateway Security, so in the New connector dialog select:
- Connection from: Microsoft 365
- Connection to: Your organization’s email server
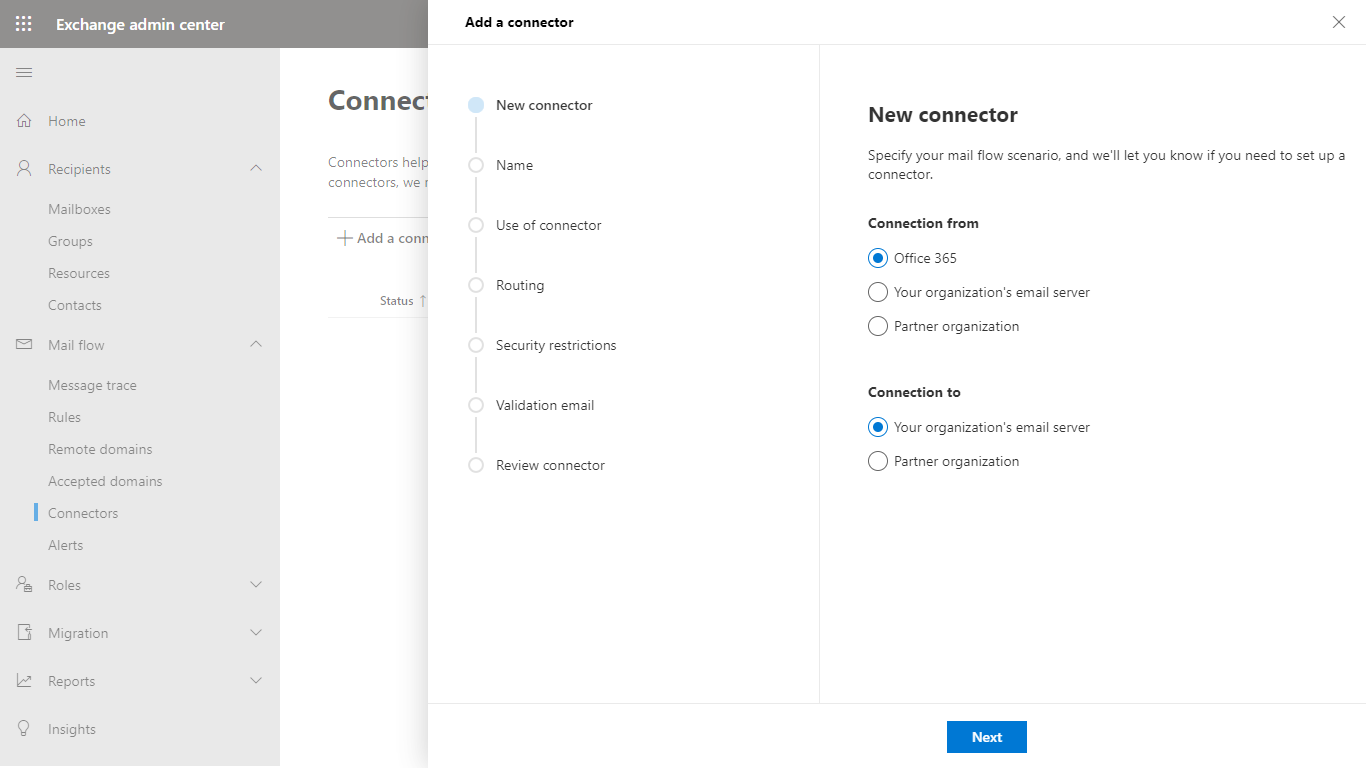
- In the Connector name dialog give a descriptive name to the connector and enable Turn it on
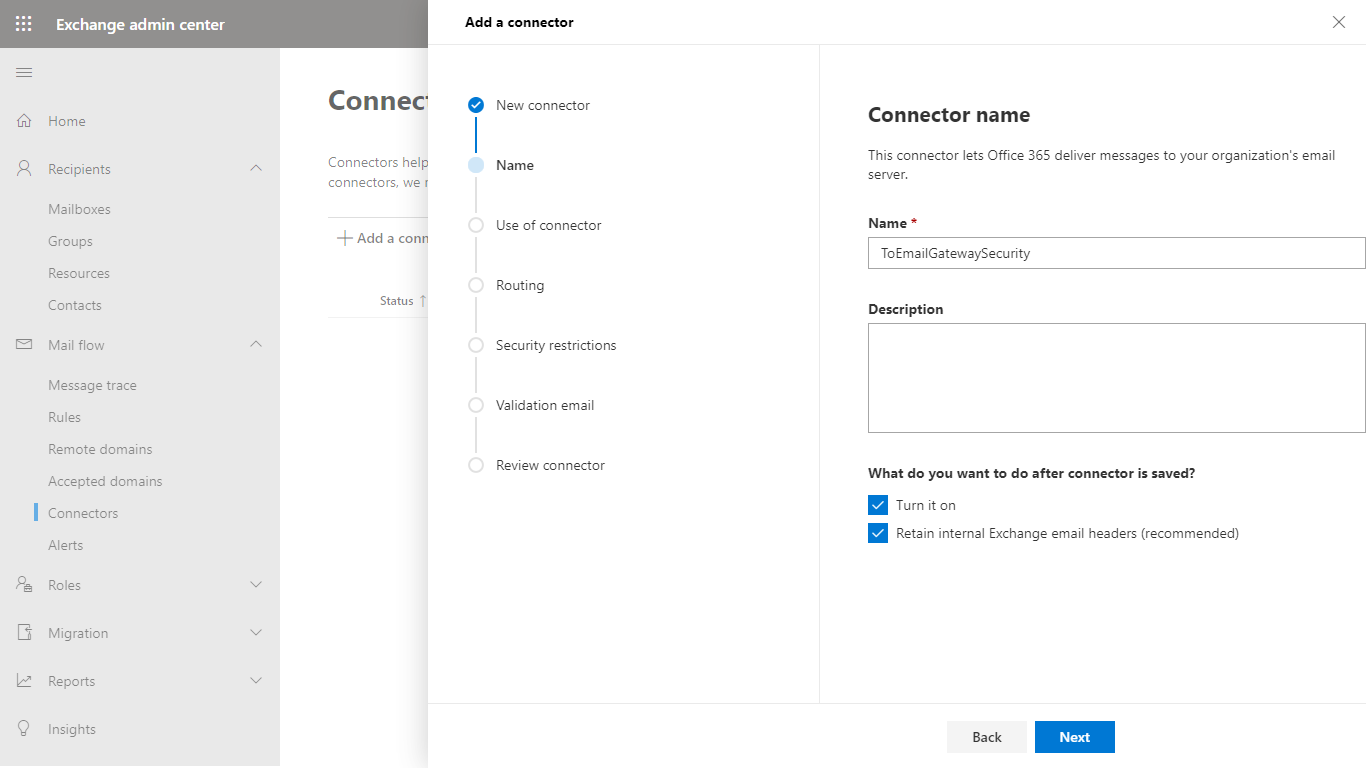
- Later we will create a transport rule to redirect messages in certain cases only to Email Gateway Security, so in the Use of connector dialog select Only when I have a transport rule set up that redirects messages to this connector.
