High Availability support for PostgreSQL Data lake
Installation
- Replication Manager is compatible solely with Linux-based operating systems.
- The Replication Manager version in use must be compatible with the major version of the installed PostgreSQL.
- All PostgreSQL servers must be of the same version and run on the same operating system.
High availability solution for PostgreSQL data lake requires a single primary server along with a minimum of two standby servers. Both PostgreSQL and Replication Manager must be installed on every server.
On the servers that target to run as standby:
- Do not create a PostgreSQL instance (i.e., do not execute
initdbor any database creation scripts provided by packages). - Ensure the destination data directory exists and is owned by the
postgressystem user.
- Select your Linux distribution here and follow the steps to install PostgreSQL accordingly.
- Follow the steps to install Replication Manager for PostgreSQL clusters - repmgr.
Primary configuration
- Choose one of the installed servers to be the primary one.
- Navigate to the folder containing
postgresql.conffile and create a replication config file namedpostgresql.replication.conf.
By default, postgresql.conf file is placed at
/var/lib/pgsql/<version>/data/on Red Hat/Rocky./var/lib/postgresql/<version>/mainon Debian/Ubuntu.
# Enable replication connections; set this value to at least one more# than the number of standbys which will connect to this server# (note that repmgr will execute "pg_basebackup" in WAL streaming mode,# which requires two free WAL senders).## See: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/runtime-config-replication.html#GUC-MAX-WAL-SENDERSmax_wal_senders = 10# If using replication slots, set this value to at least one more# than the number of standbys which will connect to this server.# Note that repmgr will only make use of replication slots if# "use_replication_slots" is set to "true" in "repmgr.conf".# (If you are not intending to use replication slots, this value# can be set to "0").## See: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/runtime-config-replication.html#GUC-MAX-REPLICATION-SLOTSmax_replication_slots = 10# Ensure WAL files contain enough information to enable read-only queries# on the standby.## See: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/runtime-config-wal.html#GUC-WAL-LEVELwal_level = 'hot_standby'# Enable read-only queries on a standby## See: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/runtime-config-replication.html#GUC-HOT-STANDBYhot_standby = on# Enable WAL file archiving## See: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/runtime-config-wal.html#GUC-ARCHIVE-MODEarchive_mode = on# Set archive command to a dummy command; this can later be changed without# needing to restart the PostgreSQL instance.## See: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/runtime-config-wal.html#GUC-ARCHIVE-COMMANDarchive_command = '/bin/true'# This config should be added if you plan to use repmgrd for# automatic failover# See: https://www.repmgr.org/docs/current/repmgrd-basic-configuration.htmlshared_preload_libraries = 'repmgr'wal_log_hints = on # for pg_rewind when rejoin- Add the replication configuration file name to the end of
postgresql.conffile and save the modifications.
...include 'postgresql.replication.conf'- In Terminal, run the following commands to create
repmgruser and database.
$ createuser -s repmgr$ createdb repmgr -O repmgrIn this guideline, although the term repmgr is used for both user and database, any names can be used.
- Edit
pg_hba.conffile to configure the authentication.
# Ensure the repmgr user has appropriate permissions in pg_hba.conf# and can connect in replication mode# pg_hba.conf should contain entries similar to the following:# Uncomment this if you want to access Postgresql database via pgadmin with user "postgres":#host all postgres 0.0.0.0/0 scram-sha-256local replication repmgr trusthost replication repmgr 127.0.0.1/32 trust#orhost replication repmgr 0.0.0.0/0 trustlocal repmgr repmgr trusthost repmgr repmgr 127.0.0.1/32 trust#orhost repmgr repmgr 0.0.0.0/0 trust- Restart PostgreSQL server.
