Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Upgrade/Deployment Strategy on K8S
For upgrading MetaDefender Core the container of the application contains the automation to upgrade the database schema and migrate the configuration data. There are 3 strategies that we would like to point out to use when upgrading it.
- Rolling Update ( Easy deployment where functionality test with new version is based on Kubernetes Probes )
- Blue-Green Deployment (2 or more activations licensed where is possible to test the new image before) - On RoadMap
- Blue-Green Deployment + Hot Backup ( When needed to go above the activations licensed ) - On RoadMap
As indicated in Deploying on K8S , the Kubernetes probes like Readiness and Liveness probes help the application to control the expected behavior, not to have a downtime, when doing an upgrade.
Rolling Update Strategy
When using the Rolling Update strategy provided by Kubernetes technology, these are the main points to consider
- Traffic wont be sent to new pods until readiness probe is successful
- Old version pods won’t be terminated until new version pods are ready to serve traffic
- Rolling Update is the default strategy for deployment
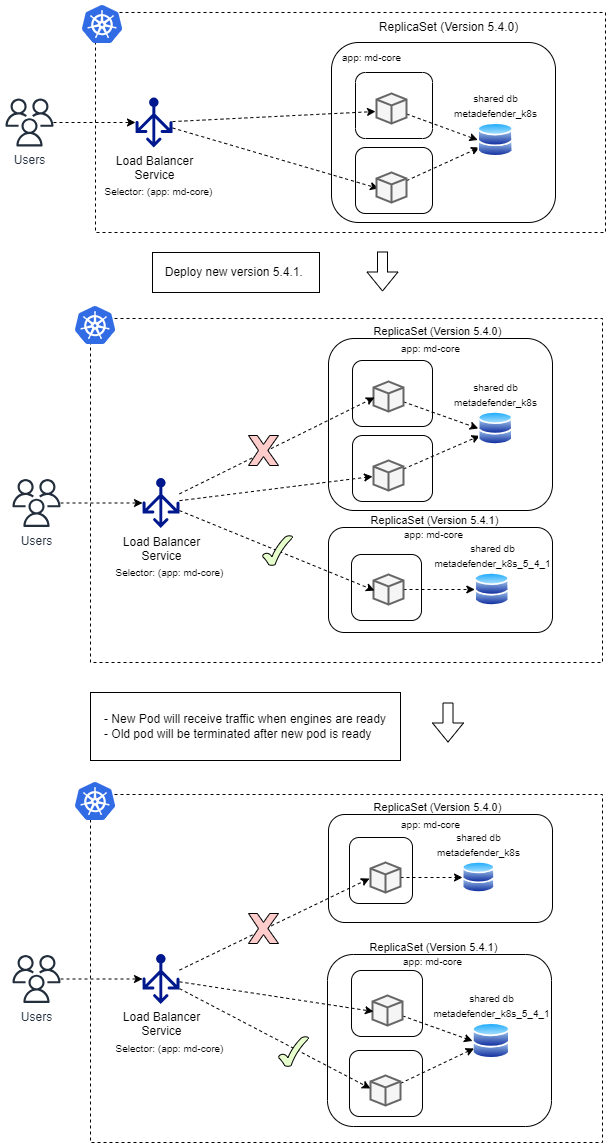
How to upgrade using Rolling Update
Decide what data to migrate from version to version
When upgrading from one version to another, MetaDefender Core will create a new database migrating different data depending on what is indicated during the process. It can be migrated only configuration data or configuration data + processing history data.
Configuration data:
- Workflow
- Health check
- User Management
Processing History Data
- Scan results of previous scanned files
Pre-steps when migrating Processing History Data
Feature available starting from version 5.10.1
As the processing history data is the heaviest part of the data stored and is not always needed to be migrated, OPSWAT offers a way to only migrate the configuration data and save the time that it takes to migrate that sometimes can be high depending on the size of the processing history data.
There is a limitation when migrating the processing history, it is that is needed to stop the current pods running as we need to terminate all the connections to the database to migrate.
Following pre-steps are needed to follow when migrating the processing history
- Must disable health check liveness probe in the helm chart before run with MIGRATE_HISTORY (Depending on the size of the database it can take a while to migrate all the data)
- Check that there is enough space in the database server before starting the migration
- Needed to stop MetaDefender Core pods
Configure Rolling Update Strategy
When using the Rolling Update strategy, there are two more options that let you fine-tune the update process:
- maxSurge: The number of pods that can be created above the desired amount of pods during an update
- maxUnavailable: The number of pods that can be unavailable during the update process
Both maxSurge and maxUnavailable can be specified as either an integer (e.g. 2) or a percentage (e.g. 50%), and they cannot both be zero.