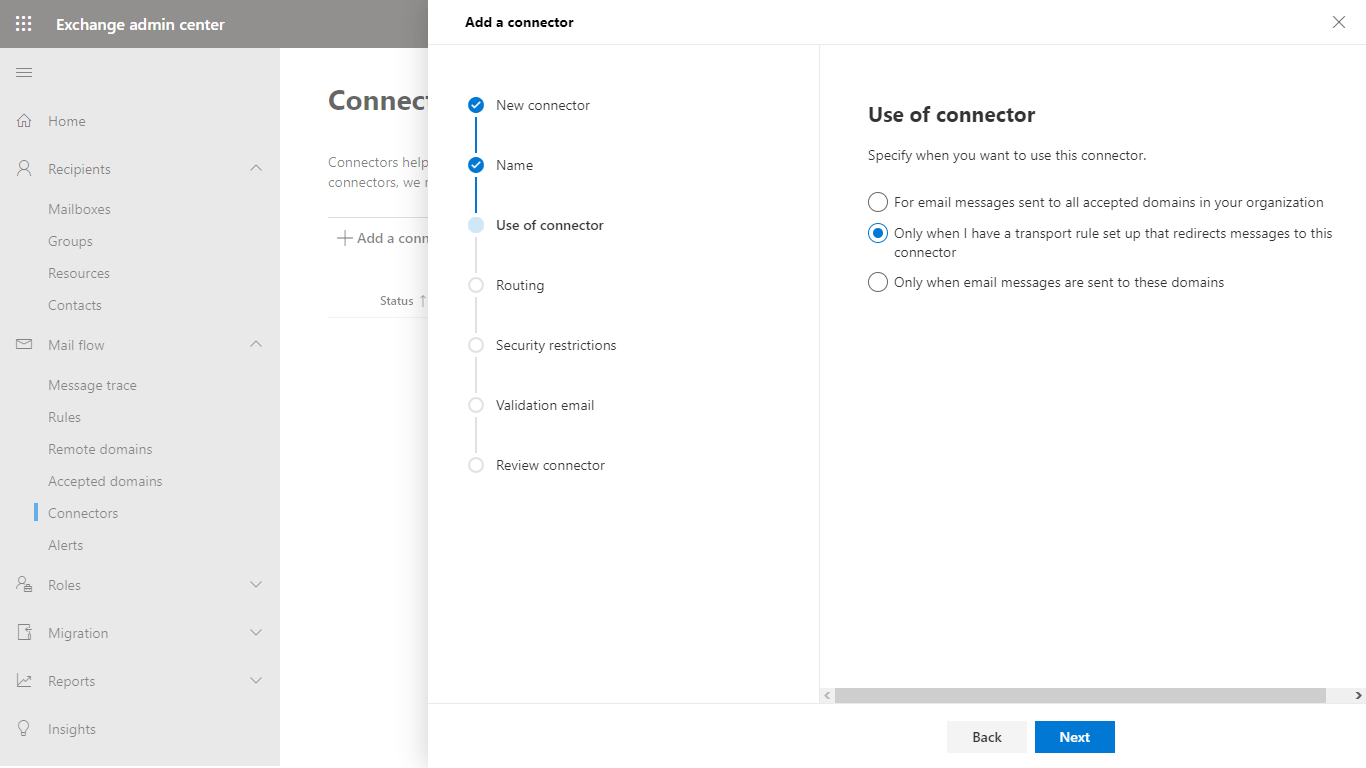
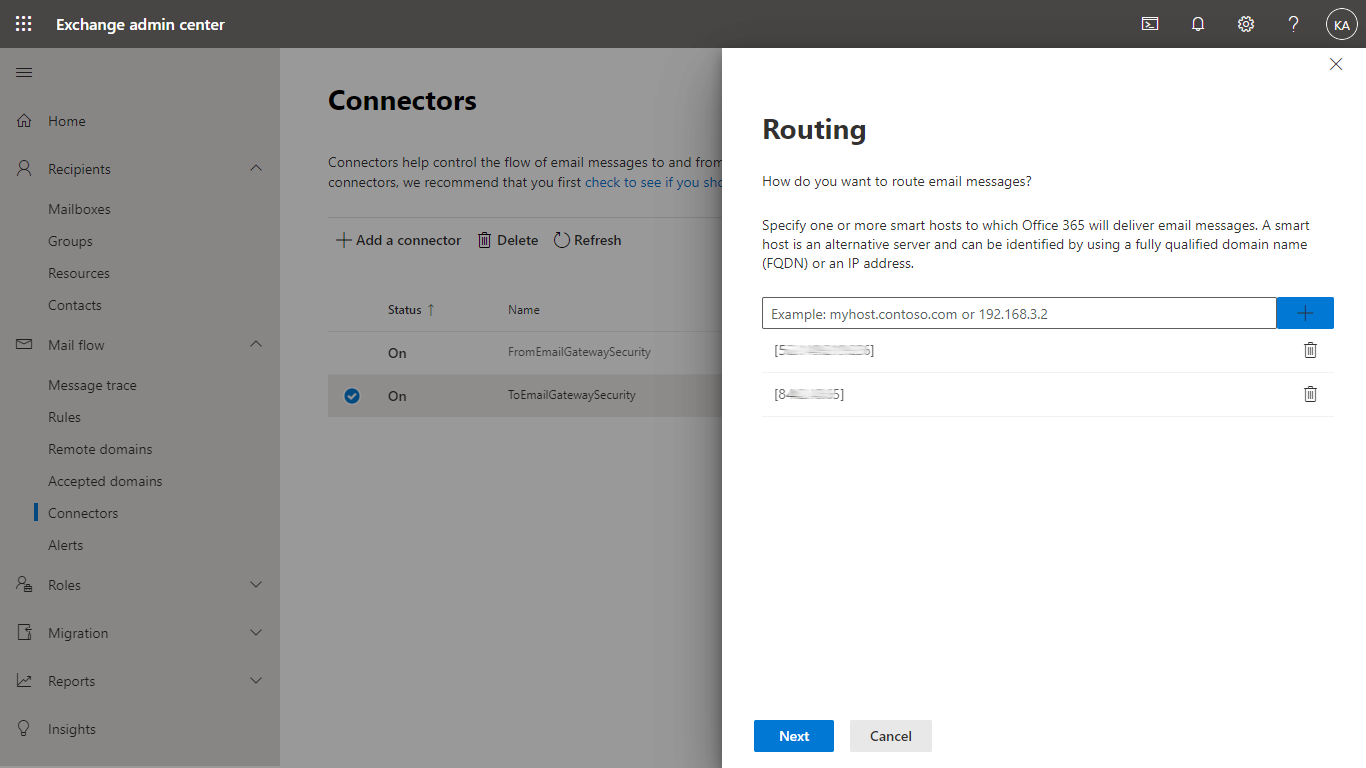
- In the Routing dialog specify the address of the Email Gateway Security instance
- In the Security restrictions dialog apply TLS settings according to your standards
- In the Validation email dialog validate the connector
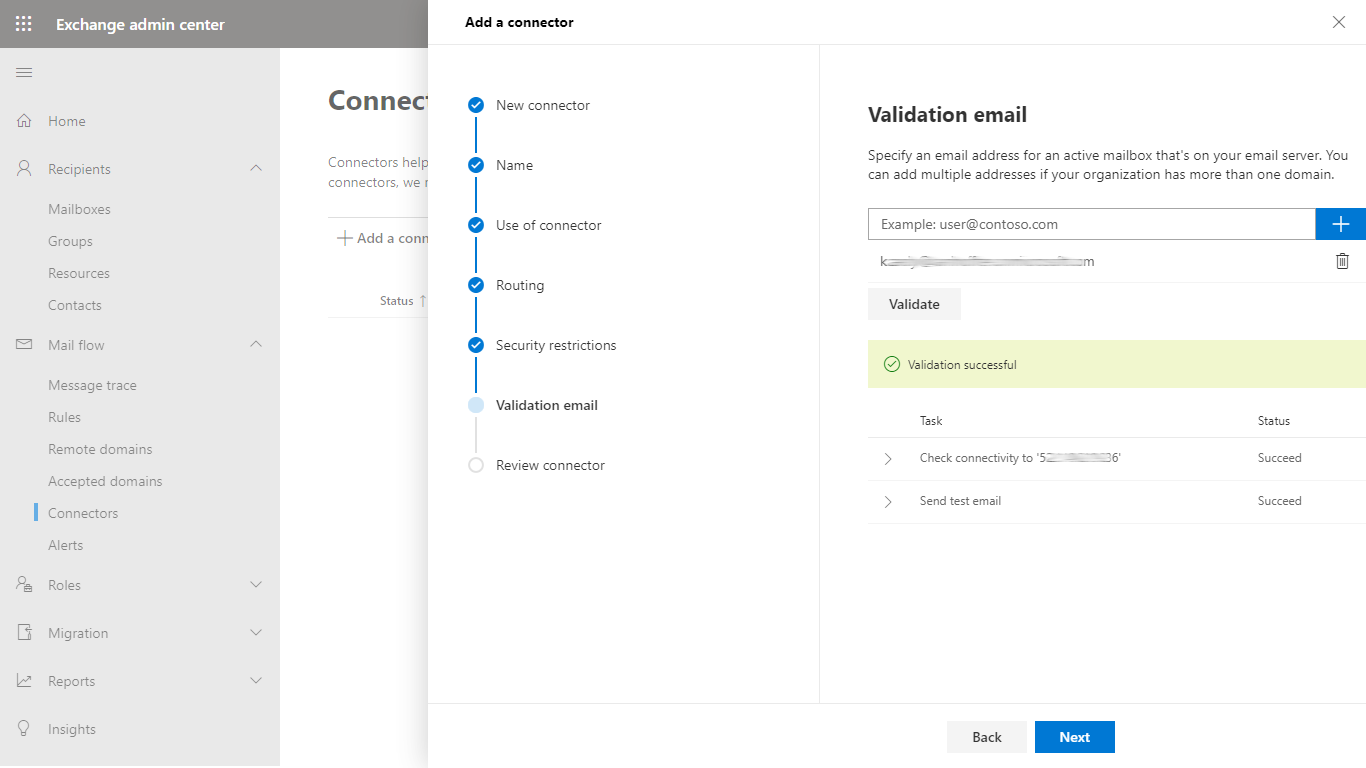
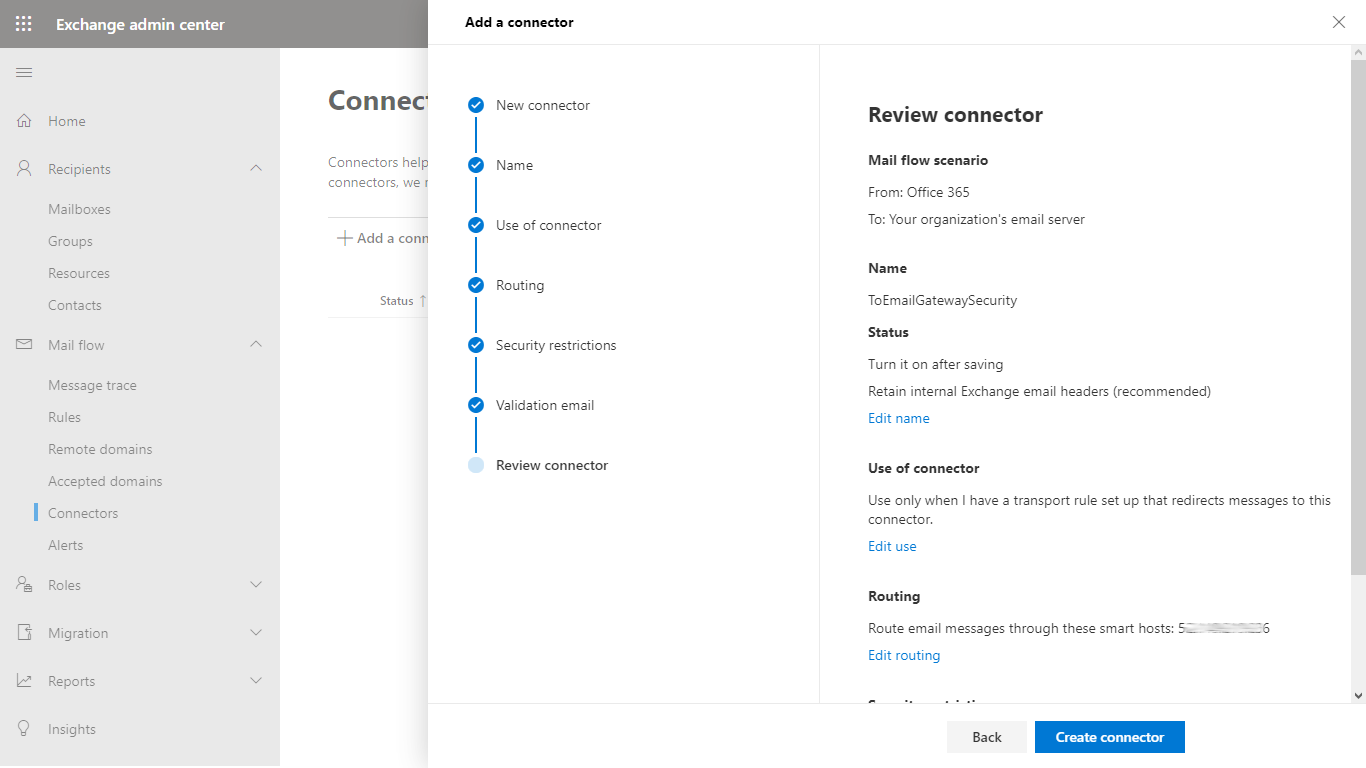
- In the Review connector dialog click Create connector to save the configuration
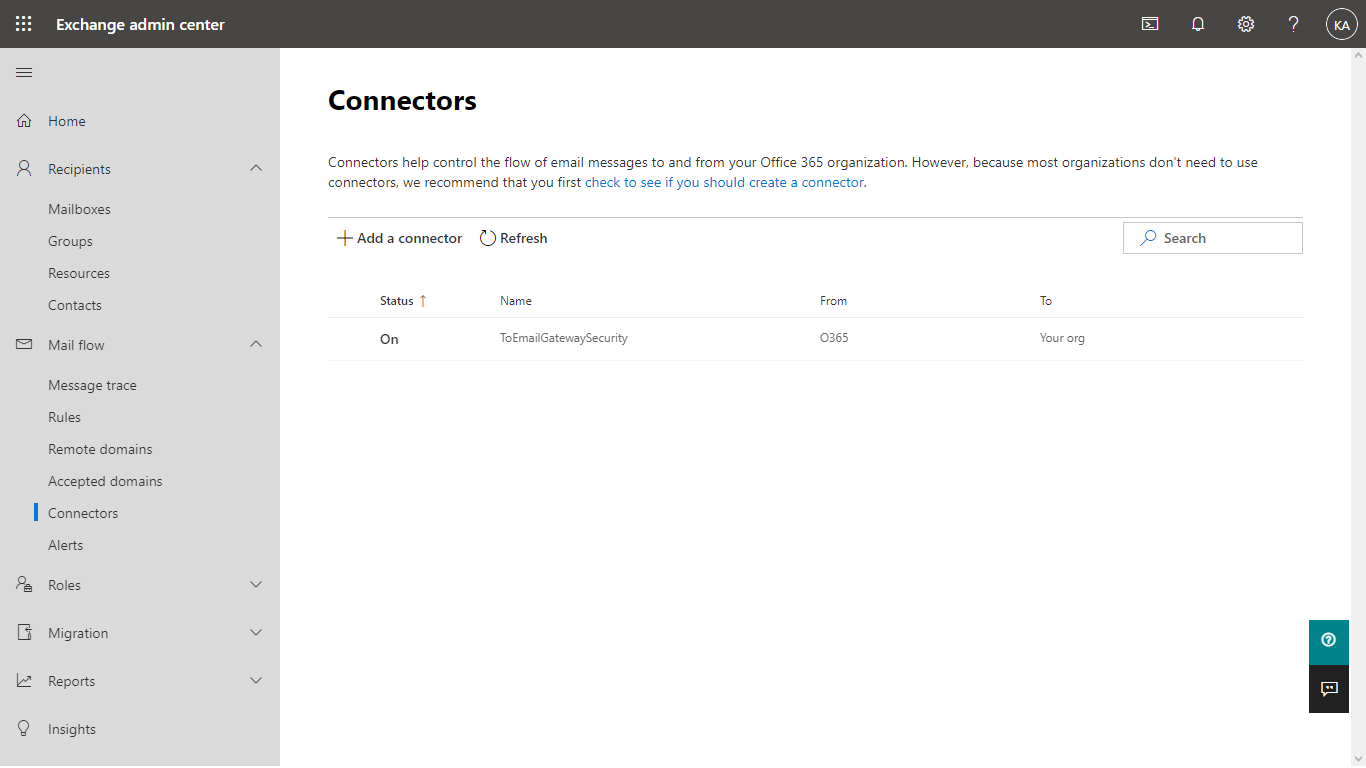
- The new connector must appear in the list of connectors. The outbound connector is now ready to route emails.
High availability and load balancing of multiple Email Gateway Security instances
When multiple Email Gateway Security instances are available to process emails in Microsoft 365, then all these Email Gateway Security instances can be specified in the Routing dialog, as a list.
In this case, Microsoft 365 - based on its own algorithm - will send the email to only one of these instances.
Microsoft 365 will be able select an Email Gateway Security instance that is functional.
Transport rule to forward to Email Gateway Security
The transport rule to forward to Email Gateway Security is required so that Microsoft 365 can forward emails to Email Gateway Security for processing.