$ cd /path/to/pg_ctl$ pg_ctl -D <postgresql_data_dir> restart- Create
repmgr.conffile, fill out information in brackets and store it in a location of your choice.
repmgr.conf file should not be placed inside PostgreSQL data folder as it may be overwritten.
node_id=<any_node_id>node_name=<any_node_name># connection info of the current nodeconninfo='host=<host_address_of_node> user=repmgr dbname=repmgr connect_timeout=2'data_directory='<postgres_data_dir>'failover='automatic' # for repmgrd (automatic failover)promote_command='<postgres_dir>/repmgr standby promote -f "<your_dir>/repmgr.conf" --log-level INFO'follow_command='<postgres_dir>/repmgr standby follow -f "<your_dir>/repmgr.conf" -W --log-level INFO'reconnect_attempts='5'reconnect_interval='1'monitor_interval_secs='1'pg_bindir='<postgres_dir>'# enable this so that repmgr only vote new primary # when none of the standbys can connect to current primaryprimary_visibility_consensus=true| Key | Red Hat/Rocky | Debian/Ubuntu |
|---|---|---|
postgres_data_dir | /var/lib/pgsql/<version>/data/ | /var/lib/postgresql/<version>/main/ |
postgres_dir | /usr/pgsql-<version>/bin/ | /usr/lib/postgresql/<version>/bin/ |
your_dir | Directory torepmgr.conf file. | Directory torepmgr.conf file. |
- In Terminal, run the following commands to register the primary server.
$ cd path/to/repmgr$ repmgr -f <repmgr_config_file_path> primary registerINFO: connecting to primary database...NOTICE: attempting to install extension "repmgr"NOTICE: "repmgr" extension successfully installedNOTICE: primary node record (id: 1) registeredStandby configuration
- Create
repmgr.conffile and modify values ofnode,node_name,conninfoaccordingly. - Store the file in your reference location.
- Stop PostgreSQL server.
$ cd /path/to/pg_ctl$ pg_ctl -D <postgresql_data_dir> stop- In Terminal, run the following commands to clone data from the primary server.
$ cd path/to/repmgr$ repmgr -h <primary_server_host> \ -U repmgr -d repmgr \ # primary repmgr <user> and <database> -f <standby_repmgr_config_file_path> \ -c \ # fast checkpoint to speed up process standby clone \ --dry-run # dry run to check if the primary can be cloned $ repmgr -h <primary_server_host> \ -U repmgr -d repmgr \ # primary repmgr <user> and <database> -f <standby_repmgr_config_file_path> \ -c \ # fast checkpoint to speed up process standby clone- Start PostgreSQL server.
$ cd /path/to/pg_ctl$ pg_ctl -D <postgresql_data_dir> start- In Terminal, run the following commands to register the standby server.
$ cd /path/to/repmgr$ repmgr -f <standby_repmgr_config_file_path> \ standby register- Check if the node was registered successfully.
$ cd /path/to/repmgr$ repmgr -f /etc/repmgr.conf cluster showAutomatic failover
In Terminal, run the following command to start Replication manager daemon on all PostgreSQL servers (including primary and standbys)
$ cd /path/to/repmgr$ repmgrd -f <repmgr_config_file_path>Rejoin after a failure
Replication manager daemon repmgrd does not automatically join a failed PostgreSQL server node to the cluster. Consequently, the cluster contains at least two primary nodes at one time, and the system administrator has to join the node to the cluster manually.
- Ensure the failed PostgreSQL server is not running. Run the following command in Terminal to stop the server if it has, by chance, already been started by the Linux system and service manager.
$ cd /path/to/pg_ctl$ pg_ctl -D <postgresql_data_dir> stop- In Terminal, run the following command to rejoin the server.
$ cd /path/to/repmgr$ repmgr -f <repmgr_config_file> node rejoin \ --force-rewind \ # use pg_rewind to help with diverge timeline -d 'host=<current_primary> dbname=repmgr user=repmgr'- If the server rejoin fails, do register it as a standby. In Terminal, run the following command.
$ cd /path/to/repmgr$ repmgr -h <current_primary_server_host> \ -U repmgr -d repmgr \ # primary repmgr <user> and <database> -f <standby_repmgr_config_file_path> \ -c \ # fast checkpoint to speed up process -F \ # this overwritten the the data folder if it was created standby clone \- Start PostgreSQL server.
$ cd /path/to/pg_ctl$ pg_ctl -D <postgresql_data_dir> start- Force register the server as a standby.
$ cd /path/to/repmgr$ repmgr -f <standby_repmgr_config_file_path> \ -F \ # forcefully overwrite an existing node record or user --force standby registerSetup instructions
- Sign to MDDC Control Center console with your Administrator account.