To change this you need to edit the deployment strategy.
core_components: md-core: strategy: type: RollingUpdate rollingUpdate: maxSurge: 0 maxUnavailable: 1Variables to use during an upgrade
- MDCORE_UPGRADE _ FROM __DB NAME: old database name to migrate from (1st installation metadefender_core)
- UPGRADE_DB: To indicate if we want to enable the DB upgrade to the new version. It will create a new database with database name metadefender_core<new___version>
- MIGRATE_HISTORY: To migrate processing history. Follow Pre-steps
Step by step using kubectl
- Set Up the environment variables for the pod to know what data will be needed to migrate
- For MIGRATE_HISTORY please see pre-steps above and decide if it is really needed or not
kubectl create configmap mdcore-env -n <namespace> --from-literal=MDCORE_UPGRADE_FROM_DB_NAME=<CURRENT_DB_NAME> --from-literal=UPGRADE_DB=true --from-literal=MIGRATE_HISTORY=<true/false> -o yaml --dry-run=client | kubectl apply -f -- Set new image version on the MetaDefender Core deployment
kubectl set image -n <namespace> deployments/md-core md-core=opswat/metadefendercore-debian:<NEW_IMAGE_TAG>Step by step using helm
- Set new image version in values.yaml helm file
- For MIGRATE_HISTORY please see pre-steps above and decide if it is really needed or not
env: MDCORE_UPGRADE_FROM_DB_NAME: <CURRENT_DB_NAME> UPGRADE_DB: "true" MIGRATE_HISTORY: <true/false> ## Change to true to migrate processing history. It will delay the upgrade depending on the database size. Needed to follow Pre-steps core_components: md-core: image: opswat/metadefendercore-debian:<NEW_IMAGE_TAG>- Run helm upgrade command with the environment variables desired if not indicated in values.yaml file when first deployment
helm upgrade mdcore mdcore/ --namespace <Namespace> -f <Additional_yaml_file> \ --set core_ingress.enabled=$ingress_enabled \ --set mdcore_license_key=<MDCORE_LICENSE_KEY> \ --set deploy_with_core_db=<boolean_k8s_db_running_pod> \ --set core_components.md-core.replicas=<replicas> \ --set mdcore_password=<mdcore_password> \ --set mdcore_user=<mdcore_user> \ --set db_user=<db_user> \ --set db_password=<db_password> \ --set MDCORE_DB_HOST=<db_host>Rollout Failed Update
kubectl rollout undo deployments/md-core -n <namespace>How to upgrade with API Export/Import Configuration (Old-Fashioned way)
The steps needed to follow are:
1. Export the current configuration, like user management, worflows or settings configured. For it is needed to use the API endpoint Export Configuration (New version)
curl --request GET \ --url 'http://localhost:8008/admin/export/v2' \ --header 'apikey: {apikey}' \ --header 'password: {password}' --output <filename>.zip2. Adapt helm configuration to upgrade to the new image version
- In case of controlling all the data from your values.yaml file, be sure that the maxUnavailable and maxSurge attributes of the deployment strategy is adapted to your deployment use case and the image version is changed to the new one
md-core: name: md-core image: opswat/metadefendercore-debian:<new_core_version> #Change <new_core_version> with any tag in Docke Hub #.... #.... #.... strategy: #Example for use case when having more than 1 pod running type: RollingUpdate rollingUpdate: maxSurge: 0 maxUnavailable: 1helm upgrade mdcore mdcore/ -f <external_file_for_csp.yaml> \ --set env.UPGRADE_DB=true \ --set env.RETRY_UPGRADE=5- In case of controlling attributes from the helm install command, be sure that the maxUnavailable and maxSurge attributes of the deployment strategy is adapted to your deployment use case and the image version is changed to the new one
helm upgrade mdcore mdcore/ -f <external_file_for_csp.yaml> \ --set core_ingress.enabled=<ingress_boolean> \ --set mdcore_license_key=<MD_Core_Lincese_Key> \ --set deploy_with_core_db=<Postgres_Pod_Boolean> \ --set core_components.md-core.replicas=<Number_of_replicas_Core> \ --set db_user=<DB_USER> \ --set db_password=<DB_PWD> \ --set MDCORE_DB_HOST=<DB_HOST> \ --set core_components.md-core.image="opswat/metadefendercore-debian:<Image_Version_TAG>" \ --set core_components.md-core.strategy.rollingUpdate.maxUnavailable=1 \ --set core_components.md-core.strategy.rollingUpdate.maxSurge=0 \ --set env.UPGRADE_DB=true \ --set env.RETRY_UPGRADE=53. Import the configuration exported in the step 1 For it is needed to use the API endpoint Import Configuration (New version) . See how to use it in the example below.
curl --request POST \ --url 'http://localhost:8008/admin/import/v2' \ --header 'Content-Type: application/octet-stream' \ --header 'apikey: {apikey}' \ --header 'password: {password}' \ --data-binary '@<file_name>.zip'