Perform the following steps:
- In Exchange admin center go to Mail flow > Rules
- Click + and select Create a new rule to add a new transport rule
- In the new rule dialog click More options…
- Configure the rule in the following way:
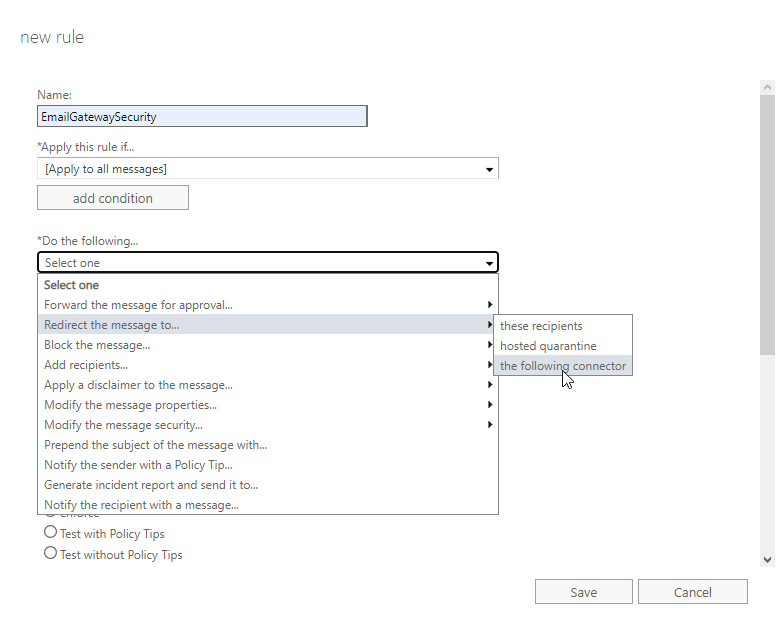
- Name: give a reasonable name
- *Apply this rule if…: [Apply to all messages]
- *Do the following…: Use the following connector…: the connector to Email Gateway Security
- Choose a mode for this rule: Enforce
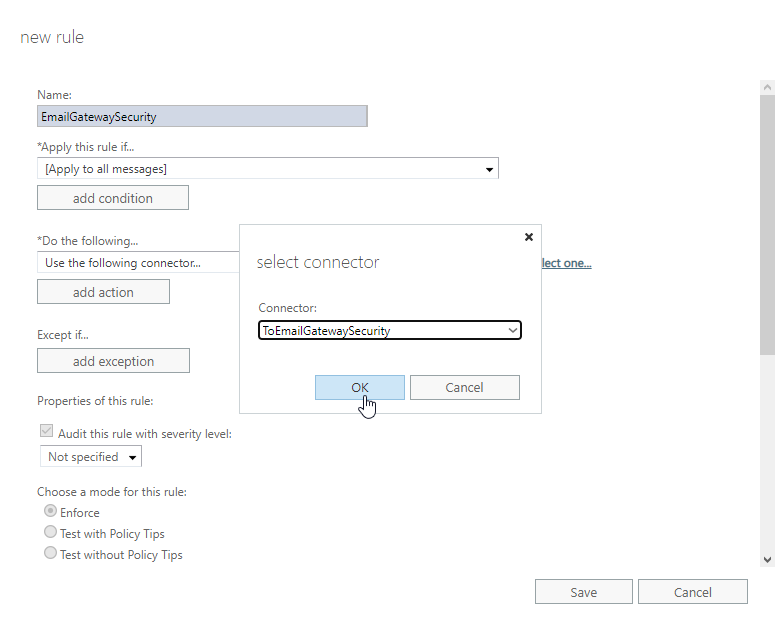
5. Stay in the new rule dialog and continue with the transport rule exception.
As the transport rule applies to all email, Email Gateway Security will process inbound, outbound and Exchange internal messages, too.
Transport rule exception
The transport rule exception is part of the transport rule. Using this exception we will avoid recursive loops of emails being sent back and forth between Microsoft 365 and Email Gateway Security. Emails that are coming from and that have already been processed by Email Gateway Security won’t be sent to Email Gateway Security again.
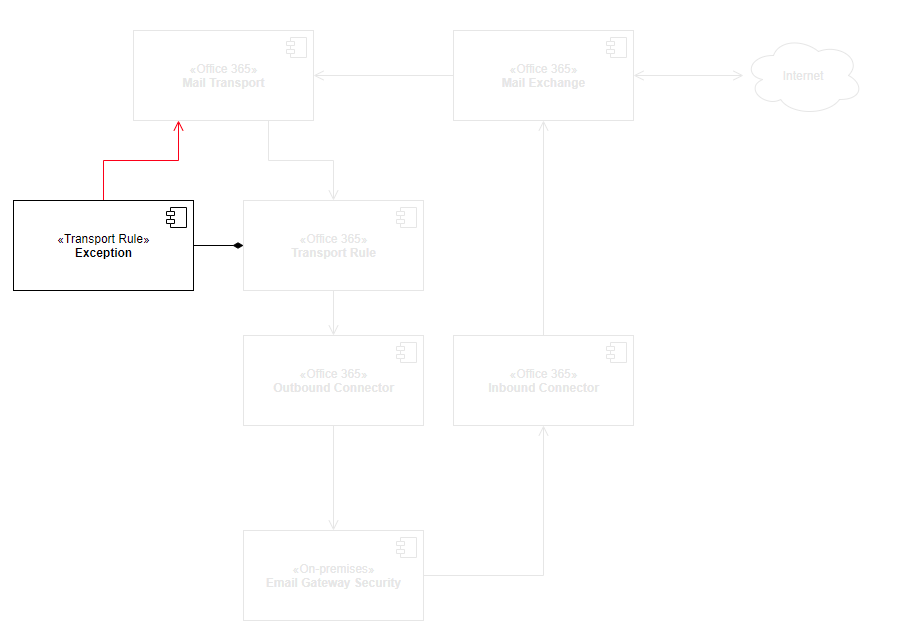
Perform the following steps:
- In the new rule dialog click add exception
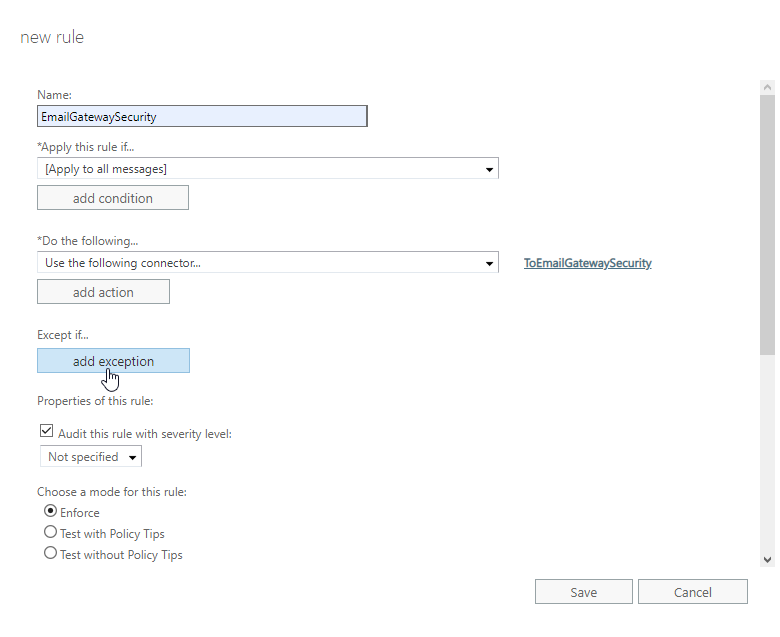
- Select The sender… > IP address is in any of these ranges or exactly matches
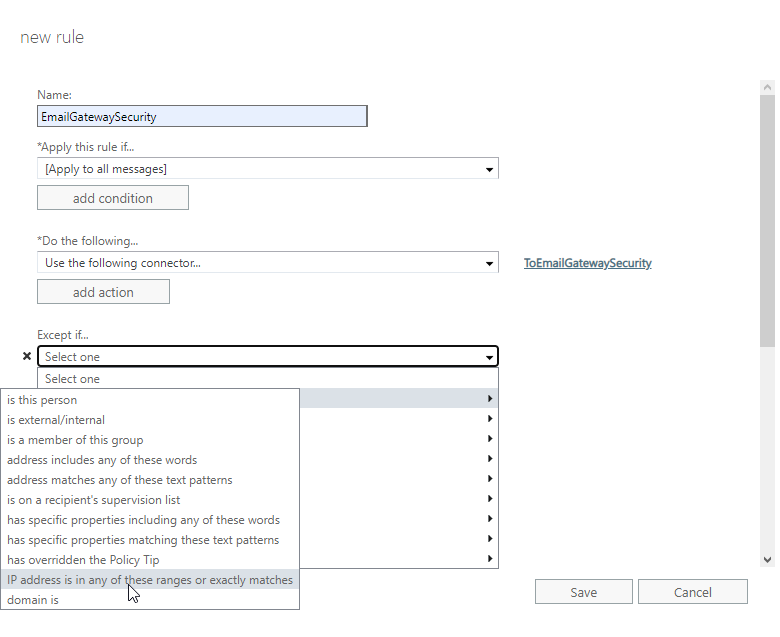
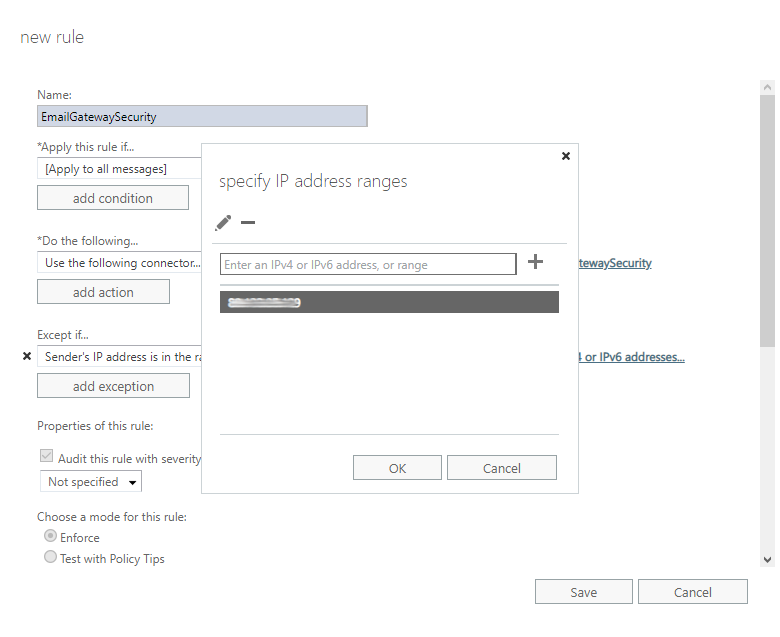
- Specify the IP address of Email Gateway Security. This way emails coming from Email Gateway Security won’t be sent there back again and again.