- Navigate to
Inventory>Services. - Expand the
Data Lakegroup. - Click
Add service. - Enter the values for
Name,Host,Port,UsernameandPasswordfields of individual PostgreSQL instance. - Click the Check icon in the bottom right to complete.
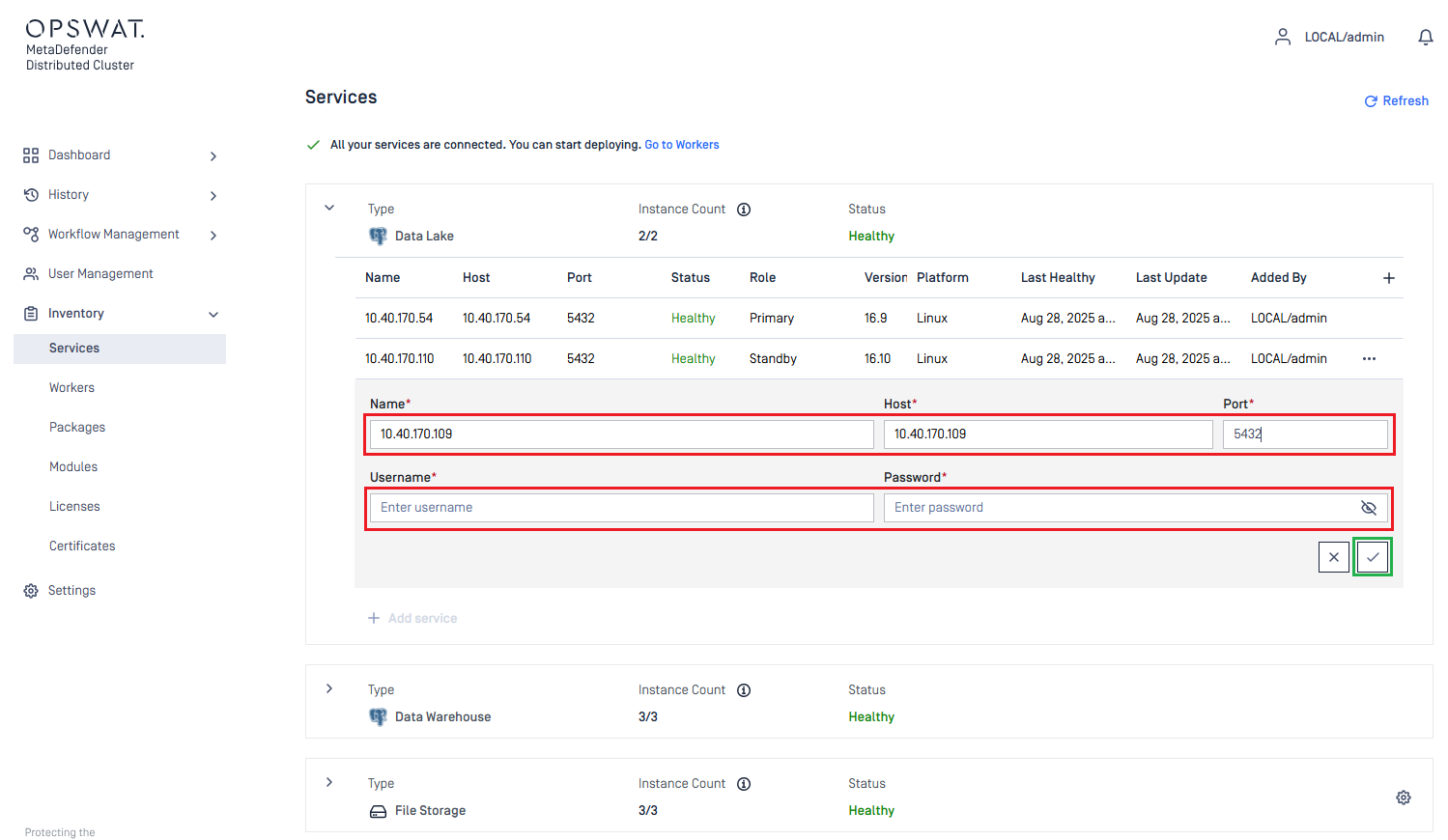
- Ensure all PostgreSQL instances are reachable by the MDDC Control Center.