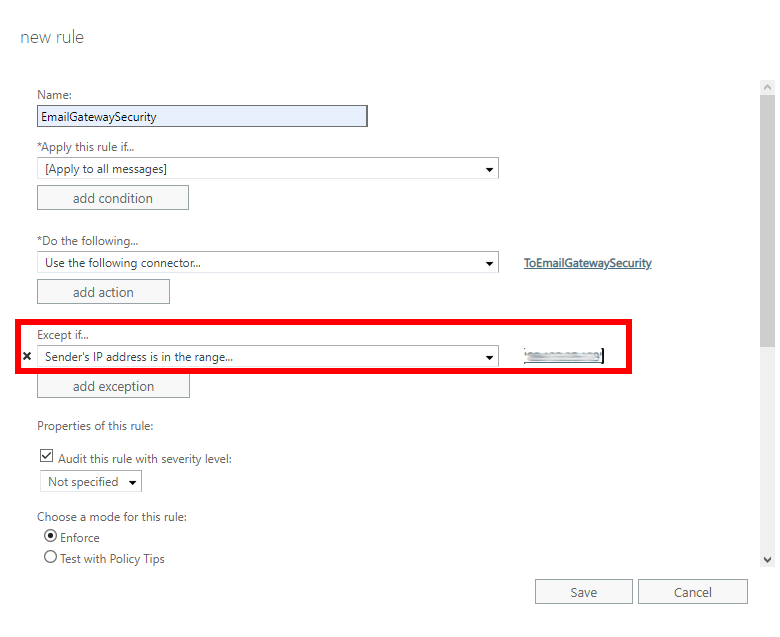
- Save the rule. It will show up in the list of rules.
Customizing what emails to send to Email Gateway Security
As the transport rule was configured to apply to all email, using this rule all email will be sent to Email Gateway Security for processing.
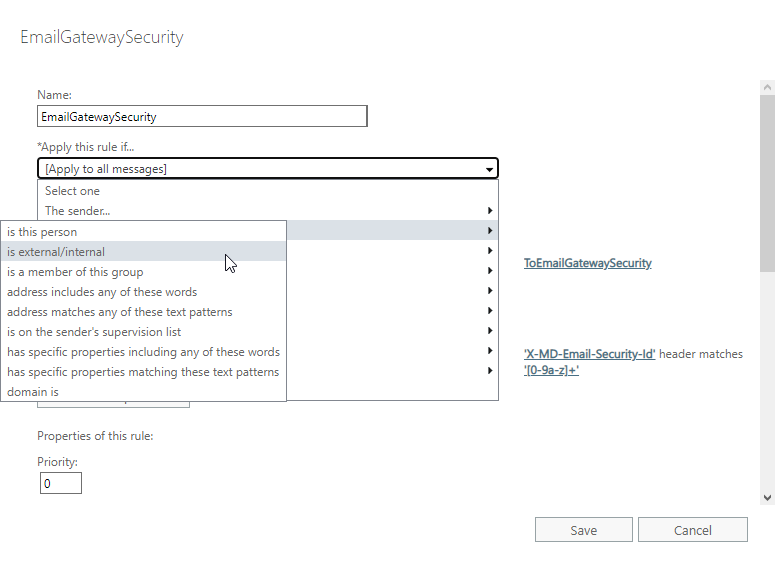
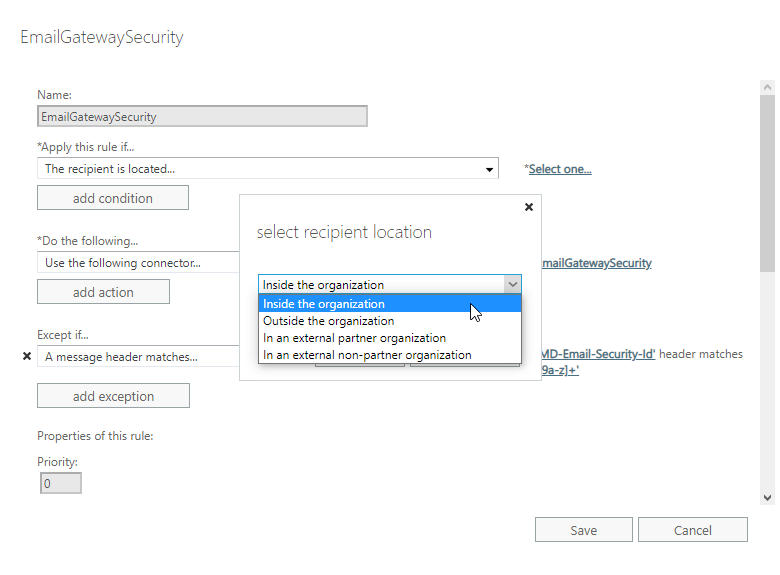
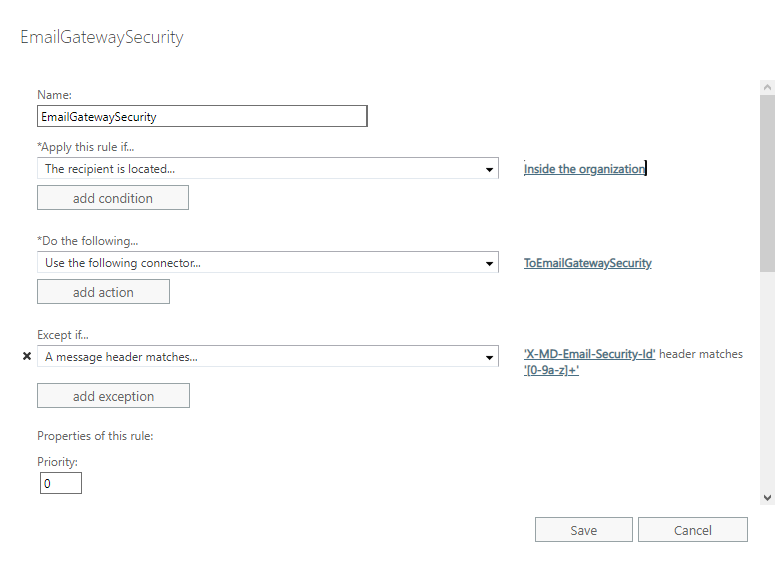
In certain cases not all email is desired to be processed by Email Gateway Security. In these cases the range of emails to be forwarded can be configured setting *Apply this rule if… accordingly.
Example
Let us assume, that at an organization only inbound email needs to be processed by Email Gateway Security.
We can easily achieve this by setting *Apply this rule if… to The recipient is located… Inside the organization.
Connector from Email Gateway Security
The connector from Email Gateway Security is required so that Microsoft 365 can receive emails from Email Gateway Security in a normal way.
Without this inbound connector Microsoft 365 may reject emails or put them to the Junk email folder.
Perform the following steps:
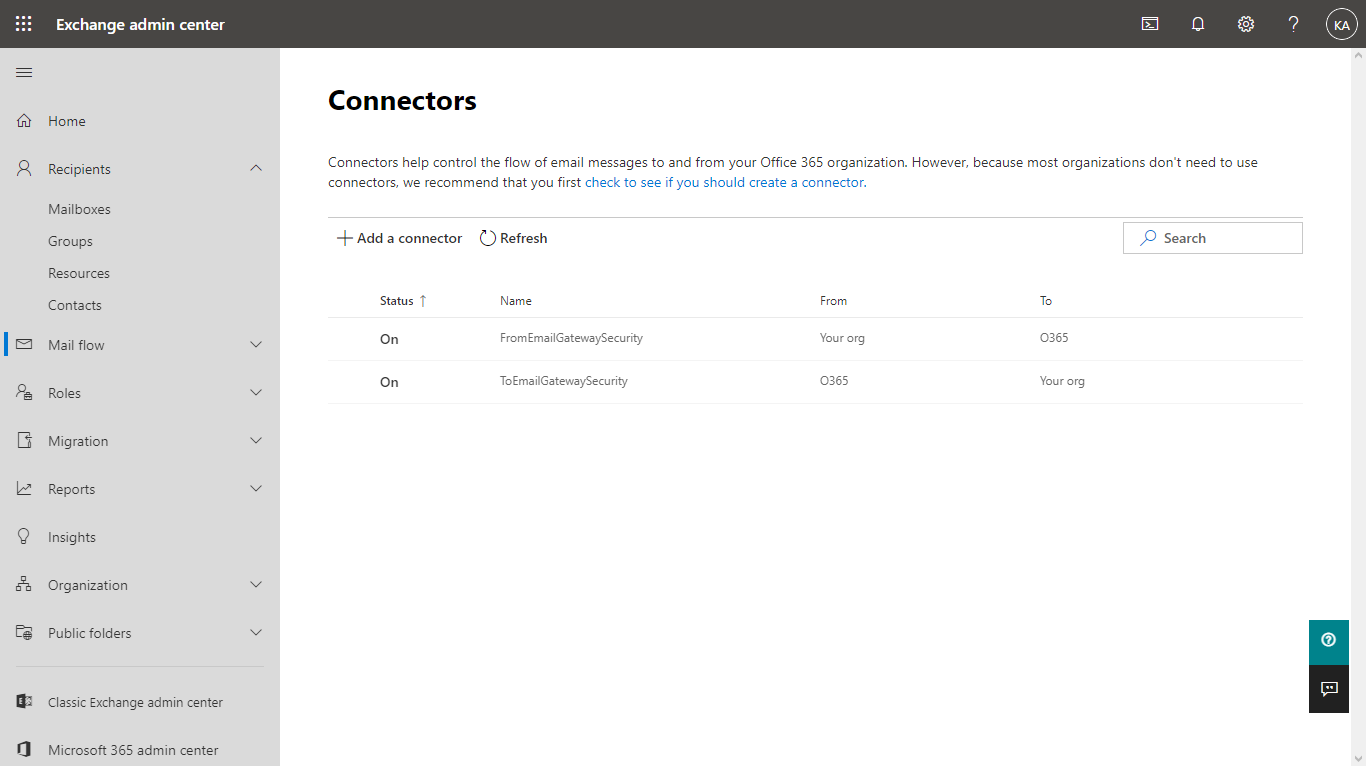
- In Exchange admin center go to Mail flow > Connectors (note that the outbound connector previously created is already in the list)
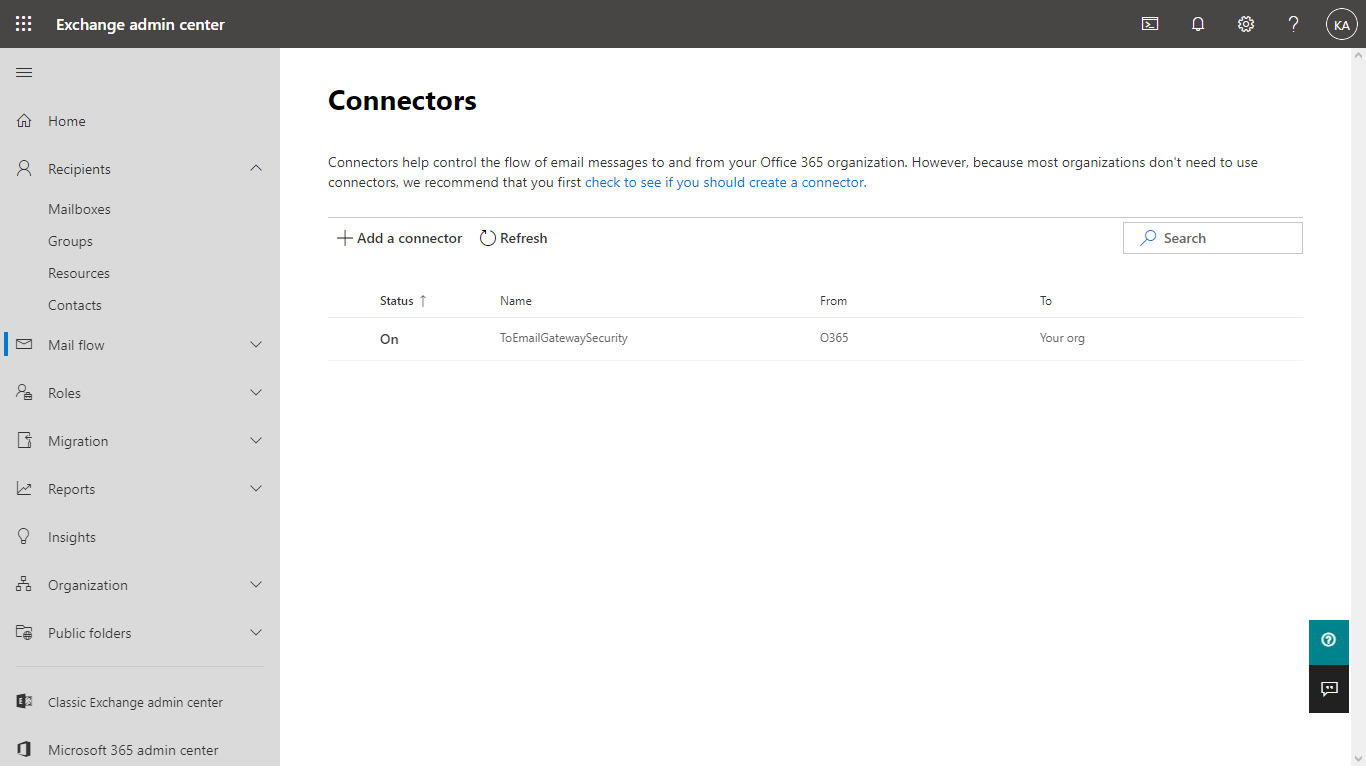
- Click Add a connector
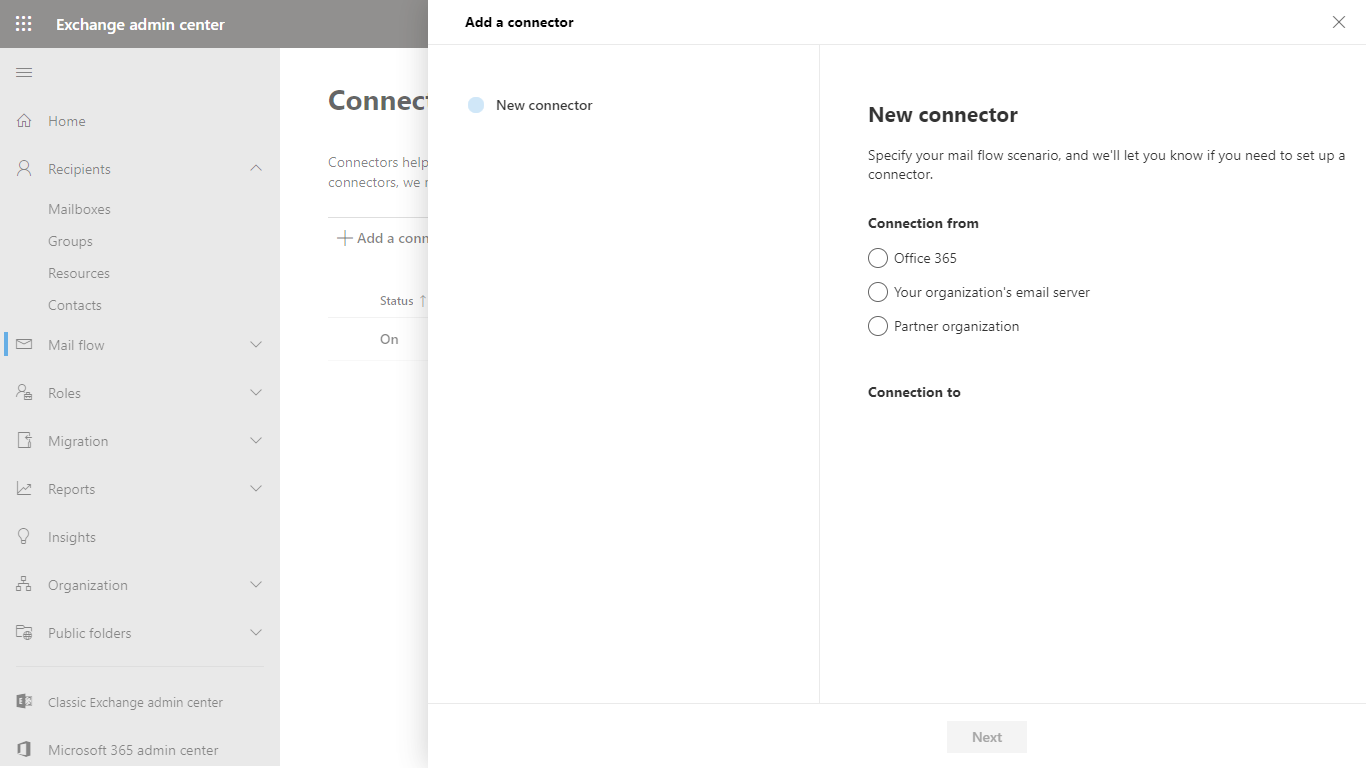
- This connector will route email from Email Gateway Security to Microsoft 365, so in the New connector dialog select:
- Connection from: Your organization’s email server
- Connection to: Microsoft 365
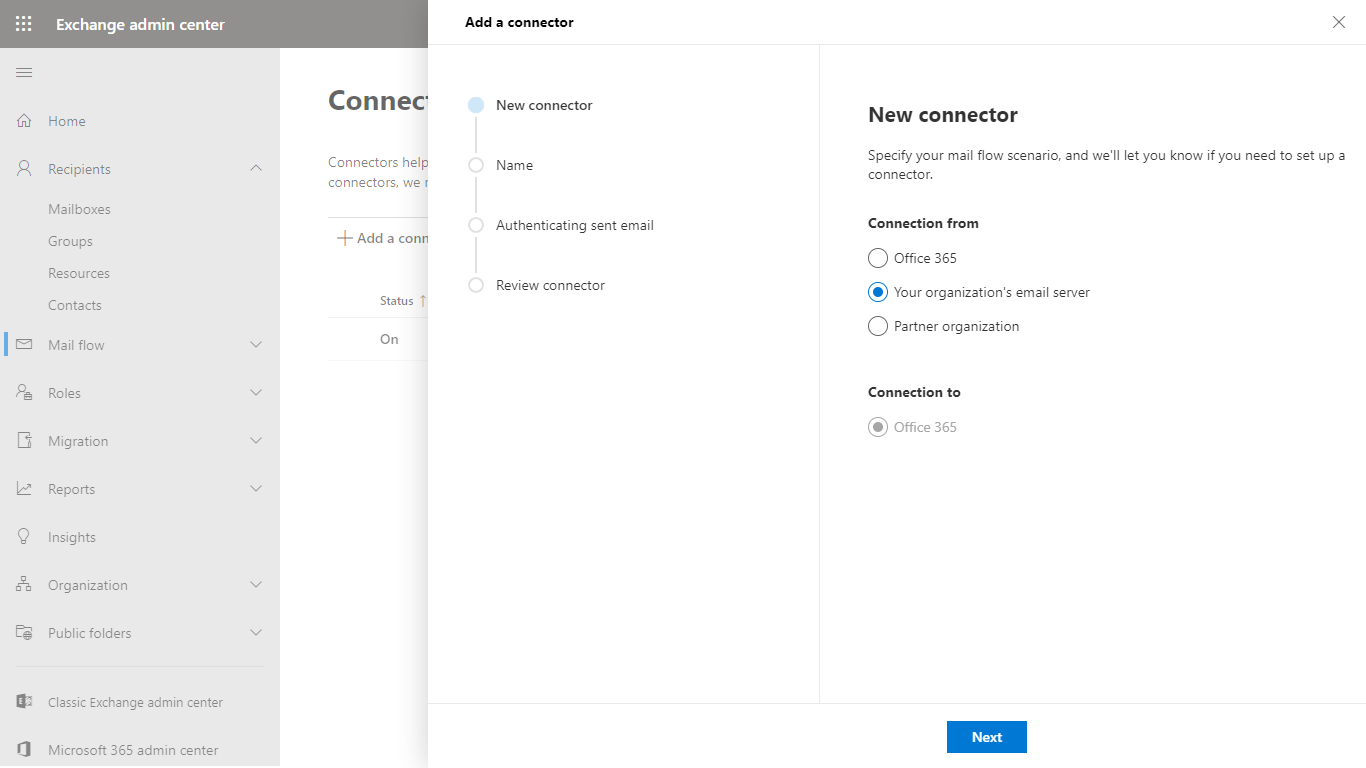
- In the Connector name dialog give a descriptive name to the connector and enable Turn it on
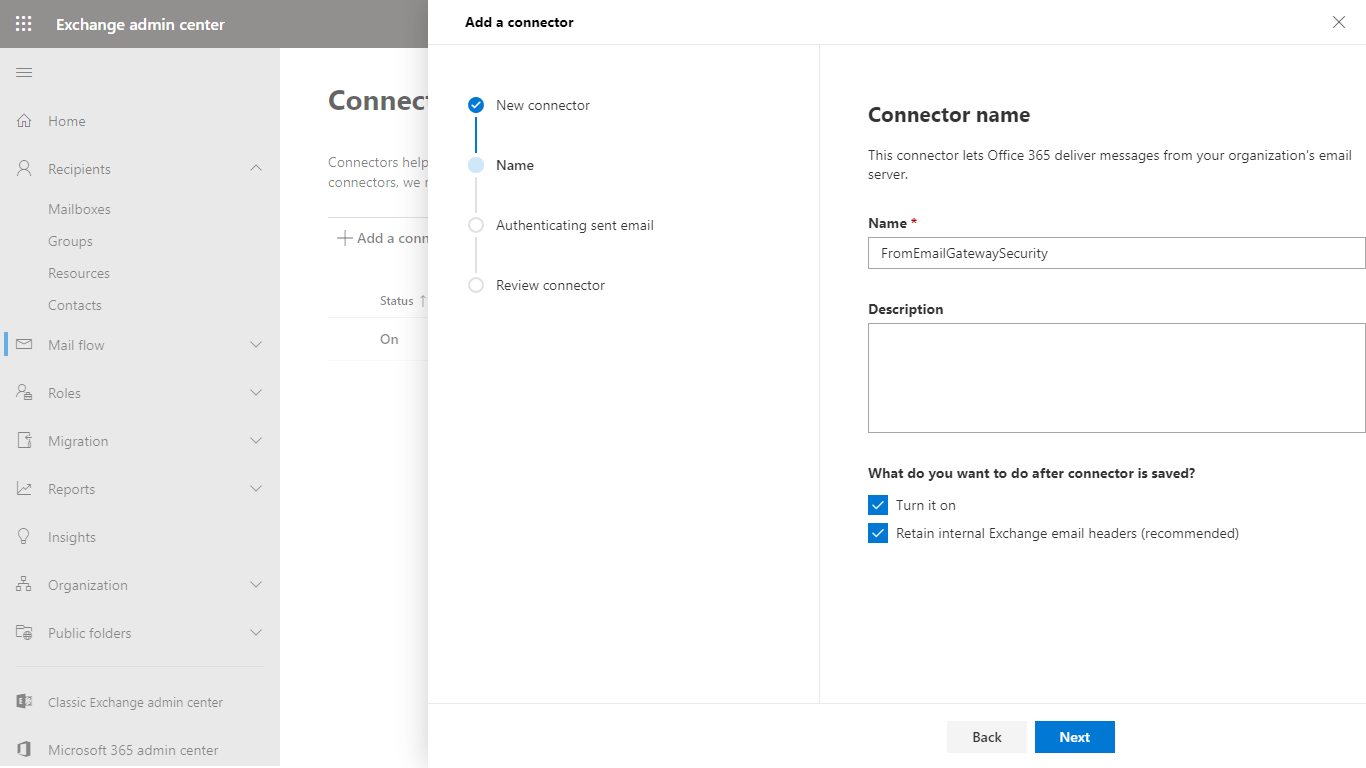
- In the Authenticating sent email dialog select By verifying that the IP address of the sending server matches one of the following IP addresses, which belong exclusively to your organization and specify Email Gateway Security’s IP address
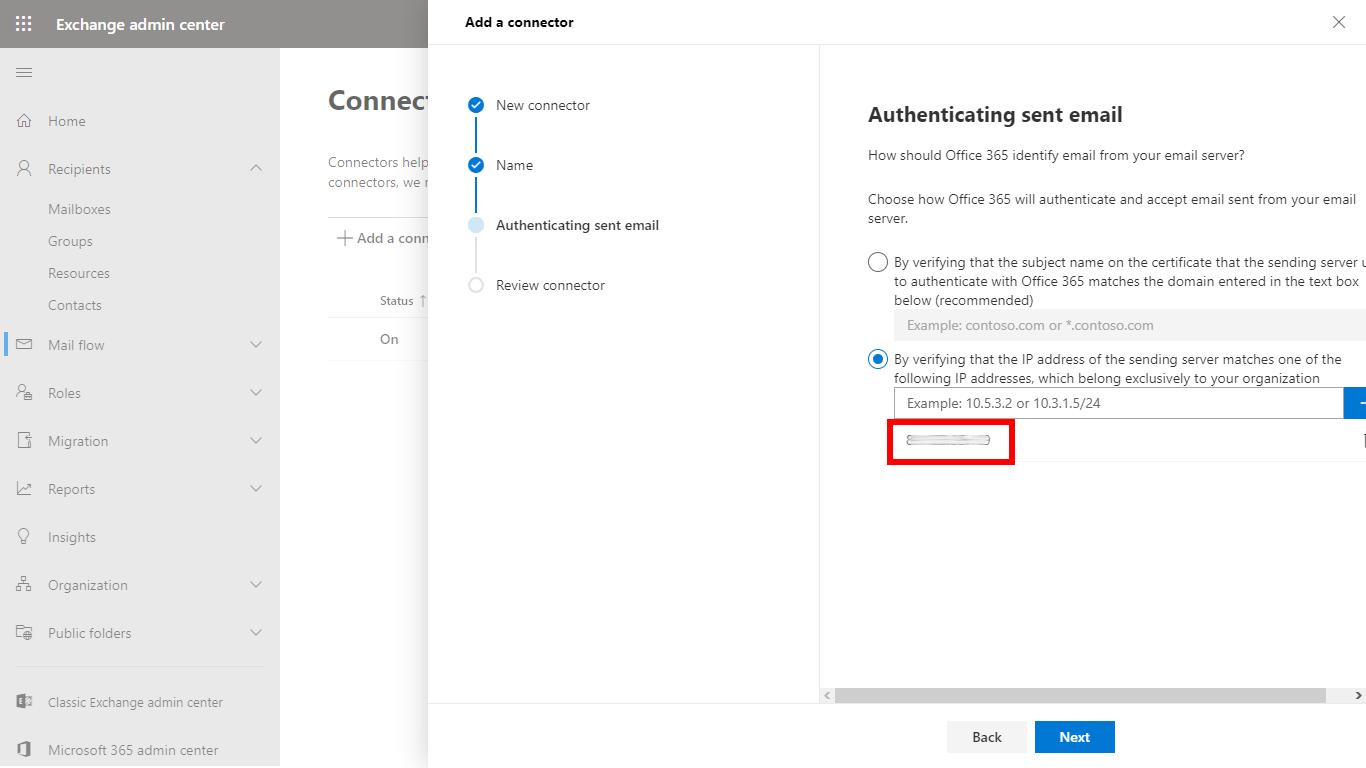
- In the Review connector dialog click Create connector to save the configuration
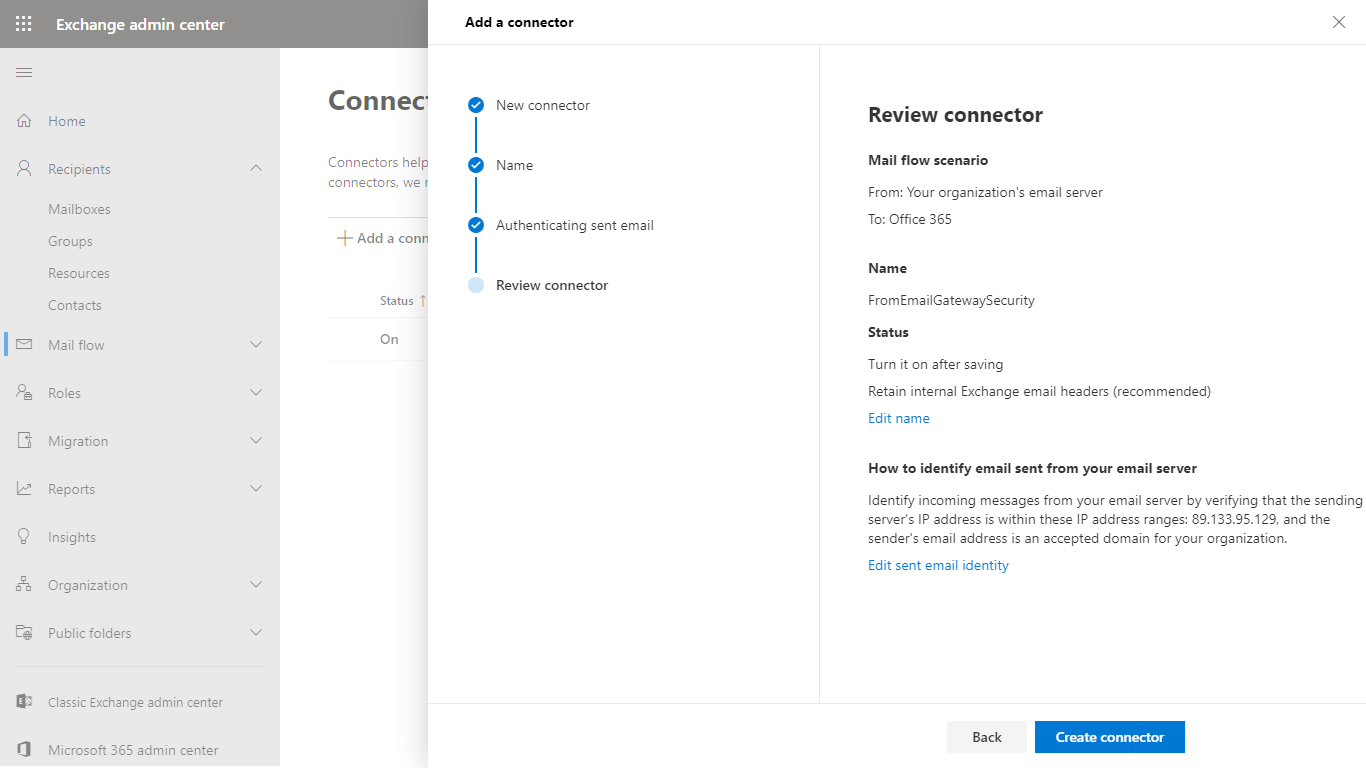
- The new connector must appear in the list of connectors. The inbound connector is now ready to route emails.
Connection filtering
In Microsoft 365 organizations connection filtering and the default connection filter policy identify good or bad source email servers by IP addresses. The key components of the default connection filter policy are:
- IP Allow List: Skip spam filtering for all incoming messages from the specified source IP addresses or IP address ranges.
- IP Block List: Block all incoming messages from the specified source IP addresses or IP address ranges.
- Safe list: The safe list in the connection filter policy is a dynamic allow list that requires no customer configuration. Microsoft identifies these trusted email sources from subscriptions to various third-party lists. You enable or disable the use of the safe list; you can't configure the servers in the list. Spam filtering is skipped on incoming messages from the email servers on the safe list.
For details see https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/security/office-365-security/connection-filter-policies-configure.
Sometimes Microsoft 365 classifies emails delivered by OPSWAT as spam and puts these emails into its quarantine or Junk Email folder.
To avoid this, OPSWAT server email addresses must be added to the IP allow list.